What are the 3 different types of Intermolecular Forces?
London Dispersion Forces (LDFs), Dipole-Dipole, and Hydrogen Bonding
What does “R” stand for in the Ideal Gas Law equation PV = nRT?
The gas constant.
What is the term for a mixture where substances are uniformly distributed?
Homogeneous mixture
What is the "universal solvent"?
Water, because it dissolves the highest number of substances.
What formula relates energy and frequency of a photon?
E = hν.
Which type of solid has the highest melting point: molecular, metallic, ionic, or covalent network?
Covalent network.
According to Kinetic Molecular Theory, what happens to gas particle motion as temperature increases?
Particles move faster.
What tool can separate a solid from a liquid in a heterogeneous mixture?
Filtration.
Which solute would be most soluble in water: NaCl, CH₄, or CCl₄?
NaCl would be the most soluble in water because it is an ionic compound and water is a polar solvent; the positive and negative ions in NaCl are strongly attracted to the polar water molecules, allowing it to dissolve well.
What happens to the energy of a photon if its wavelength decreases?
Its energy increases.
Why does water have a higher boiling point than H₂S, even though they are both molecular compounds?
Water has hydrogen bonding, which is stronger than the dipole-dipole forces in H₂S.
Real gases deviate most from ideal behavior under what two conditions?
Low temperature and high pressure.
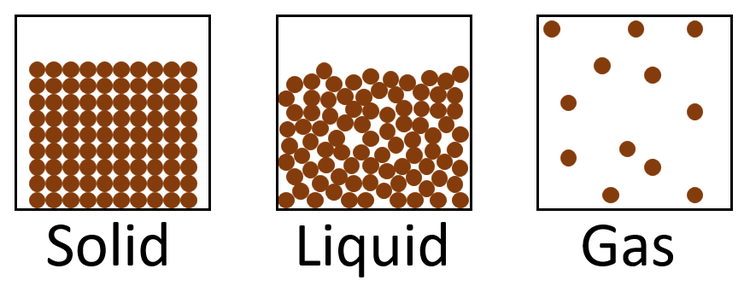
Describe what the particle diagram, for a solid, liquid, and gaseous compound would look like.
What is the difference between how microwave light and infrared light move?
Microwave light rotates and infrared light vibrates.
If a solution has a higher concentration, what happens to its absorbance, assuming everything else is constant?
Absorbance increases.
Rank the following in order of increasing strength of intermolecular forces: CH₄, NH₃, H₂O.
CH₄ < NH₃ < H₂O.
A gas has a pressure of 2.0 atm, a volume of 4.0 L, and a temperature of 300 K.
How many moles of gas are present?
0.33 mol
When a solution conducts electricity, what must be present?
Ions
At 25°C, the solubility of KNO₃ in water is 32 g per 100 mL. How many grams of KNO₃ can dissolve in 250 mL of water at this temperature?
80 g
A solution absorbs light at 525 nm. Calculate the energy of one photon of this light. (Use E = hc/λ)
3.79 × 10⁻¹⁹ J.
Why does hydrogen fluoride (HF) have a higher boiling point than hydrogen chloride (HCl)?
HF has hydrogen bonding due to the highly electronegative fluorine atom, while HCl only has dipole-dipole forces. The stronger hydrogen bonds in HF require more energy to break, resulting in a higher boiling point compared to HCl.
A gas occupies 2.00 L at 1.00 atm and 300 K. What volume will it occupy at 2.00 atm and 400 K?
1.50 L
Describe how chromatography separates components of a mixture.
In chromatography, components separate because of their different polarities: polar substances tend to stick more to a polar stationary phase and move slower, while nonpolar substances don’t stick as much and travel faster with the mobile phase, causing them to separate based on how polar they are.
A molecule absorbs visible light with a wavelength of 500 nm. What is the energy (in joules) of one photon of this light? (Use h=6.63×10−34 J⋅sh=6.63×10−34J⋅s and c=3.00×108 m/sc=3.00×108m/s)
3.98×10−19J.
Explain why the energy of a photon is inversely proportional to its wavelength.
Energy EE is related to wavelength λλ by the equation E=hcλE=λhc, where hh is Planck’s constant and cc is the speed of light. Since hh and cc are constants, as the wavelength λλ increases, the energy EE decreases, showing an inverse relationship.