This type of molecule has an unequal distribution of electrons resulting in slight negative and positive charges on different regions of the structure.
What are polar molecules?
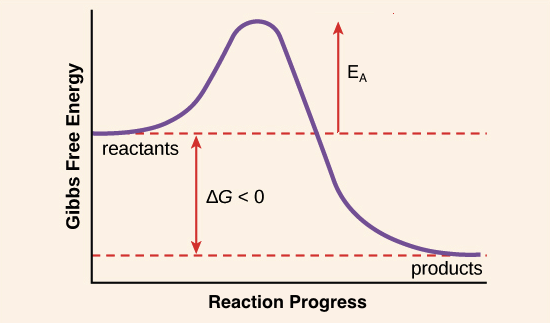 It is represented by Ea and is lowered by enzymes.
It is represented by Ea and is lowered by enzymes.
What is activation energy?
Which macromolecule is the major structure of the plasma membrane?
What are phospholipids?
This is a collection of hydrogen bonds that hold water molecules.
What is cohesion?
These are the reactants needed for photosynthesis to occur (3 factors)
What are carbon dioxide, light, and water?
The slight negative charge of oxygen in one water molecule is attracted to the slight positive charge of hydrogen in another water molecule.
What are hydrogen bonds?
(Fill in the blank) "Raising the temperature slightly will ____________________ the rate of a reaction.
What is increase?
A solution that has higher water concentration than the cell's interior.
What is a hypotonic solution?
The enzyme that allows carbon dioxide to be converted into glucose during the Calvin cycle.
What is Rubisco?
This is a reaction in which two (2) molecules become covalently bonded to each other through the loss of a small molecule, usually water.
What is dehydration synthesis?
This type of inhibition occurs when a substrate binds to a site other than the active site to prevent enzyme catalysis.
What is allosteric inhibition?
Substances that cannot passively flow through the plasma membrane are this.
What is polar/charged/hydrophilic/large?
This chemical reaction in a cell releases energy and is denoted with a negative delta "G".
What is an exergonic reaction?
The atomic ratios of this macromolecule are C- 1, H- 2, O- 1
What are carbohydrates?
40 degrees represents this value for this particular enzyme.
What is optimal temperature?
These structure are embedded in the cell membrane and can play a role in cell signaling.
What are glycoproteins?
Acts as a source of electrons and protons during the light-dependent reactions.
What is water?