Identify the specific segment of the nephron responsible for generating the medullary osmotic gradient.
Bonus: What specific part of the structure?
What is the loop of Henle?
Bonus: ascending limb
This hormone stimulates the kidneys to reabsorb water in the collecting ducts.
What is antidiuretic hormone (ADH)?
What are the main differences between Type I and Type II alveolar cells in structure and function?
Type I alveolar cells are thin and flat, forming the structure for gas exchange. Type II alveolar cells are cuboidal and produce surfactant, which reduces surface tension to keep alveoli open.

In the carbohydrate digestion experiment, a tube contains starch and amylase enzyme. After incubation, iodine is added and the solution turns yellow-brown instead of blue-black. What does this color change indicate?

Iodine normally reacts with starch to produce a blue-black color. If the solution turns yellow-brown instead, it means that the starch has been broken down into smaller sugar molecules (like maltose or glucose) by the amylase enzyme during incubation. These smaller sugars do not react with iodine to produce the blue-black color. Therefore, the color change indicates that carbohydrate digestion has occurred successfully.
A 23-year-old female presents with dysuria (painful urination), increased frequency, and suprapubic discomfort. Urinalysis reveals cloudy urine with white blood cells and bacteria. What is the most likely diagnosis?
BONUS: What is the clinical term for WBC in the urine?
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI).
BONUS: Pyruria
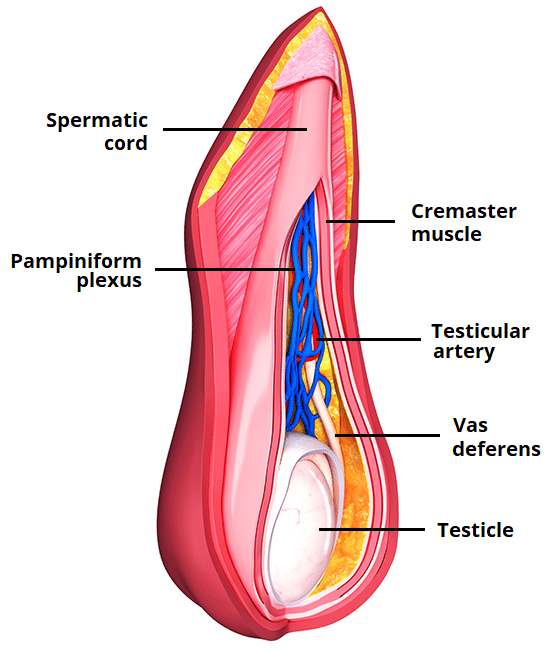
The spermatic cord contains several structures. Name the at least two of the three key components involved in testicular blood supply and temperature regulation.
What are the testicular artery, pampiniform plexus, and vas deferens?
Ovulation is triggered by a surge in this hormone.
What is luteinizing hormone (LH)?
What role do goblet cells play in the respiratory epithelium, and how is this important for airway protection?
Goblet cells produce mucus that traps dust, microbes, and particles. This mucus is then moved by cilia to clear the airway, protecting the lungs from infection and irritation.
Explain the role of the hepatic portal vein in nutrient regulation after digestion.
It transports nutrient-rich blood from the intestines to the liver for processing and detoxification before entering systemic circulation.
Name A, B, and C on the urinary system model (male and female).
Name the organ depicted by the slide below. Name A and B.
BONUS: Which structural feature of this significantly increases its absorptive surface area, and what connective tissue core supports it?
BONUS: Villi supported by the lamina propria.
Aldosterone promotes the reabsorption of _____ in the _____ tubule.
What is sodium and the distal tubule?
Identify Sertoli and Leydig cells in this slide of the testes.
Bonus: What hormones do Leydig cells produce?
BONUS: Testosterone
Explain the mechanism by which aldosterone regulates sodium and potassium balance in the distal tubule.
Aldosterone increases sodium reabsorption and potassium secretion by making the kidney cells produce more sodium-potassium pumps and sodium channels. This helps the body keep sodium and get rid of extra potassium through urine, maintaining the right balance of these ions.
This condition is suggested by sweet-smelling urine, glucosuria, ketonuria, and symptoms like weight loss, thirst, and frequent urination in a young adult.
BONUS: This acid-base imbalance commonly occurs in diabetic ketoacidosis due to excess ketone production.
What is diabetic ketoacidosis?
BONUS: What is metabolic acidosis?
The respiratory zone begins at this structure within the lungs, where gas exchange begins.
Bonus (no pts tho): Gas exchange primarily occurs here.
What are the respiratory bronchioles?
Bonus: Alveoli
How does hemoglobin’s affinity for oxygen change in response to pH and CO2 concentration? Name this effect.
What is the Bohr effect: decreased pH and increased CO2 reduce hemoglobin affinity, facilitating oxygen release?
Describe the histological features and functional roles of the muscularis mucosae and the muscularis externa in the gastrointestinal tract.
The muscularis mucosae is a thin layer of smooth muscle found within the mucosa, responsible for local movements of the mucosal layer to aid secretion and absorption. The muscularis externa consists of thicker layers of smooth muscle (usually an inner circular and outer longitudinal layer) that produce peristaltic contractions to propel food along the digestive tract.
You performed a Benedict’s test on a solution after incubating starch with salivary amylase for 15 minutes. The test turns orange-red. What does this indicate about the enzymatic activity and the digestion of starch?

The orange-red color indicates the presence of reducing sugars (like maltose or glucose), showing that salivary amylase broke down starch into simpler sugars.
Label:
BONUS: Why are women more prone to UTIs than men?
BONUS: Women are more prone to UTIs because their urethra is shorter and closer to the anus, making it easier for bacteria (especially E. coli) to enter the urinary tract.
Name the organ that is depicted in this slide. Name A, B, C.
Explain the steps of carbohydrate digestion from the mouth to the small intestine, including how enzymes like salivary amylase, pancreatic amylase, and brush border enzymes work.

1. In the mouth, salivary amylase in saliva begins breaking starch into maltose.
2. In the small intestine, pancreatic amylase continues breaking starch down into maltose.
3. At the small intestine’s lining, brush border enzymes like maltase break maltose into monosaccharides such as glucose, which are then absorbed into the blood.
Name:
Trypsin is added to a solution containing proteins. After some time, the solution is tested with the Biuret reagent and shows less purple color than before. What does this tell you about what trypsin did to the proteins?
Trypsin broke down the proteins into smaller pieces, so there are fewer peptide bonds for the Biuret reagent to react with, resulting in less purple color.
More detailed: The Biuret reagent detects peptide bonds in proteins, and when it binds to these bonds, it produces a purple color—the more peptide bonds, the stronger the color. Trypsin is a protease enzyme that breaks proteins into smaller peptides and eventually into individual amino acids by cutting at specific sites in the protein chain. When trypsin breaks down the large proteins into smaller fragments, the number of intact peptide bonds that the Biuret reagent can bind to decreases. This leads to a weaker purple color or a lighter reaction with Biuret reagent compared to the original protein solution. So, the decrease in purple color indicates that trypsin has successfully digested the proteins into smaller pieces, reducing the amount of intact peptide bonds.
Label:
BONUS: Name the pathway of sperm (including accessory organs).
BONUS:
1. Seminiferous tubules in the testes (sperm is produced).
2. Epididymis (sperm matures).
3. Vas Deferens (transports sperm).
4. Seminal Vesicles (add fructose-rich fluid).
5. Ejaculatory Duct (mixes sperm + fluid).
6. Prostate Gland (adds enzymes and milky fluid).
7. Bulbourethral Glands (add lubricant/mucus).
8. Urethra (semen exits through penis).