The nucleus of an atom is made up of these particles.
What is Protons and Neutrons?
This is the type of bond between a hydrogen and oxygen in a molecule of water.
What is a covalent (polar covalent) bond?
These are the 4 basic macromolecules that make up life.
What is carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids?
This is the term for a single sugar
What is a monosaccharide?
These are the 3 types of lipids.
What are fats, steroids, and phospholipids?
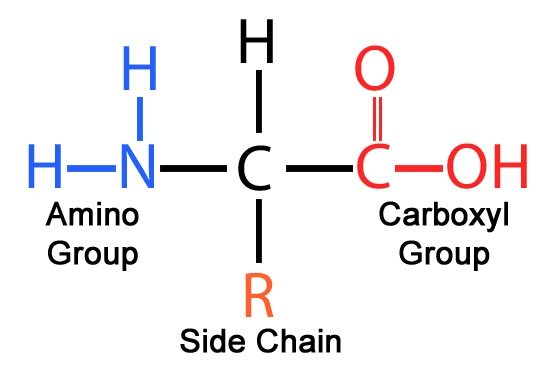
This is the basic structure of an amino acid.
This is the structure of DNA.
What is a double helix?
These are the 6 elements that make up 99% of all living things.
What is C, H, O, N, P, and S?
Attractive forces between water molecules that leads to water's many emergent properties.
What is a hydrogen bond?
This is a single unit that bonds to other single units to form long chains.
What is a monomer?
This is the term for the bond between 2 monosaccharides.
What is glycosidic linkage?
These are the two components of triglycerides.
What are glycerol and fatty acids?
This is the type of bond that connects amino acids together
What is a peptide bond?
These are the three parts to nucleotides.
What are phosphate groups, pentose sugars, and nitrogenous bases?
This is a pure substance that cannot be broken down chemically.
What is an element?
This property of water allows for plant water transport due to the polarity of water allowing the water molecules to "stick" to other things.
What is adhesion?
This is the process used to turn polymers into monomers.
What is hydrolysis?
These are the two basic structures of polysaccharides.
What is linear or branched?
This is a type of fat that has at least one double bond in its fatty acid chain.
What is an unsaturated fat?
This is the reason why proteins denature.
What is changes in pH, temperature and salt concentration?
These are the nitrogenous bases that are distinctly different in DNA and RNA.
What is uracil and thymine?
Type of covalent bond in which electrons are not shared equally.
What is a polar covalent bond?
This is the reason why ice is less dense than water and can preserve life in large bodies of water.
What is solid water slows down and gets closer, causing more hydrogen bonds to form and separating?
This is the process that turns monomers into polymers.
What is dehydration?
This is the function for linear polysaccharides such as cellulose and chitin.
What is structural?
This is the function of steroids.
What is a signaling molecule?
This is the reason why polypeptides fold.
What is r group interactions with each other forming hydrogen bonds and van der waals forces?
This is the difference in function between DNA and RNA.
What is DNA stores genetic information while RNA translates and transcribes genetic information?
This is the reason why carbon is most fundamental to sustaining life.
What is carbon develops ALL macromolecules essential to life?
These are the 6 fundamental properties of water.
What is cohesion/adhesion, surface tension, temperature moderation, high specific heat, high heat of vaporization, and universal solvent?
This is the type of bond that connects one monomer to another after dehydration synthesis.
What is a covalent bond?
This is the function of branched polysaccharides such as glycogen and starch.
What is storage?
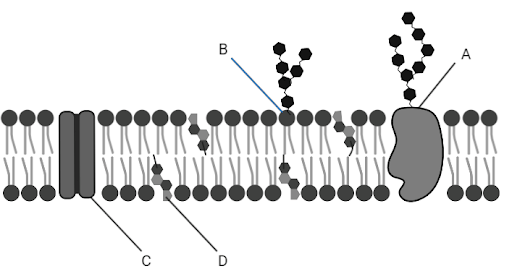 The following letter(s) represent substances that are ONLY polar.
The following letter(s) represent substances that are ONLY polar.
What is B?
This causes the secondary structure of proteins to form.
What is interactions between the carboxyl and amine groups?
These are the pairs of nitrogenous bases and how many bonds connect them.
What are adenine and thymine or uracil with 2 hydrogen bonds and guanine with cytosine with 3 hydrogen bonds?