Besides the term "cell or plasma membrane," what term/phrase best describes the following statement?
'The membrane is held together by weak hydrophobic interactions, allowing lipids and proteins to move.'
Fluid Mosaic Model
What are the four structures ALL cells have in common?
Plasma membrane, cytosol (cytoplasm), chromosomes (genetic material), ribosomes
Describe the composition of the phospholipid bilayer.
Differentiate between hypotonic, hypertonic, and isotonic.
Hypotonic - water goes in the cell
Hypertonic - water leaves the cell
Isotonic - water enters and leaves the cell
Which statement(s) below is false?
Water will flow:
(1) Low water potential to areas of high water potential
(2) Low solute to areas of high solute
(3) Low areas of pressure to high areas of pressure.
Which organelle contains hydrolytic enzymes, which are important in intracellular digestion?
Lysosomes
Which organelle is responsible for detoxification and lipid synthesis?
Smooth ER
What type of molecules can pass freely across the plasma membrane?
Small, uncharged, nonpolar, or hydrophobic molecules.
- Ex: Oxygen (O2), Carbon Dioxide (CO2), or Nitrogen gas (N2).
Why? - Because of their size and polarity, it allows them to diffuse through the hydrophobic core of the phospholipid bilayer without the need for transport proteins.
Aquaporins are proteins that act as water channels in cell membranes, allowing water to pass through cells. Which type of transport would they be a part of?
Osmosis or Facilitated diffusion.
Aquaporins in general are used when larger portions of water need to be transported quickly! Example: Situations where maintaining proper water balance is crucial, like in the kidneys for urine concentration.
Which cell would be the most efficient at exchanging material across its plasma membrane and which would be best for storage?
Exchanging - Cell D because 1.6 is the highest SA/V ratio.
Storage - Cell B because 0.9 is the lowest SA/V ratio, which is optimal for storing material.
When a cell is exporting a folded protein in mass quantities, what 3 organelles or structures are involved? (they don't have to be in order)
Rough ER, Golgi Body, Vesicle
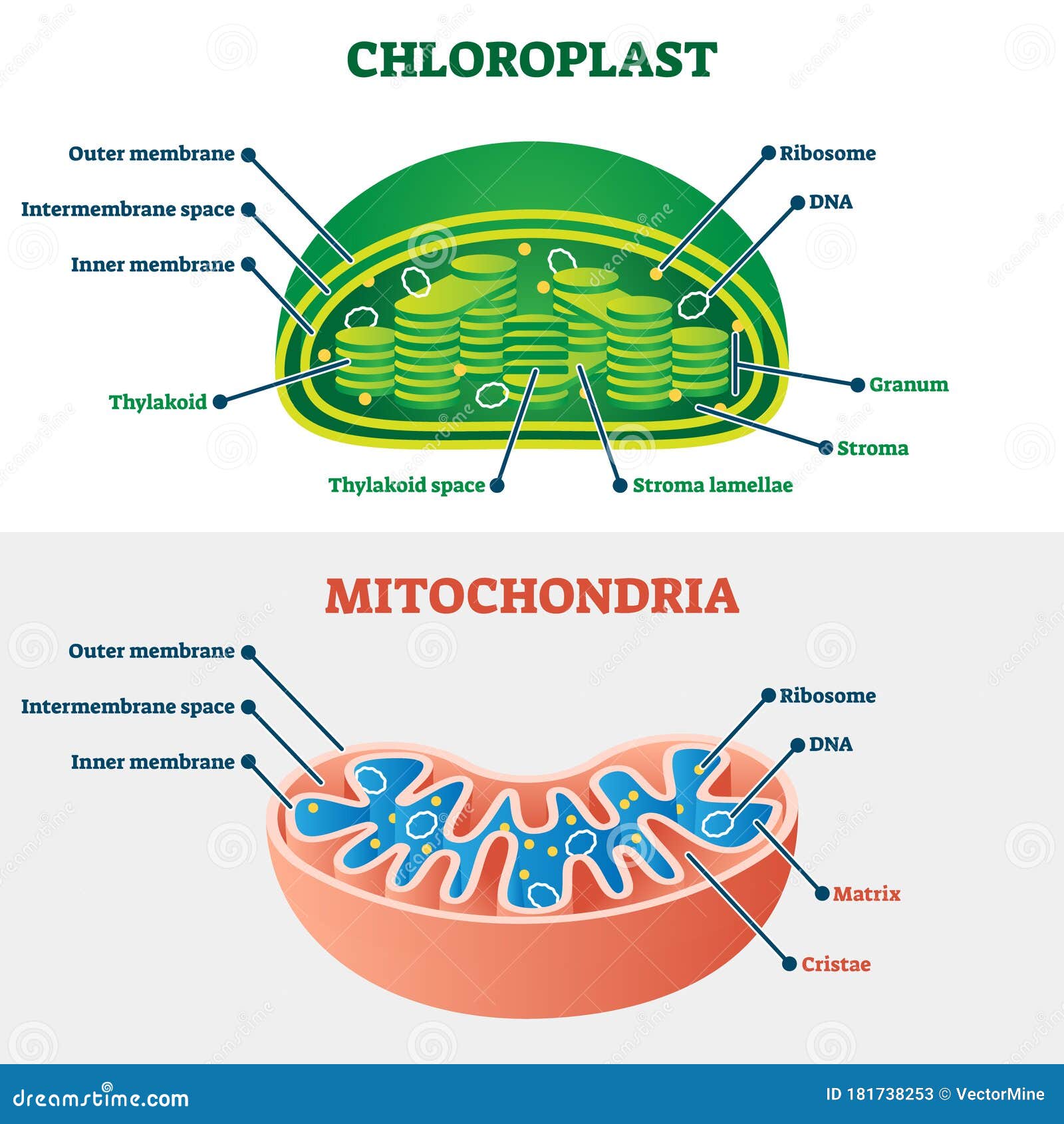
Based on the Endosymbiotic theory, what 2 organelles have double-membranes?
Chloroplasts and mitochondria
Identify the structure that represents:
(1) An integral protein, (2) Glycoprotein, (3) Hydrophilic Head, (4) Peripheral Protein
(1) B
(2) C
(3) D
(4) A
Which specific type of endocytosis is shown below?
Pinocytosis because it's engulfing a liquid!
A dialysis bag containing a 0.1 M NaCl solution is placed in a beaker containing a 0.4 M NaCl solution. The dialysis bag acts as a semipermeable membrane, allowing water to pass but not NaCl. Which way will the water move?
Water will move out of the dialysis bag, causing it to shrink.
Which of the following does not provide evidence of the endosymbiotic theory AND why?
a. Prokaryotes and eukaryotes are both surrounded by a phospholipid bilayer.
b. Mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own circular DNA, similar to bacterial genomes
c. Energy organelles both have ribosomes similar to those found in prokaryotic cells.
d. Organelles are capable of functioning and reproducing on their own.
A - Prokaryotes and eukaryotes are both surrounded by a phospholipid bilayer.
Why? - The Endosymbiotic theory explains how mitochondria and chloroplasts (energy organelles) came to be. It specifically proposes that these organelles were originally free-living prokaryotes (bacteria) that were engulfed by an ancestral eukaryotic cell.
The phospholipid bilayer (aka the cell membrane) already exists in ALL types of cells. Therefore it's not evidence of the endosymbiotic theory.
What is the function of plasmodesmata in plant cells, and how do they contribute to cellular communication and transport?
Plasmodesmata are cytoplasmic channels in plant cell walls that provide direct connections between adjacent plant cells. These channels help facilitate communication, such as signaling from one cell to another, or transport of molecules. This essentially acts as a pathway for the movement of substances like sugars, small proteins, and signaling molecules within a plant organism.
Describe the amphipathic nature of phospholipids in the plasma membrane and explain how this property regulates transportation across the membrane.
Description - Phospholipids have a hydrophilic/polar head and two hydrophobic/nonpolar tails.
Explanation - The hydrophilic heads face outward toward the aqueous environment, and the hydrophobic tails face inward, creating a bilayer that restricts the passage of polar and large molecules while allowing small nonpolar molecules to diffuse freely.
During endocytosis, cells can take in nutrients from their surroundings and then store them using these organelles.
Vacuoles (central vacuole specifically in plants)
Explain how does the efficiency of cellular processes differ between small and large cells.
Small cells have a higher surface area to volume ratio so they optimize the exchange of materials at the plasma membrane much more effectively! The cell functions at a more efficient rate too!
Large cells have a lower surface area to volume ratio so they lose efficiency exchanging materials and better at storage. The cellular demand for resources increases since the cell is larger.