The water molecule is ____ (size) and ____ (polarity)
Small and polar
What type of organelles do eukaryotes have that prokaryotes don't?
Membrane bound (mitochondria is an acceptable answer)
What is the second law of thermodynamics?
For a spontaneous process, the entropy of the universe increases.
What is the first key stage of cellular respiration (hint: occurs for both anaerobic and aerobic respiration)
Glycolysis
How many rotations of the Calvin cycle does it take to produce one full glucose?
2
When looking at the table for elements of life, Iodine is considered a ______ (crucial element or trace element)
Trace
What does folding the inner membrane of the mitochondria do to help it?
Increases surface area (for energy/reactions) for less volume
What is the difference between endergonic and exergonic reactions?
The investment (exergonic/exothermic) vs investment of energy (endergonic/endothermic)
In what parts of the mitochondria does cellular respiration occur?
The matrix and inner membrane
When did photosynthesis first develop?
In early prokaryotic organisms.
What macromolecule uses ester bonds to make it's polymer?
Lipids
What cell reaches a plasmolysed state in a _______ environment?
Under what circumstances do enzymes denature and why?
Harsh/incorrect temperature/pH, made of proteins
To make ATP, glycolysis/Krebs cycle.
When is O2 released as waste?
Light reactions
List the properties of water
Solvent of life, polar, density of ice, evaporative cooling, high specific heat
Describe a characteristic of the plasma membrane that allows oxygen to passively pass through it.
Hydrophobic/nonpolar/space between phospholipids
In an experiment, variety A seedlings at both temperatures were treated with a chemical that prevents NADH from being oxidized to NAD+. Predict the most likely effect of the chemical on metabolism and oxygen consumption of the treated seedlings.
As metabolism/respiration and oxygen consumption decreases/stops
Describe ONE contribution of the formation of a proton gradient by the electron transport chain in ATP synthesis.
movement of hydrogen ions acting as a concentration gradient from the matrix to the intermembrane space generates ATP through ATP synthase
Explain how cyclic photophosphorylation differs from noncyclic photophosphorylation
In noncyclic photophosphorylation, plants use photosystems II and I in series, first one and then the other, to produce both ATP and NADPH. A single photosystem is used that generates ATP via electron transport. The process then returns the electrons to the reaction center.
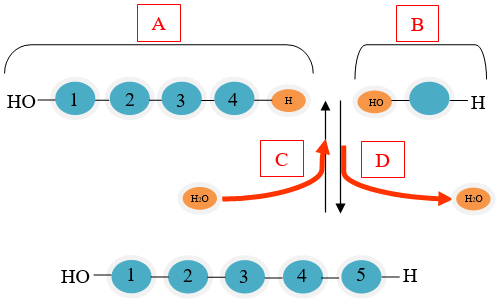
Which part of the diagram shows a condensation reaction?
D, condensation reactions occur when monomers are connected by the removal of a water molecule.
A magnesium sulfate solution taken orally can cause a net movement of water into the large intestine, which results from water molecules diffusing through aquaporins embedded in the cells of the intestinal lining.
By which of the following mechanisms do the water molecules most likely move into the large intestine?
A. By passive transport from an area of low osmolarity to an area of high osmolarity
B. By passive transport from an area of high osmolarity to an area of low osmolarity
C. By active transport from an area of low osmolarity to an area of high osmolarity
D. By active transport from an area of high osmolarity to an area of low osmolarity
A.
(Based on the information presented, the water molecules move through aquaporins by diffusing from an area of low osmolarity to an area of high osmolarity, which is an example of passive transport.)
In an experiment, a researcher prepares a reaction mixture by dissolving a substance in a buffered solution. The substance is the substrate of a certain enzyme. The researcher adds a small amount of the enzyme to the reaction mixture and measures the amount of product that is formed over time. The data are represented in Figure 1.
Which of the following best predicts the immediate result of adding more substrate to the reaction mixture at the point indicated by the arrow in Figure 1?
A.The amount of product will decrease until the reaction rate goes to zero.
B.The amount of product will decrease until the reaction reaches its equilibrium point or until the enzyme is been used up by the reaction.
C.The amount of product will increase until the reaction reaches its equilibrium point or until the substrate is used up by the reaction.
D. The amount of product will increase without stopping because the enzyme will be unchanged by the reaction.
C
The graph shown in Figure 1 indicates that the amount of product became constant as a consequence of the reaction reaching its equilibrium point or as a consequence of the substrate being used up. Adding more substrate will likely result in an increase in the amount of product because the reaction catalyzed by the enzyme will convert the added substrate into product.
If photosynthesizing green algae are provided with CO₂ synthesized with heavy oxygen (¹⁸O), later analysis will show that all but one of the following compounds produced by the algae contain the ¹⁸O label. That one is
A) 3-phosphoglycerate.
B) glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P).
C) glucose.
D) ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP).
E) O₂
E.
A researcher claims that the initial rise of oxygen in Earth’s early atmosphere, which occurred approximately 2.3 billion years ago, resulted from the metabolic activity of prokaryotic organisms. The claim is based on an interpretation of the geochemical and fossil evidence represented in Figure 1.

Which of the following types of evidence will best support the researcher’s claim?
ResponsesA.Evidence that some of the earliest eukaryotes used oxygen to produce ATP by cellular respiration
B. Evidence that the earliest plants produced oxygen as a by-product of photosynthesis
C. Evidence that some of the earliest organisms carried out photosynthesis without producing oxygen
D. Evidence that the cyanobacteria produced oxygen as a by-product of photosynthesis
D
Based on Figure 1, cyanobacteria appear in the fossil record before the rise of oxygen in Earth’s early atmosphere. The researcher’s claim will be supported by evidence that the cyanobacteria that were on Earth more 2.3 billion years ago produced oxygen as a by-product of photosynthesis. Also, cyanobacteria are prokaryotes, which is consistent with the researcher’s claim.