Energy!
Energy!
These monomers make up enzymes!
What are amino acids? (Enzymes are proteins!!)
Enzymes have a pH range of function. If the pH is much lower or higher than the range of function, the enzyme could __________________
What is denature?
Process in which CO2 is incorporated into organic molecules!
What is the CALVIN CYCLE?
The 2 stages of photosynthesis!
What are the Light Reactions & the Calvin Cycle?
These are the 3 steps in aerobic cell respiration!
1. Glycolysis
2. Krebs Cycle
3. ETC
The reactant(s) on which an enzyme works is called the _____.
What is a substrate?
Metabolic pathways that break down molecules, releasing energy OVERALL!
What is CATABOLIC?
Process in which CO2 is released as a by-product of the oxidation of glucose!
What is the KREBS CYCLE?
Process that replaces e- lost by P680 in the Light Reactions!
What is PHOTOLYSIS!
This is where the e- in the ETC came from!
What is GLUCOSE!?
"C" in the diagram below!
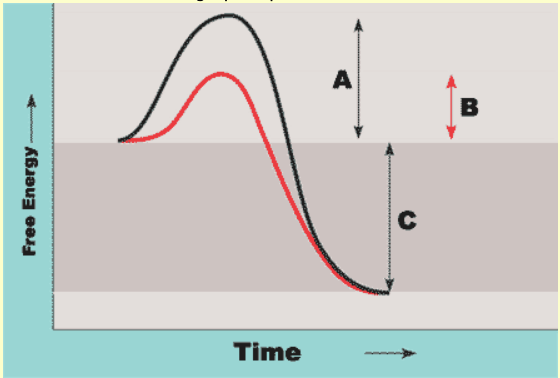
What is ΔG (free energy)?
Type of metabolic reaction that will DECREASE the entropy of a cell!
What is an ANABOLIC reaction?
Process that uses ATP to phosphorylate intermediates in the cycle!
What is the CALVIN CYCLE?
2 High-energy molecules made in the Light Reactions & used in the Dark Reactions!
What are ATP and NADPH?
Process of cell respiration that occurs with or without oxygen present!
What is GLYCOLYSIS?
"A" represents this in the graph!

What is activation energy without an enzyme?
A substance that can bind to allosteric sites changing the activity of the enzyme.
What is a NONCOMPETITIVE INHIBITOR?
Sends high energy e- to the ETC via these TWO molecules! (Name the cycle AND the 2 molecules!)
What is the KREBS CYCLE...and...NADH & FADH2!
1 Turn of the Calvin Cycle makes this 3-C sugar!
What is G3P (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate)?
Step of aerobic cell respiration that makes the MOST ATP!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
What is the ETC?!!??!
By doubling the [enzyme], the free energy of the reaction is affected in this way!
What is: Stays the same?
A substance that resembles the normal substrate & competes with the substrate for the active site!
What is a COMPETITIVE INHIBITOR?
Distinguish between the cycles using OXIDATION and REDUCTION...and the associated e- carriers!
Calvin Cycle: Reduction-donates e- from NADH
Krebs Cycle: Oxidation-removed e- & makes FADH2 & NADH
This is how the proton gradient is established in order to make ATP!
What is...
The reason why NADH can generate more ATP than FADH2!
What is because the e- of FADH2 move through FEWER complexes of the ETC?
