The elements found in nucleic acids
What is CHONP?
The diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane.
What is osmosis?
ATP and NADPH are created during this process of photosynthesis.
DNA is replicated during this part of the cell cycle
What is S phase?
The function of nucleic acids
What is store and transmit genetic information?
Capillary action is created by these two properties of water.
What are cohesion and adhesion?
The type of transport shown here.
What is active transport?
This is released as a byproduct after water splits in the light reactions
What is oxygen?
The phase of mitosis shown here

What is telophase?
The process of breaking apart polymers using water, as shown below.

What is hydrolysis?
When double-stranded DNA contains 20% cytosine, it will contain this much adenine.
What is 30% adenine?
This organelle breaks down defective organelles.
Protons diffuse through this enzyme during oxidative phosphorylation to create ~36 ATP
What is ATP synthase?
The type of feedback mechanism where the response amplifies the original stimulus.
What is positive feedback?
The cell membrane is mainly composed of these two structures?
What are phospholipids and proteins?
Process that creates polymers from smaller molecules, as seen here. 
What is dehydration synthesis?
Mitochondria have a convoluted inner membrane to increase this, allowing the mitochondria to make more ATP.
What is surface area or surface area to volume ratio?
This step in cellular respiration is where carbon dioxide is released
What is the Krebs Cycle?
The signaling molecule that begins the cell signaling pathway.
When double-stranded RNA contains 18% cytosine, it contains this much thymine.
What is 0%?
Below is the structure of this macromolecule.
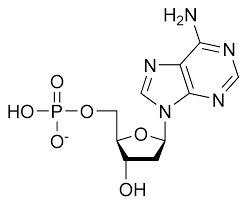
What is a nucleic acid?
The value for Ψ in root tissue was found to be -3.3 bars. If you take the root tissue and place it in a 0.1M solution of sucrose at 20°C in an open beaker, this is the Ψ of the solution, this is the direction of net flow of water.
What is -2.43 and into the root tissue?
This is the final electron acceptor in the ETC.
What is oxygen?
These are the proteins responsible for regulating the cell cycle.
What are CDKs?
The monomer of the macromolecule shown below.

What is a monosaccharide?