What is the difference between Meiosis and Mitosis?
Meiosis is the cell division of gametes, has 2 rounds of division, and makes four genetically unique cells
Mitosis is the cell division of body cells, 1 round of division, makes 1 daughter cell genetically identical to the parent
When does DNA Replication occur?
S phase of Interphase
Why are photosynthesis and cellular respiration important?
They are responsible for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between living organisms and the environment.
They allow living organisms to breathe and survive.
What are macromolecules made of?
They are polymers made up of repeating units of monomers.
What tools/diagrams are used to represent evolutionary relationships?
Cladograms/Phylogenetic Trees
What phase of the cell cycle has many metabolic reactions, and consists of G1, S, and G2 stages?
Interphase
Which strand is built continuously? Which is built in fragments?
Continuously- Leading Strand
Fragments- Lagging Strand
Where does sunlight go to initiate photosynthesis? Be specific.
Chlorophyll within the chloroplasts
What makes adenine and guanine purine bases?
They have a 2 ring structure.
What is species composition vs species diversity?
Species diversity- the variety of species and the quantity of individuals in each of the species.
Species Composition-the identity/role of each species in the community
If the parent cell has 46 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will the daughter cell have after Mitosis? How many after Meiosis?
Mitosis - 46
Meiosis - 23
Why is DNA helicase necessary?
It seperates the nitrogen bases so new nucleotides can be added to create the new strand.
In Cellular Respiration which processes first produce Carbon Dioxide?
Electron Transport Chain, Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle
Krebs Cycle
 What macromolecule is pictured?
What macromolecule is pictured?
Lipid
What trophic level receives the least amount of energy?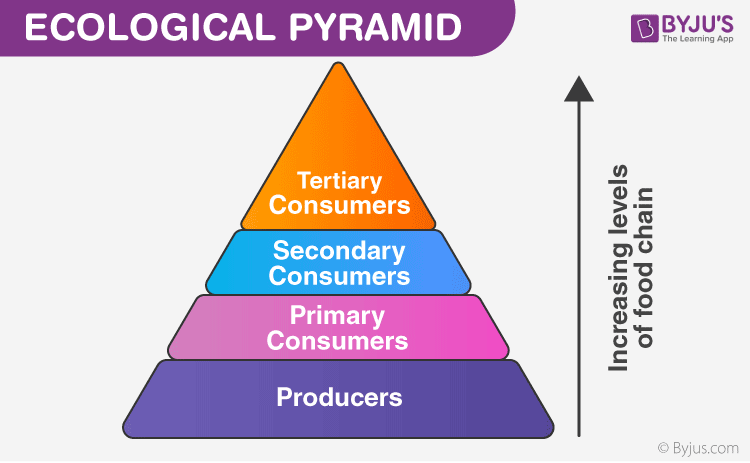
Tertiary Consumers
What is the function of Cyclins?
Proteins that control the progression of the cell cycle.
What is mRNA splicing?
Introns that do not code for amino acids are removed and the remaining sections of exons-that do code for amino acids- are stuck back together.
What is the formula for photosynthesis?

What role does the R group have in protein shape?
The R group can be polar or nonpolar, and its polarity will affect the way the protein is shaped.
Cite 3 factors that affect population density.
Competition, territoriality, disease, predation, natural disasters
What's the difference between Meiosis I and II?
Meiosis I includes crossing over of genetic material between chromosome pairs, while meiosis II does not
What enzymes are used in DNA Replication?
DNA Helicase, Topoisomerase, RNA Primase, DNA Polymerase I and II, DNA Ligase
Name the molecules involved in Cellular Respiration.
ATP, ADP, NADH, Phosphate, FADH2, H, O
What is the polarity of a carbohydrate?
It is hydrophilic/polar.
Cite 4 types of Prezygotic/Postzygotic Barriers
habitat isolation, behavioral isolation, mechanical isolation, temporal isolation, gametic/genetic isolation