Give the name & # of two cranial nerves responsible for movement of the tongue.
Glossopharyngeal Nerve (IX)
Hypoglossal Nerve (XII)
The semicircular canals mediate which of the special senses?
Dynamic balance
Briefly describe what is meant by a ‘tropic’ hormone & give one example.
Tropic hormones go from the AP out to other endocrine organs to trigger secretion of yet another hormone that then triggers target cells.
Examples:
TSH (thyrotropin), ACTH (corticotropin), FSH & LH (gonadotropins)
Which of the formed elements is noted?
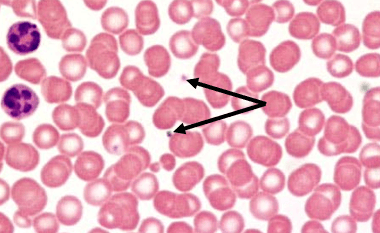
thrombocytes (platelets)
List two specific benefits of fever.
Increased body temperature:
1) Raises metabolism, speeding antibody production, leukopoiesis, tissue repair, etc.
2) Sequestration of iron/zinc in the liver/spleen (binding proteins are denatured just enough to lock it up), preventing bacteria from using them as cofactors for reproductive enzymes.
Describe what occurs in:
systole
diastole
Systole refers to ventricular contraction (represents the force of the heart contraction).
Diastole refers to ventricular relaxation (represents the resistance in the peripheral vessels).
Give the name & # of the cranial nerve responsible for equilibrium & hearing.
Vestibulocochlear Nerve (VIII)
Name the type(s) of energy/stimuli involved in each of the 6 special senses.
Smell – odorants (volatile chemicals)
Taste – tastants (dissolved chemicals)
Hearing – sound/vibration
Static balance – gravity
Dynamic balance – momentum
Vision – photons/light waves
Name the two primary hormones responsible for calcium homeostasis & describe the overall effect of each.
PTH - targets osteoclasts (resorption), GI (absorption), & kidneys (reabsorption) in order TO RAISE blood Ca2+ when it is too low.
CT or CALC - stimulates osteoblasts to build bone matrix & inhibits osteoclasts in order TO REDUCE blood Ca2+ when it is too high.
Also... E2/T - serve to block PTH receptors on osteoclasts to preserve bone density
Name & briefly describe the functions of each type of leukocyte.
Granulocytes:
neutrophils – bacteria slayers; most common type of WBC
basophils – contain histamine; degranulation triggers inflammation/allergies
eosinophils – scavenge & neutralize histamine (reduces inflammation/allergies); also target parasitic worms
Agranulocytes:
monocytes – motile macrophages
lymphocytes – T-cells (target virally infected or cancerous cells); B-cells (produce antibodies)
Describe two primary functions of the lymphatic system.
fluid balance
recovering liver proteins from plasma
immune surveillance
Name the three tunics of blood vessels.
Tunica interna (intima) – deepest, endothelial layer
Tunica media – intermediate, smooth muscle layer
Tunica externa (adventitia) – most superficial, dense irregular connective tissue layer
List two functions of the Vagus Nerve.
motor - innervates visceral organs (for PNS)
sensory - taste from posterior 1/3 of tongue
Name the structures noted below:
A = lens
B = cornea
Name the three groups of corticosteroids & give one example of each.
mineralocorticoids - ALD
glucocorticoids – CORT
gonadocorticoids - T (androgens)
A person with blood type O+ will produce which type of antibodies?
anti-A & anti-B antibodies
Name the structures noted & describe their functions.
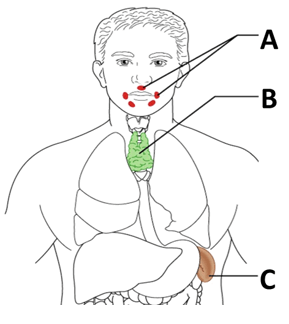
A - tonsils; ring of lymphatic tissue that protects pharynx from ingested or inhaled antigens
B - thymus; training center for T-lymphocytes
C - spleen; blood filter, safely removes dead RBCs & surveils blood for antigens
Name two things that can decrease BP.
Vasodilation
ANP
Inflammation
alcohol
Identify the brain lobe(s) that contains each of the following functional areas:
A) Gustatory cortex
B) Auditory cortex
C) Olfactory cortex
D) Visual cortex
E) Somatosensory cortex
Gustatory cortex - Parietal lobe & insula
Auditory cortex - Temporal lobe
Olfactory cortex - Frontal lobe
Visual cortex - Occipital lobe
Somatosensory cortex - Parietal lobe
Name the two special senses that use chemically gated receptors.
taste & smell
Name two hormones that trigger gluconeogenesis.
GLU
CORT
Describe the functions of each of these cells:
A) hemocytoblast
B) megakaryocyte
c) reticulocyte
A) hemocytoblasts - produce all formed elements of blood (RBC, WBC, platelets)
B) megakaryocyte - releases platelets
C) reticulocyte - name for RBC that has just been released from bone marrow, still unoxygenated
List two specific functions of the spleen.
filter old, dead RBC's from blood
immune surveillance
sequester iron
blood reservoir
Name the structure pictured below: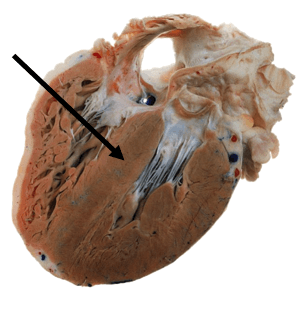
Interventricular septum
Name the cranial nerve noted below, origin, target & general function:
Optic Nerve (CN II) originates from the retina and carries sensory impulses for vision to the occipital lobe.
Name three special senses that use mechanically gated receptors.
static balance
dynamic balance
hearing
Name two hormones that are secreted in order to regulate lactation & describe each of their roles.
PRL – triggers milk production
OXT – triggers milk ejection/letdown
How does the hemocytoblast know which pathway to follow for:
erythropoiesis
leukopoiesis
thrombopoiesis
EPO (hormone) triggers RBC production (erythropoiesis) when blood oxygen levels are low.
cytokines (chemicals released from WBCs) triggers the production of the appropriate WBC to fight infection or other immune function.
TPO/THPO (hormone) triggers the production of new platelets (thrombopoiesis) when platelet levels are low (thrombopenia).
Name three cells of immunity & describe their specific functions.
phagocytes (i.e., macrophages, dendritic cells, neutrophils, etc.) - consume & destroy foreign particles, present antigens to T cells
B-cells - produce antibodies
T-cells - target cancer cells or cells infected by intracellular pathogens (e.g., viruses)
basophils - circulating WBCs that release histamine during inflammation
eosinophils - WBCs that target parasitic worms or reduce allergies by scavenging immune complexes
Name the valve that blood flows through as it leaves the left ventricle.
Aortic semilunar (SL) valve
Name the cranial nerve noted below & list its targets & general function(s):

Accessory Nerve (CN XI) targets the trapezius & sternocleidomastoid muscles to move the head/neck.
Name the gelatinous “membrane” where hair cells are embedded in each of the following special senses:
dynamic equilibrium
hearing
static equilibrium
dynamic balance = cupula
hearing = tectorial membrane
static balance = otolith membrane
Name two hormones that are secreted in response to GnRH.
FSH & LH
Name the three branches off of the aortic arch:
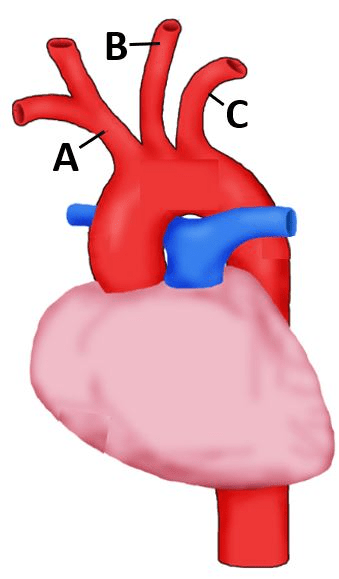
A) brachiocephalic trunk
B) left common carotid artery
C) left subclavian artery
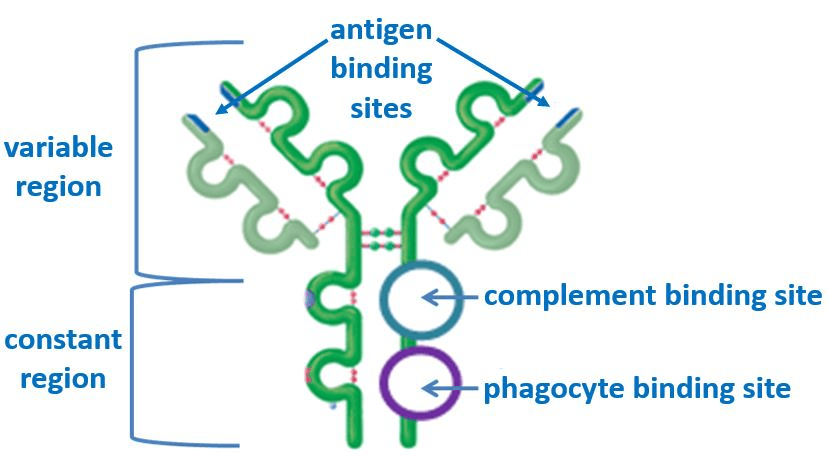
Draw a typical IgG & label the 3 binding sites and 2 functional regions.
Name the structure noted:
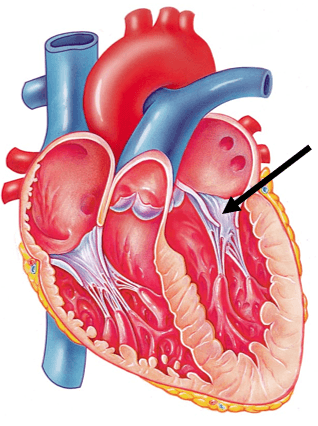
Left atrioventricular (AV) valve OR bicuspid valve OR mitral valve
Name the cranial nerve noted below & list its target(s) & general function(s):

Abducens Nerve (CN VI) targets the lateral rectus extrinsic eye muscles to abduct the eye
Name and describe the location, function, & viscosities of the two humors of the eye.
aqueous humor – fluid anterior to lens, circulates, nourishes, cleans, determines IOP
vitreous humor – gel-like substance posterior to lens, supports retina & lens
If blood pressure is too low…
What hormone will be secreted?
Where will it be secreted from?
Where will it go?
What will it do?
ALD from the adrenal cortex will go to the kidneys to stimulate sodium reabsorption. This increases water reabsorption via osmosis, thus decreasing urine output & increasing BV & BP.
OR
Renin is secreted from the kidneys & interacts with angiotensinogen from the liver to make ANG I.
ANG I is converted to ANG II in the lungs/liver by ACE enzymes. ANG II triggers ALD & ADH secretion & serves as a potent vasoconstrictor, thus raises BV & BP.
Name the vessel noted below: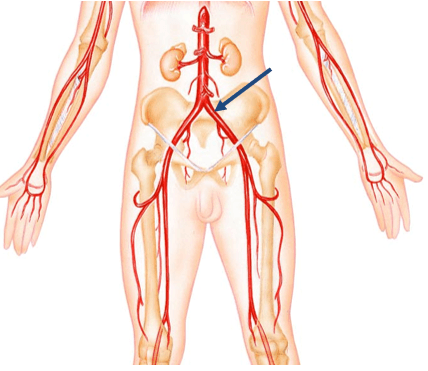
common iliac artery
Name & describe the differences of the five classes of antibodies.
IgA - secretory dimers (e.g., in saliva, mucus, & breast milk)
IgG - most diverse monomers, circulate in plasma
IgM - pentamer antibody binds many antigens at once, leading to agglutination; circulates in plasma
IgE - bind & sensitize histamine containing cells (basophils & mast cells); antigen binding leads to degranulation & inflammation
IgD - serve as B cell receptors
Name two things that assist in venous return.
Internal valves in veins (shaped like SL valves) catch blood to prevent backflow against gravity
Adequate blood volume
Vasoconstriction
Skeletal muscle pump
List two specific physiological responses of the body while under each one:
Parasympathetic NS
Sympathetic NS
Parasympathetic NS – heart rate reduced (due to vagal tone), pupils constrict, GI motility increases, increased saliva production
Sympathetic NS – heart & respiratory rates increase, bronchioles & pupils dilate, decreased saliva production
Name the structure noted below:
incus (second of the three ear ossicles)
in between the malleus & stapes
If blood oxygen concentrations are too low…
What hormone will be secreted?
Where will it be secreted from?
Where will it go?
What will it do?
EPO will be secreted from kidneys & go to bone marrow to stimulate hemocytoblasts to start erythropoiesis (RBC formation).
Increased RBC# will increase oxygen carrying capacity of the blood.
Identify which is the brachial vein, cephalic vein, & basilic vein:
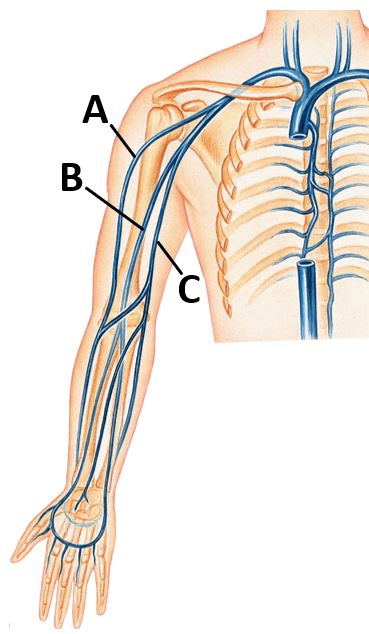
A) cephalic vein
B) brachial vein
C) basilic vein
Briefly describe what is meant by artificial active immunity & give one specific example.
Artificial refers to the intentional exposure to antigens. Active means the recipient will actively mount an immune response & leave behind memory.
Ex: vaccinations; these are meant to spare the recipient the signs/symptoms of a particular disease & to help speed up the primary humoral response by providing a large dose of weakened or killed antigen, thus increasing the chances for Th cell interactions/permission, etc.
Briefly explain the RAAS as it applies to regulating BP.
Low BP triggers renin secretion from the kidneys which interacts with angiotensinogen (from the liver) to become ANG-I. ANG-I is converted into ANG-II by ACE enzymes in the lungs/liver. ANG-II triggers secretion of ADH & ALD, both of which act on the kidney to reduce urine output, thus raising BV & BP. ANG-II & ADH (aka: vasopressin) are both also potent vasoconstrictors & serve to raise BP directly.
Name the sympathetic NS receptor types that would be found on the:
salivary glands
Sympathetic would want to limit saliva production, so beta-adrenergic receptors (recall: betas block)
Name two smooth muscles of the eye & describe their unique functions.
Iris – controls amount of light entering eye through pupil
Ciliary body – controls shape of lens to focus
If blood solute concentrations are too high…
What hormone will be secreted?
Where will it be secreted from?
Where will it go?
What will it do?
ADH from PP goes to kidneys to open aquaporins & retain water.
This decreases urine output, increases BV & BP & dilutes the blood.
Name the vessel noted:
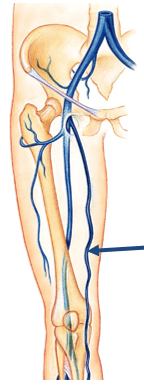
great saphenous vein
Describe three specific ways in which primary & secondary humoral responses differ.
Secondary humoral responses are FASTER, because memory B cells made during the first response do not need to wait for permission from helper T cells to make antibodies.
Memory B cells make MORE ANTIBODIES than the original B cells made during the first response.
Antibodies made by memory B cells have a HIGHER AFFINITY for the antigen than the original ones made during the first response.
Which vessel does blood flow into from the right ventricle?
Pulmonary trunk
Explain how beta-blocker drugs work, regarding the specific receptors/neurotransmitters involved.
Beta-blocker drugs bind & block beta1-receptors on the heart to inhibit the typical FOF (sympathetic) effects of EPI.
Patients with irregular heart rates (ex: A-fib), hypertension, anxiety or other conditions may be prescribed these drugs in order to keep the heart rate from getting too high when under stress.
Name & describe the functions/locations of the 2 types of photoreceptors.
Cones – fine/sharp, color focus – concentrated in fovea centralis, fewer in macula lutea & less in periphery
Rods – peripheral vision, sensitive in low light – few in macula lutea, abundant in periphery
If blood pressure is too high…
What hormone will be secreted?
Where will it be secreted from?
Where will it go?
What will it do?
ANP from heart will go to kidneys to inhibit reabsorption of sodium.
The excreted sodium will draw water out with it, increasing urine output & decreasing BV & BP.
Name the vessel that drains the intestines, spleen, pancreas, & stomach.
The hepatic portal vein transports blood from areas of the GI directly to the liver (first pass metabolism).
(Not to be confused with the hepatic veinS which drain the liver itself)
Define opsonization.
When an antigen is coated with 'handles' which serve as affinity sites for phagocytes.
These 'handles' are called opsonins & can be either complement proteins or antibodies.
Differentiate between:
atherosclerosis
arteriosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is the buildup of fatty plaques within BVs.
Arteriosclerosis is the hardening of the arteries, in which the connective tissue on the surface of the BV becomes more collagenous due to atherosclerosis.