Identify what term the following definition refers to:
The region from which innovative ideas originate. This relates to the important concept of the spreading of ideas from one area to another.
Hearth
What are Pro-Natalist Policies and Anti-Natalist policies, and give examples of each?
Pro-Natalist- Decisions made to boost fertility rates and, ultimately, population growth. EX: Russian mother medals, tax incentives, child care incentives
Anti-Natalist- Decisions made to lower fertility rates and, ultimately, population decreases. EX: China's one-child policy, forced sterilization, cash incentives
What is the difference between Material and Non-Material Culture and give 2 examples of each
Material: The physical, visible objects made and used by members of a cultural group; includes buildings, furniture, clothing, food, artwork, and musical instruments.
Non-Material: Intangible elements of culture including a wide range of beliefs, values, myths, and symbolic meanings passed from generation to generation within a given society.
Define a Nation-state and give an example
The ideal political geographical unit; one in which the nation’s geographic boundaries (a people and its culture) exactly match the state’s territorial boundaries (governance and authority).
Japan, Iceland, South Korea, North Korea, etc...
Describe the difference between Environmental Determinism and Possibilism
Environmental Determinism: The belief that the physical environment is the dominant force shaping cultures and that humanity is a passive product of its physical surroundings.
Possibilism: The belief that any physical environment offers a number of possible ways for a society to develop and that humans can find ways to overcome environmental challenges.
What stage of the Demographic Transition Model is Country A and B in? 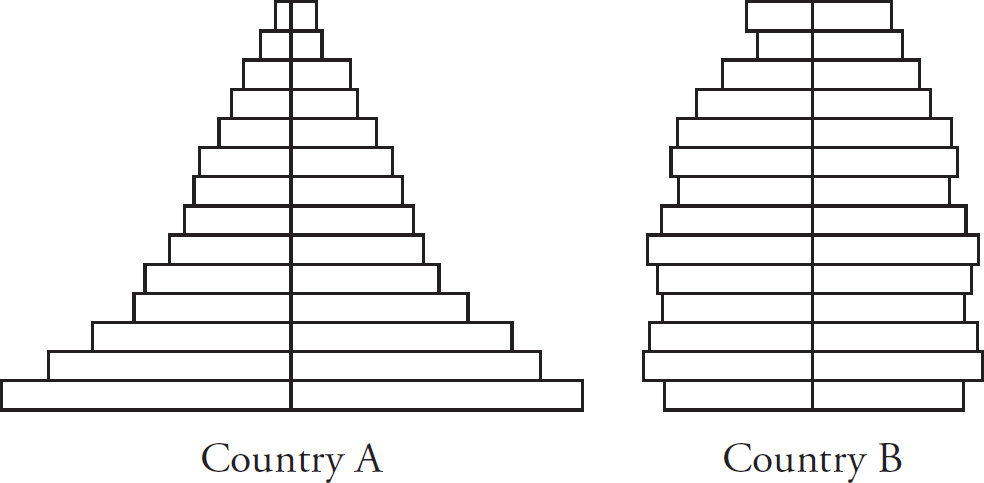
Country A- Stage 2
County B- Stage 4
Centrifugal: A force that threatens the cohesion of a neighborhood, society, or country.
Centripetal: A force that brings people together and unifies a neighborhood, society, or country.
Define a Nation and a State and give an example
Nation: A community of people bound to a homeland and possessing a common identity based on shared cultural traits such as language, ethnicity, and religion.
Japanese, Kurds, Muslims
State: An independent political unit with a centralized authority that makes claim to sole legal, political, and economic jurisdiction over a region with defined boundaries.
Germany, Nigeria, Brazil
Finish the Phrase: All Maps...
All Maps Lie Flat, All Flat Maps Lie!
What is the Scale of Analysis and Type of Map? 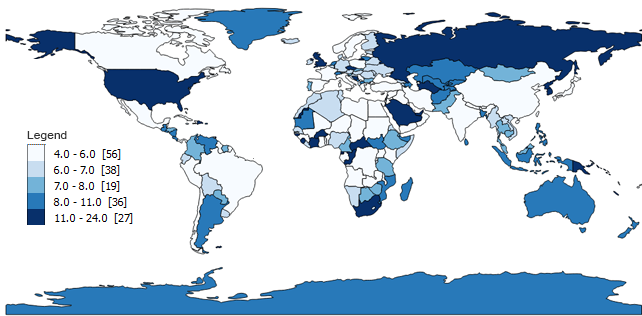
National Scale of Analysis
Choropleth Map
What is the difference between Crude Birth Rate and Total Fertility Rate?
CBR: How many people are born in a given year. The average number of births divided by 1000 people; the traditional way of measuring birth rates.
TFR: The average number of children born per woman during her reproductive lifetime, considered to be from 15 to 49 years of age.
What is the difference between a universalizing and an ethnic religion? Give examples for both
Universalizing: A religion that is spread with the intention of converting others to its beliefs
Christianity, Islam, Buddhism
Ethnic: A religion that is relation to ethnic heritage and geographical regions
Judaism, Hinduism, Animism
Identify this boundary type and explain what it means
Consequent Boundary
A boundary that is drawn to accommodate existing cultural differences.
Define a borderland and use the example that Mr. Newberg gave in class that all of you must go to once in your life.
A region straddling both sides of an international boundary where national cultures overlap and blend to varying degrees.
Fuzzy's tacos
What is the Scale of Analysis and Type of Map? 
Local Scale of Analysis
Isoline Map
Describe the characteristics of an area in stage 2 of the DTM and identify a modern country in this stage. 
The death rate drops rapidly due to advancements in medicines and industrial inventions.
The birth rate remains high resulting in rapid population growth
Modern Examples: Afghanistan, Nigeria, Pakistan, Bolivia, Yemen
What is the difference between assimilation and acculturation? What are the benefits and downfalls of each?
Assimilation: Occurs when an ethnic or immigrant group blends in with the host culture and loses many culturally distinctive traits.
Acculturation: Occurs when an ethnic or immigrant group adopts enough of the ways of the host society to be able to function economically and socially.
Identify this type of boundary and explain what it means
Relic Boundary
A boundary that no longer functions as an international border.
Give an example for each type of Diffusion:
Relocation
Stimulus
Hierarchical
Reverse Hierarchical
Contagious
Relocation: Most migration where ideas are brought and shared, like Polish Culture in Chicago
Stimulus: McDonalds, Barbie, Santa
Hierarchical: Fashion, Technology, Religious Doctrine
Reverse Hierarchical: Walmart, Rap/Grunge Music, Tik Tok trends
Contagious: Illnesses, Viral Videos,
Identify what Map Projection is below and describe its strengths and weaknesses.
Peters Projections
Strength: Land area more accurate
Weakness: Shape is distorted away from the equator
Identify and Explain the following effects of Migration:
Political
Economical
Social
Political:
Snow Belt-to-Sunbelt migration is changing the U.S. political landscape as the southern states gain seats in the House of Representatives at the expense of northern states.
Economic:
Supply and Demand
People typically migrate from areas of low employment or low wages to areas of higher employment or higher wages.
Average wages may increase at the origin (low-wage area) and decrease at the destination (high-wage area).
Heavy net out-migration may cause the values of land and real estate to decline.
Areas experiencing net in- migration often benefit from the increased labor supply, higher demand for goods and services, and rising land and housing prices.
Social:
Spread of culture
Spread of diseases
Migration may spread disease (e.g., cholera outbreak in India, early 1800s) or migration may result from disease outbreaks
Social cohesiveness or disorganization
Places that experience net in-migration, are likely attracting people with diverse cultural backgrounds. That place may be more – or less – tolerant than where the migrants originated
1830s Irish immigrants in New York
List and explain 3 Different things that are a part of a cultural landscape and what they tell.
Answers may vary:
Architecture, Language, Signs, Land Use, Food Preferences, Innovations, Physical Landscape, Religion, Gender Use, etc.
Define Neo-colonialism and give an example
The set of economic and political strategies by which wealthy and powerful countries indirectly maintain or extend their influence over less wealthy areas.
DeBeers Diamond Compay in Africa
Banana Wars in South/Latin America