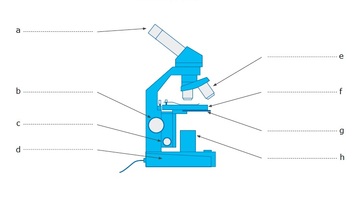
 The letter e
The letter e
Objectives/objective lens
Organelle which is the site of steroid and lipid synthesis
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum
A depression or hollow in a bone.
Fossa
Define concha.
Bone curled like a seashell.
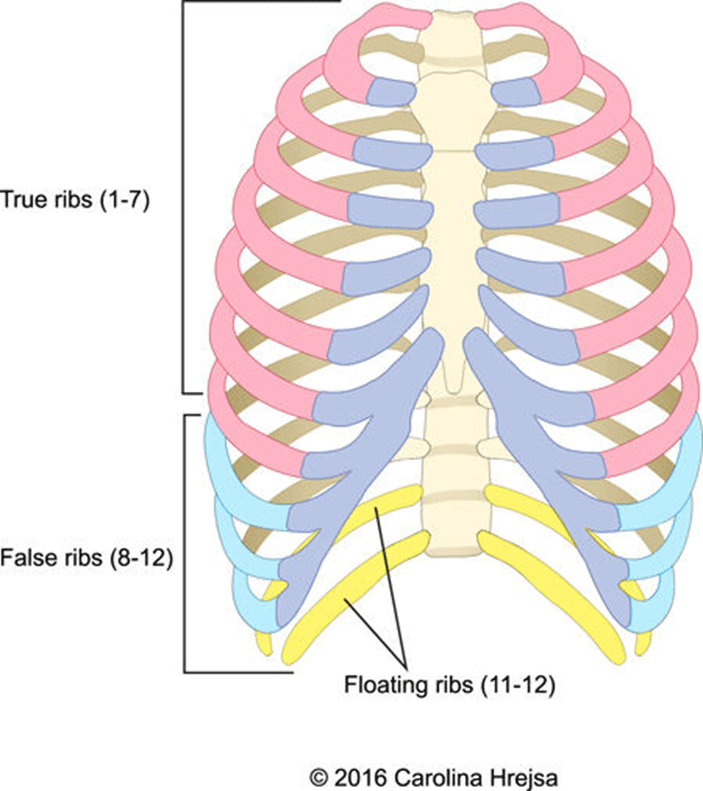
The number of total pairs of ribs.
12
Describe the anatomical position.
Hands are held unnaturally forward. 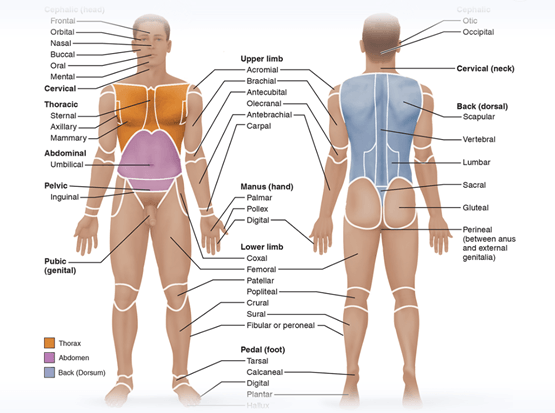
Stage of cell division. 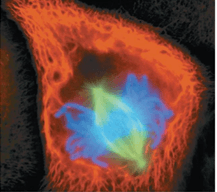
Metaphase
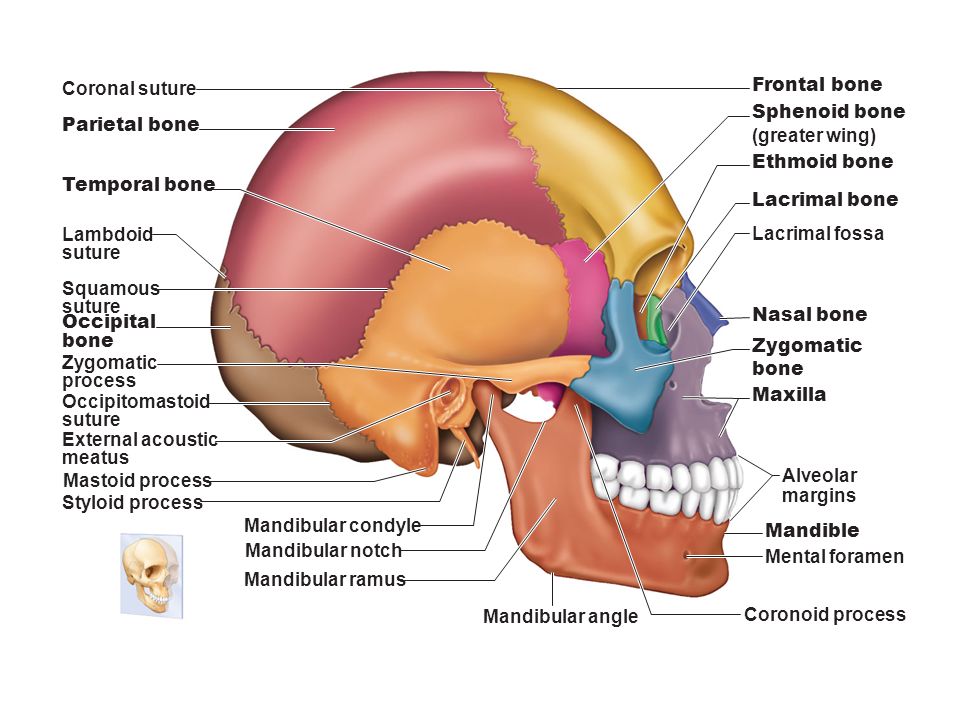
Two bones that make up the cheekbone.

Temporal bone
Zygomatic bone
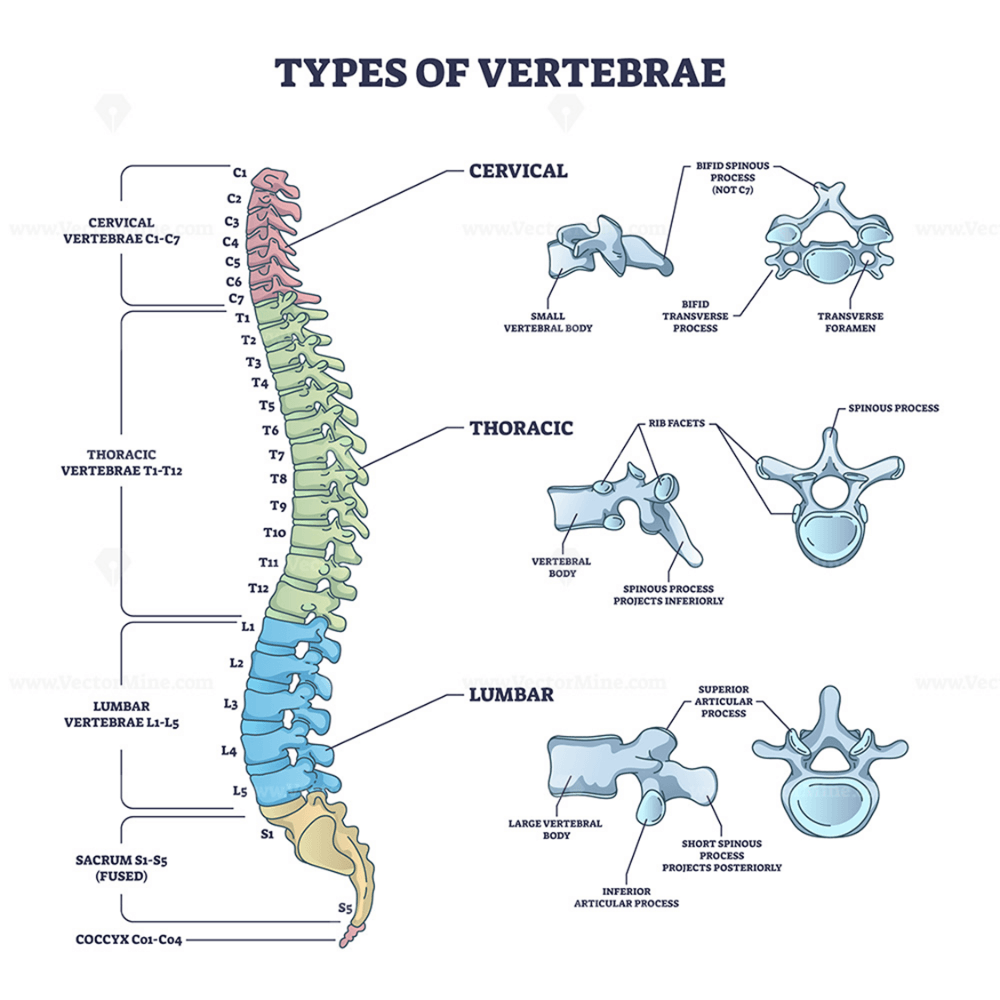
List the three types of vertebrae and numbers of each.
Cervical 7
Thoracic 12
Lumbar 5
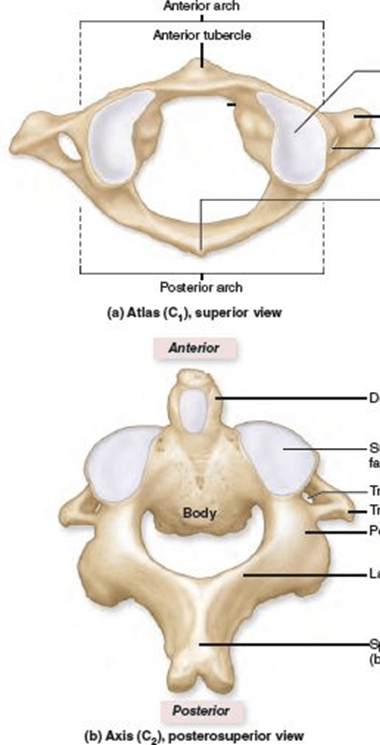
Vertebrae also known as C2.
Axis
Calculate the total magnification for the 40x objective.
40x * 10x = 400x
Type of tissue is this
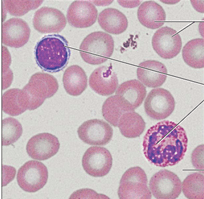
Connective tissue blood
The two holes passing through the mandible. 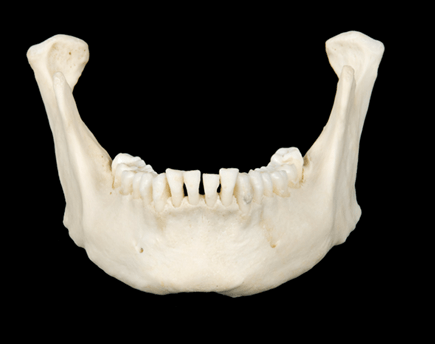
Mental foramen
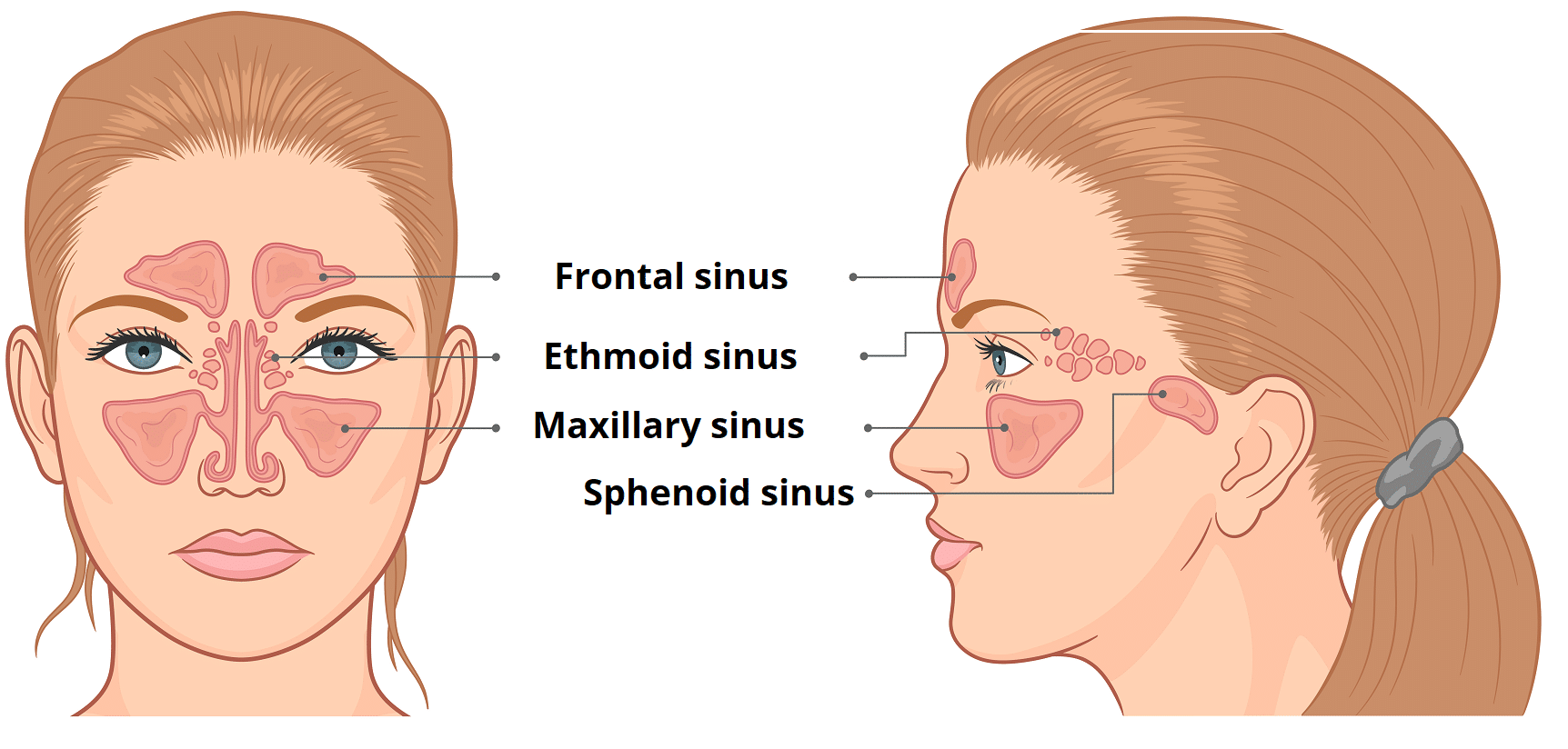
The four paranasal sinuses.
Frontal
Sphenoid
Ethmoid
Maxillary
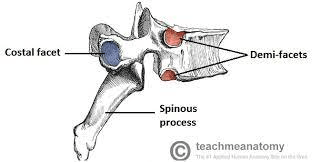
Costal facets articulate with ________ vertebrae.
Thoracic
What is working distance?
How far the bottom of the objective lens is from the surface of the slide. 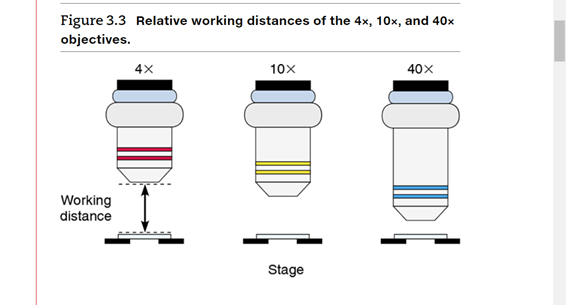
Type of tissue is this
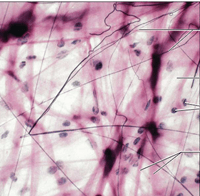
Connective tissue proper, loose connective tissue aereolar
The mastoid process is a feature on what bone.
Temporal bone

What is this feature.
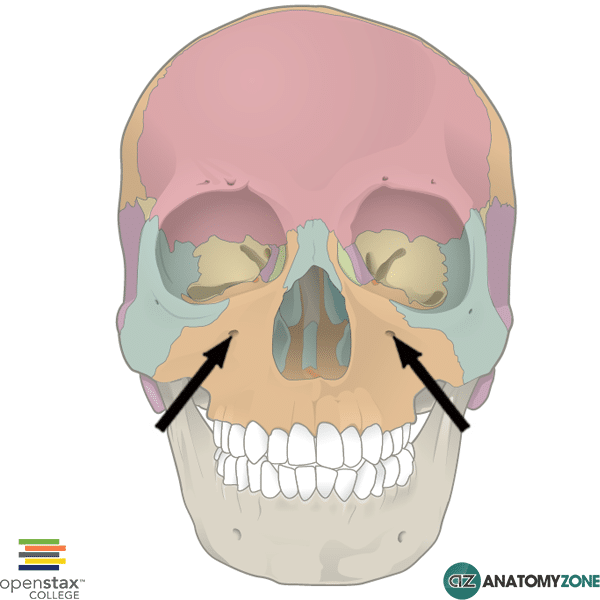
Infraorbital foramen
What tissue is this.
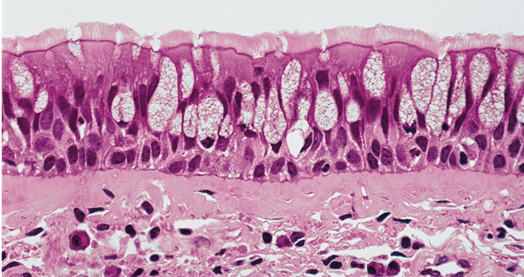
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Describe how you would prepare a wet mount.
Place the object in drop of water on clean slide.
Hold a coverslip at 45 degree angle with fingertips.
Lower the coverslip slowly.
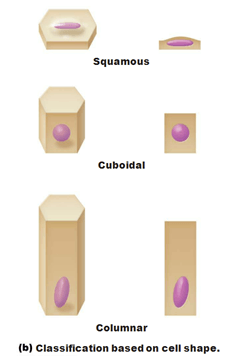
List the five names of epithelial tissues (2 indicate # of layers, 3 indicate shape of cells)
Simple and stratified, squamous cuboidal and columnar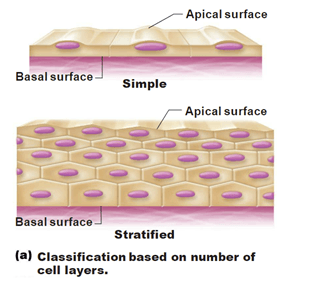
List and identify the 8 cranial bones on a model.

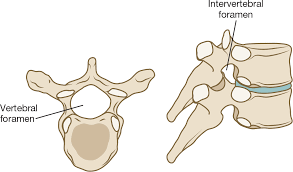
_____________ pass(es) through the intervertebral foramen.
Spinal nerves
This feature on the sacrum is known as the ________.
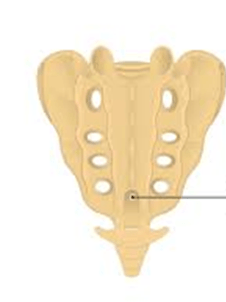
Sacral hiatus

Three kinds of microscopes we learned about and what are they used for.
Compound/light microscope
Electron microscope
Dissection microscope
List an example, tissue location, and tissue function of simple columnar epithelium.
Stomach, jejunum, colon.
Digestive tract.
Secretion of mucous/absorption.
List the four sutures surrounding the parietal bone.
Lambdoid suture
Squamous suture
Coronal suture
Saggital suture
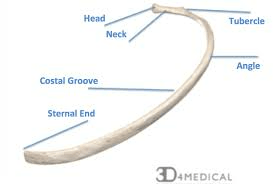
List three features located on a rib.
Tubercle
Angle
Head
Costal groove
What tissue is this.
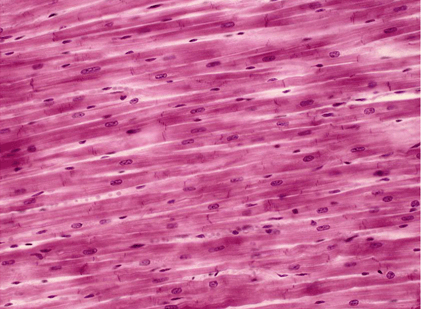
Cardiac muscle