This is the number of neutrons in an isotope of Uranium with a mass number of 238
146
 Name two of the three intermolecular forces present between molecules of methanol shown above.
Name two of the three intermolecular forces present between molecules of methanol shown above.
Dipole-Dipole Interactions
Hydrogen Bonding
London Dispersion Forces
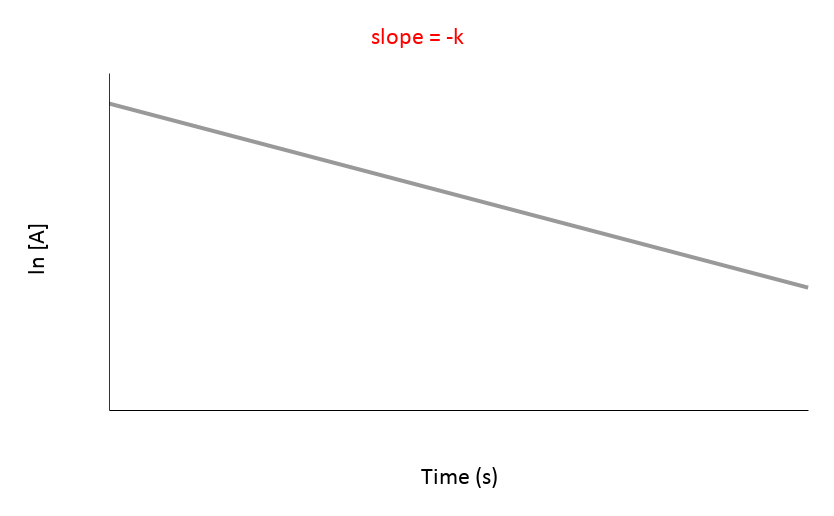 This image represents this order for a chemical reaction.
This image represents this order for a chemical reaction.
First Order
When Q < K, this shift occurs
Shift to the right (More products must be made)
This is the direction (and process that occurs) of electron flow through the electrodes of a galvanic cell.
Anode (oxidation) to Cathode (reduction)
This is the shorthand electron configuration for Tin
[Kr] 5s2 4d10 5p2
This is the weakest type of intermolecular force and is found in all substances
London Dispersion Forces
In a reaction mechanism, this is the term for a species that is formed and then consumed during the reaction
Intermediate
A +2B ⇌ 3C Keq = 1.042
This is the value of the equilibrium constant for the reverse reaction
0.9597
This is the value of the equilibrium constant (Keq) when ΔG° is negative.
K > 1
This rule states that electrons will fill degenerate orbitals singly before pairing up.
Hund's Rule
These types of solids have significantly weak IMFs, due to its structure of nonmetal atoms covalently bonded to one another.
Molecular Solids
Transition State
This is how equilibrium is affected in a constant volume container when a catalyst is added.
Equilibrium does not change
This is when a reaction will be spontaneous given the following information:
ΔG = Unknown
ΔH= Positive
ΔS = Positive
High Temperatures
This is the reason why atomic radii decrease as you move across a period on the periodic table
Increasing nuclear charge (nucleus attracts electrons more stongly)
 The graph above show this sample at the highest temperature
The graph above show this sample at the highest temperature
Sample C
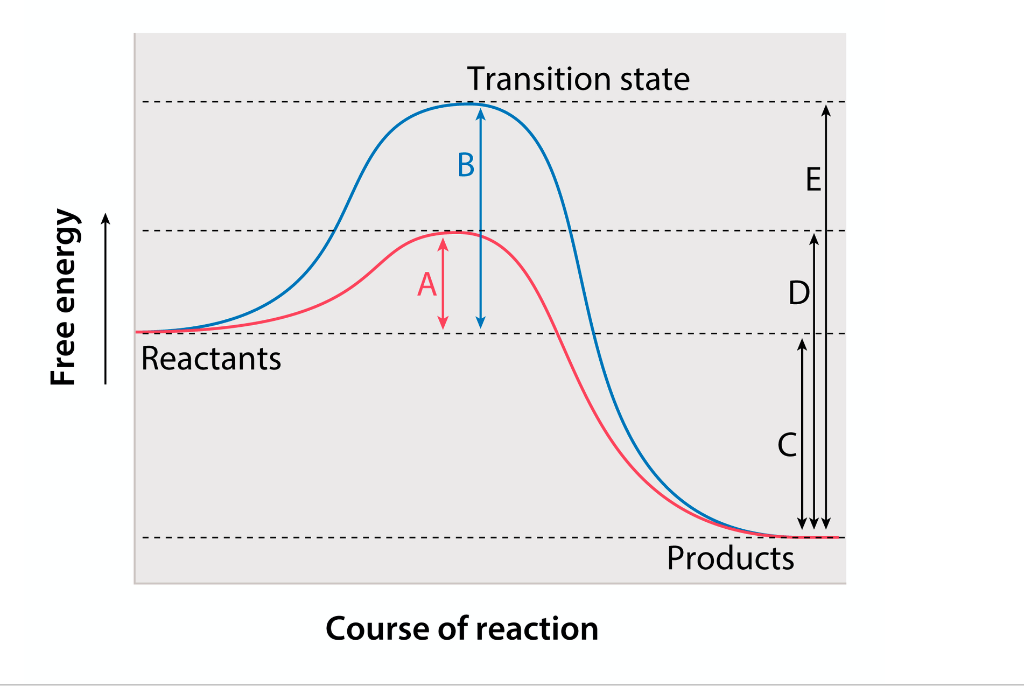 This is the reason that Reaction B has a greater activation energy than Reaction A
This is the reason that Reaction B has a greater activation energy than Reaction A
Reaction B is uncatalyzed
A saturated solution of CaF₂ is in equilibrium with its ions. When solid NaF is added to the solution to create a fluoride ion concentration of 0.25 M, what is the new solubility of CaF₂?
(Ksp for CaF₂ = 3.9 × 10⁻¹¹)
6.24 x 10-10 M
This is the cell potential of the following reaction
2K+ + Mg → Mg2+ + 2K
K+ + e- → K Reduction Potential = -2.93 V
Mg2+ + e- → Mg Reduction Potential = -2.37 V
+ 0.56 V
Below is the PES of Phosphorus. This change is necessary for the PES of Chlorine.
Peak at 1 MJ/mol increase to 5 electrons
 The Graph above shows this sample as the lightest sample.
The Graph above shows this sample as the lightest sample.
Sample C
This is the rate law for the table below
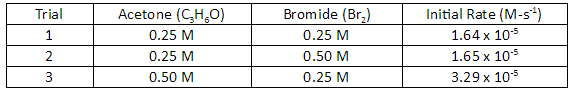
Rate = k[C3H6O]
This is the value of Kp for the reaction at equilibrium for methane gas (0.20 atm) and dihydrogen sulfide gas (0.25 atm) to produce carbon disulfide gas (0.52 atm) and hydrogen gas (0.10 atm).
4.2 x 10-3
This is the standard entropy of the following reaction:
2C2H6(g) + 7O2(g) → 4CO2(g) + 6H2O(l)
S∘ C2H6(g) = 229.5 J/mol K
S∘ O2(g) = 205.0 J/mol K
S∘ CO2(g) = 213.7 J/mol K
S∘ H2O (l) = 69.9 J/mol K
-619.8 J/mol K