This property of water allows it to stick to other substances, aiding in the movement of water against gravity in plants.
What is adhesion?
These structures within all cells on Earth are responsible for protein synthesis, consisting of RNA and proteins.
What are ribosomes?
This molecule acts as the primary energy currency of the cell, storing and supplying the cell with needed energy.
What is ATP (adenosine triphosphate)?
This molecule fits into a receptor like a key into a lock, starting a cascade of events inside the cell.
What is a ligand?
This process ensures the formation of haploid cells from diploid ones, and is crucial for sexual reproduction and genetic variation.
What is meiosis?
This process involves the decoding of instructions within DNA to synthesize proteins, crucial for cell function and regulation.
What is gene expression?
This type of selection, practiced by humans, involves choosing specific traits for breeding, significantly impacting species diversity.
What is artificial selection?
This term describes the variety of species within a given ecosystem.
What is biodiversity?
This kind of chemical reaction allows monomers to be covalently bonding together to form a polymer.
What is dehydration synthesis?
These are the three examples of passive transport.
What are simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis?
This molecule serves as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain of mitochondria.
What is oxygen?
A disruption in this tightly regulated process can lead to uncontrolled cell growth, a hallmark of cancer.
What is the cell cycle?
Mendel used this law to explain how alleles for different traits are distributed to gametes independently of one another.
What is the law of independent assortment?
The primary enzyme involved in transcription.
What is RNA polymerase?
These diagrams are used to illustrate hypotheses about the evolutionary relationships among species, showing patterns of descent from common ancestors.
What are phylogenetic trees and cladograms?
This type of symbiotic relationship occurs when one species benefits and another species is harmed.
What is parasitism?
The specific sequence of these biological molecules make up a protein's primary structure.
What are amino acids?
This term describes what happens to a plant cell when it is placed in a hypotonic solution.
It becomes turgid and water will enter the cell.
This process splits glucose into two pyruvate molecules and results in a net gain of 2 ATP molecules.
What is glycolysis?
This form of signaling involves hormones traveling through the bloodstream to distant cells.
What is endocrine signaling?
These are the segments of DNA produced on the lagging strand during DNA replication.
What are Okazaki fragments?
These regions of eukaryotic genes are removed during RNA processing.
What are introns?
This type of speciation occurs when a population becomes geographically separated.
What is allopatric speciation?
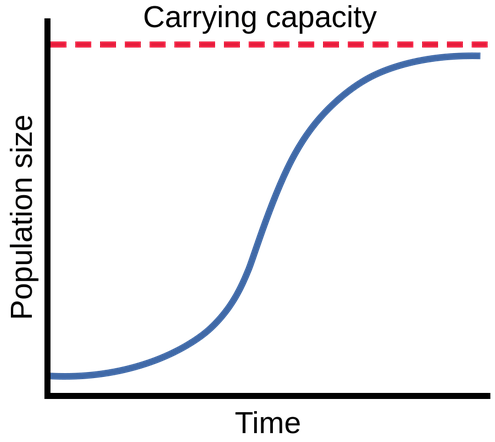
This is point represents the maximum population size that an environment can sustain.
What is carrying capacity?
All amino acids contain these three components.
What are the carboxyl group, amino group, and an R group?
This type of protein completely spans the hydrophobic interior of the plasma membrane.
What is an integral protein (or transmembrane protein)?
These are the two main processes of photosynthesis.
What are the light-dependent and light-independent (Calvin cycle) reactions?
This phase of mitosis is characterized by chromosomes lining up in the center.
What is metaphase?
This is the type of inheritance pattern shown.
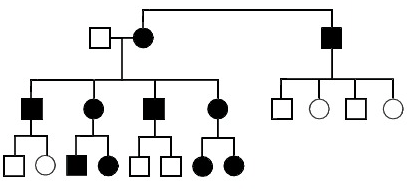
What is mitochondrial inheritance?
This term describes a set of multiple genes that are all under the control of a single promoter, which allows for coordinated gene expression in prokaryotes.
What is an operon?
These are the two most important examples of genetic drift.
What are bottleneck effect and founder effect?
This type of growth describes how a population's growth rate slows and eventually stops following a period of exponential growth, often due to resource limitation.
What is logistic growth?
This type of eukaryotic cell has a cell wall that contains chitin and ergosterol.
What is fungi?
This crucial ratio explains why cells tend to be small in size since it affects the efficiency of nutrient intake and waste elimination.
What is the surface area-to-volume ratio?
Pathway plants use to fix carbon dioxide into sugars.
What is the Calvin cycle?
Substances (such as cyclic AMP and calcium ions) act as intracellular signals to amplify a signal received from outside the cell.
What are second messengers?
This process increases genetic variation by exchanging DNA between non-sister chromatids during meiosis.
What is crossing over?
This protein/RNA complex is responsible for removing introns from pre-mRNA in eukaryotic cells.
What is the spliceosome?
These 5 conditions must be met in order to maintain a stable, non-evolving population.
1. Large population size
2. Random mating
3. No mutation
4. No migration
5. No natural selection
This graphical representation shows the energy loss at each trophic level in an ecosystem.
What is an energy pyramid?
These fatty acids contain double bonds that create a “kink” in their structure.
What are unsaturated fatty acids?
This organelle is responsible for transporting proteins and lipids to different parts of the cell, including to the cell membrane. It is the site of protein synthesis for many proteins.
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
This type of inhibition occurs when a substance blocks an enzyme's function without interacting with its active site.
What is allosteric inhibition?
These enzymes control cell cycle progression by phosphorylating specific target proteins.
What are cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs)?
This enzyme is responsible for synthesizing new DNA from an existing template RNA and is essential for the life cycle of retroviruses such as HIV.
What is reverse transcriptase?
The addition of this molecular tag to nucleotides typically leads to gene silencing in eukaryotes.
What is DNA methylation?
Red flowers (R) are dominant to white flowers (r). In a population of 1,000 flowers, 36% are white.
How many are heterozygotes?
480 flowers
This type of succession occurs in an area that previously supported life but was disturbed by an event like a forest fire or farming.
What is secondary succession?