Organisms that are short-lived and produce many offspring at a young age are known as this type of species.
r-selected species
During this phenomeon trade winds weaken and warm water is allowed to flow toward the west coast of the Americas. This can cause a warmer winters in the Pacific NW and stormy conditions in the south. This can also affect fisheries along the coast of South Americ.
El Nino
(BONUS POINTS: Explain La Nina)
Describe point and nonpoint source pollutants.
Point source pollutants have a specific, easily identified source, while nonpoint source pollutants do not.
BONUS POINTS: Give an example of each
This fossil fuel is the world's largest energy source.
Oil
When ocean temperatures rise, algae die and leave these organisms brittle and vulnerable.
gives EPA the authority to control hazardous waste from cradle to grave. This includes the generation, transportation, treatment, storage, and disposal of hazardous waste
Resource Conservation and Recovery Act

Why does the North Twin island have the least species richness?
North Twin is a small island, furthest from the mainland. Species will have a harder time getting to that island due to its distance and size.

List the four stages of the demographic transition model in order.
preindustrial --> transitional --> industrial --> postindustrial
 What type of soil is 60-30-10 (sand-silt-clay)?
What type of soil is 60-30-10 (sand-silt-clay)?
sandy loam
These chemicals entering the atmosphere can lead to photochemical smog forming during the day time.
NO2, O3, and VOCs
leach toxins into soil and groundwater, contaminate drinking water, habitat loss, land degredation
CO2 in the atmosphere dissolves into the ocean resulting in carbonic acid. Carbonic acid (H2CO3) further dissociates into H+ ions and carbonate ions.
Ocean acidification
BONUS POINTS: Explain how ocean acidification affects marine organisms
an agreement to lower the amount of greenhouse gases released into the atmosphere
Kyoto Protocol
Fruticose lichen can only grow in areas where air pollution is low. The presence of this type of lichen indicates good air quality.
indicator species
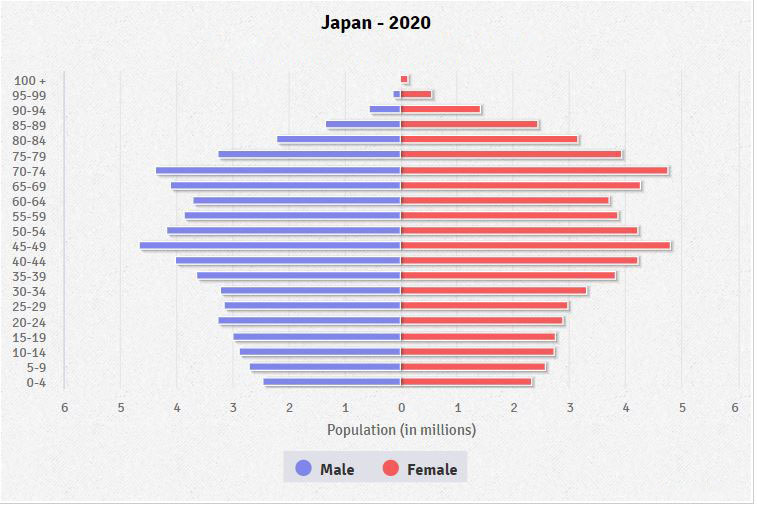 Using the diagram above, describe what is happening to Japan's population.
Using the diagram above, describe what is happening to Japan's population.
Japan's population is declining.
Identify a soil conservation stategy that could be used to prevent soil erosion in agricultural fields.
rotational grazing, contour plowing, terracing, perennial crops, wind breaks, no tillm strip cropping
process of accumulation of chemicals in an organism that takes place if the rate of intake exceeds the rate of excretion
bioaccumulation
BONUS POINTS: Define biomagnification
These source of energy requires large pools of water to cool reactors. It is not considered renewable, but it is "clean".
Nuclear
BONUS POINTS: Give an example of where this type of energy caused major losses.
CFCs entering the stratosphere react with ozone molecules to form oxygen gas molecules.
Ozone deleption
BONUS POINTS: explain how this causes the hole in the ozone layer
global agreement to protect the stratospheric ozone layer by phasing out the production and consumption of ozone-depleting substances
Montreal Protocol
If 356 kJ of energy is transferred to the secondary consumer from the primary consumer, how much energy does the producer absorb from the sun? MUST SHOW WORK
35600 kJ
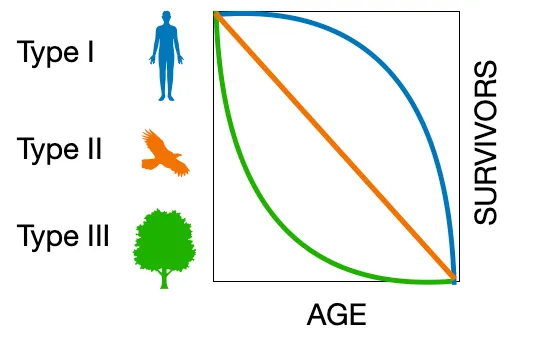
This organism is most likely an r-selected species
Tree (Type III)
Describe an economic advantage of using GM crops.
increased yield, decreased insectiside
BONUS POINTS: identify and describe one pest control method other than synthetic pesticides.
Identify a disease caused by contaminated water
Cholera, dysentry
BONUS POINTS: Identify and describe a disease that spreads easier in densely populated areas.
This type of energy is used mostly used in developing countries.
Biomass
BONUS POINTS: Why does biomass have a different effect of atmosphereic carbon than burning fossil fuels?
Greenhouses gases from cars, cows, factories, and landfills are released into the troposphere. These gases make it difficult for infared rays to leave the atmosphere.
Global warming
BONUS POINTS: what are some environmental impacts of global warming?
prohibits the FDA from approving the use of any food additive found to cause cancer in animals or humans
Delany Clause
Ecosystems offer aesthetic enjoyment and recreational opportunities. Example: National parks and scenic landscapes attract tourists.
Ecosystem services: cultural service
Spain's crude death rate is 9.1 per 1000 people while its crude birth rate is 8.0 per 1000 people. Calculate the population growth rate for Spain in 2022. SHOW YOUR WORK.
0.11% decrease
(EXTRA POINTS: Calculate the doubling time of Spain's population if there is an emigration rate of 1.3 per 1000 residents and an immigration rate of 4 per 1000 residents)
As populations increase, people tend to move away from urban centers into less dense suburban areas.
BONUS POINTS: what causes urban sprawl? what is a possible solution to slow urban sprawl?
establishes federal standards for mobile sources of air pollution and their fuels and for sources of 187 hazardous air pollutants, and it establishes a cap-and-trade program for the emissions that cause acid rain
Clean Air Act
Chemical X weighed 333 g when it was first collected. After 36 years, the same sample of chemical X weighs 20.81 g. What is the half life of chemical X?
9 years
This international agreement designed to regulate the trade of endangered species
Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITIES)
provides a Federal "Superfund" to clean up uncontrolled or abandoned hazardous-waste sites as well as accidents, spills, and other emergency releases of pollutants and contaminants into the environment
Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA)