A testable conjecture about how something works.
Hypothesis
The number of protons in the nucleus of a particular element.
Atomic number
The process by which producers use solar energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose.
Photosynthesis
A cold and treeless biome with low-growing vegetation, characterized by permafrost
Tundra
The relative proportion of individuals within the different species in a given area.
Species evenness
This type of ecological succession occurs on surfaces that are initially devoid of soil.
Primary succession
A measure of the value of all products and services produced in one year in one country.
Gross domestic product (GDP)
A group that experiences exactly the same conditions as the experimental group, except for the single variable under study.
Control group
A property of water that results from the cohesion of water molecules at the surface of a body of water.
Surface tension
The energy captured by producers in an ecosystem minus the energy producers respire.
Net primary productivity
The most diverse marine biome on Earth, found in warm, shallow waters beyond the shoreline.
Coral reefs
The process in which humans determine which individuals breed, typically with a preconceived set of traits in mind.
Artificial selection
A growth model that describes a population whose growth is initially exponential, but slows as the population approaches the carrying capacity of the environment.
Logistic growth model
If a population of 190,000 people has a growth rate of 1.9% annually, how many years will it take for this number to double?
Numerical value that helps provide insight into the state of an environmental system
Environmental Indicator
The physical law stating that when energy is transformed, the quantity of energy remains the same, but its ability to do work diminishes.
2nd law of thermodynamics
Explain the main difference in the transport of energy and matter through an ecosystem
Energy flows in one direction (from the sun to the consumers), while matter cycles through it
A biome with warm summers and cold winters with over 1 m of precipitation annually. Dominated by broadleaf deciduous trees such as beech, male, oak and hickory.
Temperate Seasonal Forest
A change in the genetic composition of a population as a result of descending from a small number of colonizing individuals.
Founder effect
Mention the 3 types of symbiotic relationships learned about during class AND how the species interact:
1. Parasitism (-/+)
2. Mutualism (+/+)
3. Commensalism (+/0)
In a stable population from a developing country, what is generally the approximate number of replacement-level fertility?
2
It refers to how close repeated measurements of the same sample are to one another.
Precision
A system in which exchanges of matter or energy occur across system boundaries.
Open system
All land in a given landscape that drains into a particular stream, river, lake, or wetland.
Watershed
Describes a lake with a low level of productivity.
Oligotrophic lake
What is a niche?
The whole of biotic and abiotic conditions under which a species can survive, grow, and reproduce. It determines their role in the ecosystem
A factor that influences an individual’s probability of survival and reproduction in a manner that depends on the size of the population. Give 2 examples
Density dependent factor
- Competition, predation, disease, parasitism
Name 3 intrinsic factors of a population that can affect the population growth:
Birth rates, death rates, emigration, immigration, fertility, population size, life expectancy
Tell me the steps followed in the scientific method:
1. Observe and question
2. Form a hypothesis
3. Conduct and experiment/collect data
4. Interpret results
5. Disseminate findings (optional)
As members of a species reproduce, they create more offspring that will be able to reproduce in turn, creating a cycle that increases the population size. This is called a ______________.
Positive feedback loop
State the Intermediate disturbance hypothesis
The hypothesis that ecosystems experiencing intermediate levels of disturbance are more diverse than those with high or low disturbance levels.
Which biomes drastically reduce the severity of floods and filter pollutants from the water near coastal areas?
Freshwater wetlands (at least 2 if being specific - mangrove/swamps, salt/marshes)
Tell me a reason why a species may go through sympatric speciation:
Resource partitioning (to avoid competition, members of the same species may start to prefer different foods/areas/times of activity, etc)
Different mating behaviors become popular
Functional mutation equally as likely to survive as original phenotype
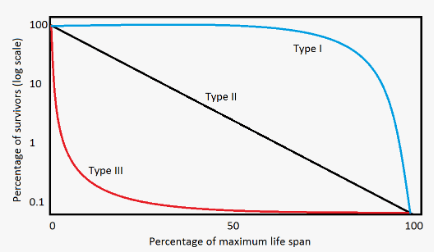
What type of survivorship curve do r-specialist species present? Give an example of one
Type III (tortoises, seeds from trees, insect eggs, fish eggs, etc)
Describe the 4 stages of demographic transition:
1: preindustrial, high birth rates and high death rates. 2: begins to industrialize, death rates drop rapidly, but birth rates do not change (rapid growth). 3: birth rates decline, deaths are low (stable growth). 4: birth rates and death rates are low (stable or decline).