Largest bone in the body
Femur
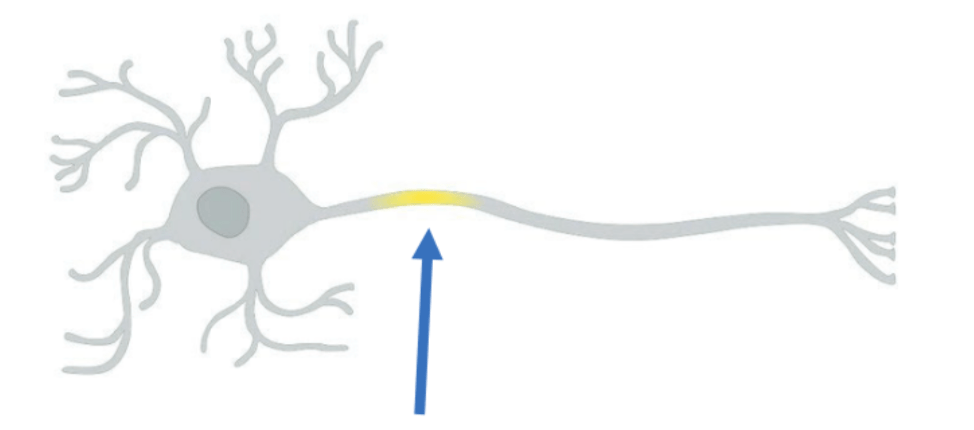
The name for this portion of a neuron
How are Red Blood Cells different from almost every other cell in the body in terms of internal structure?
They are missing a nucleus/organelles.
Allows cells to take in glucose for energy or storage.
Main muscle that controls breathing.
Diaphragm
What is the difference between mechanical and chemical digestion?
Mechanical digestion involves the physical breakdown of food into smaller pieces through actions like chewing and stomach churning, while chemical digestion involves breaking down food into its molecular components using enzymes and acids.
What is the body's primary energy source, which it uses to make ATP?
Glucose
Multiple Sclerosis is a type of autoimmune disorder that can cause fatigue, vision loss, and muscle weakness. What is an autoimmune disorder?
How many bones are there in the body? You can be in the range of ±15.
206 bones
Specialized nerve cells (receptors) that are able to detect differences in temperature
Thermoreceptors
Arteries and Veins are two main types of blood vessels that carry blood throughout the body.What is the major difference between Arteries and Veins?
(Do NOT mention the oxygenation of blood in your answer)
Arteries carry blood away from the heart, and veins carry blood towards the heart.
This gland is known as the "master gland" because of its ability to regulate most of the other hormone-producing glands
Pituitary Gland
Cilia are tiny hair-like structures that line the respiratory tract that can move in coordinated, wave-like motions. What is the function of cilia in the respiratory tract?
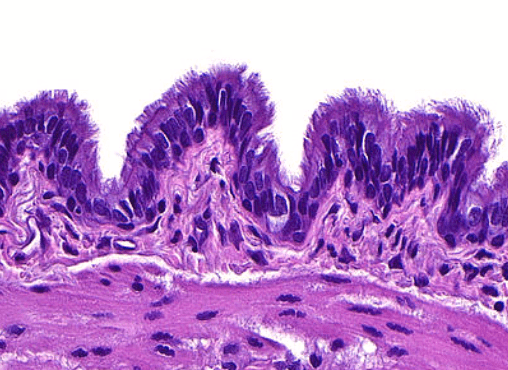
Helps move mucus, trapped particles, and fluids across the surface of cells for protection and clearance.
What is the pH of the stomach? Your answer has to fall within the normal range.
1.5 to 3.5
How does the body switch between using carbohydrates, fats, and proteins as energy sources during periods of fasting?
First glycogen, then fats, then proteins.
Down syndrome is a genetic disorder which causes to developmental delays, intellectual disability, and characteristic physical features. It is caused by a trisomy (extra copy) of this chromosome.
Chromosome 21
Name any 3 long bones
Acceptable answers:
- Femur (thigh bone)
- Tibia (shin bone)
- Fibula (calf bone)
- Humerus (upper arm bone)
- Radius (forearm bone, thumb side)
- Ulna (forearm bone, pinky side)
- Clavicle (collarbone)
Is the lungs under somatic or autonomic control?
Somatic
The normal pulse rate for a person is 60 - 100 beats per minute. However, many pro athletes have pulses as low as 30 bpm and are healthy. EXPLAIN how this is possible.
The heart of an athlete can pump a greater volume of blood with each contraction , so it doesn't need to beat as frequently to deliver the same amount of oxygen and nutrients to the body, reducing overall strain.
What is homeostasis?
(Do NOT use the word "balance" in your answer)
Maintenance of specific internal body conditions.
What structural feature(s) of the alveoli facilitate efficient gas exchange in the lungs?
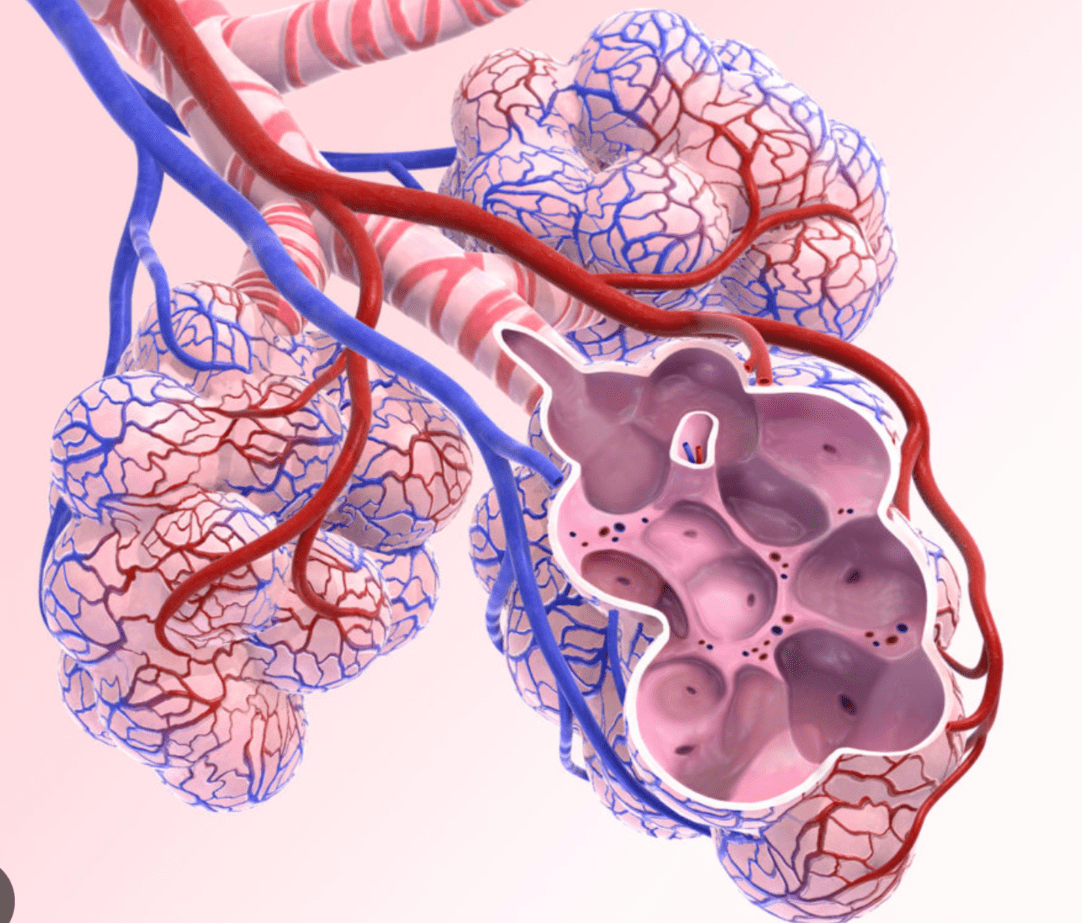
Alveoli are very thin tissue (one cell thick) and have a large surface area covered in capillaries which allows for facilitated gas exchange.
What is the function of bile and where is it stored?
Facilitates lipid absorption and digestion, stored in gallbladder.
What is metabolism?
The whole sum of reactions that occur throughout the body
How does diabetes affect the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar, and what are the potential complications if it’s not managed properly?
No insulin -> sugar can't move into cells, blood sugar spikes
Damage to nerve endings and blood vessels.
List any 3 functions of bones
Acceptable answers:
Structure, protection, mineral storage, blood cell production, etc.
Function of the cerebellum
Fine motor coordination
These are two ways for the body to compensate for a drop in blood volume, such as from dehydration or blood loss.
Constricting blood vessels
Increasing heart rate
What is the difference between endocrine and exocrine hormones?
(Note: "Endo" means internal and "Exo" means external)
Endocrine hormones are released directly into the bloodstream to act on distant target organs, while exocrine hormones are secreted through ducts to specific local sites.
What difference does breathing through your nose make as opposed to breathing through your mouth?
Warms and humidifies the air, filters out dust and pathogens.
List any 3 functions of the liver
Acceptable answers:
Detoxification, Protein Production, Production of Bile, Storage of glycogen
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a genetic disorder in which the body is unable to break down the amino acid phenylalanine, leading to major neurological and developmental issues. What is the number one recommended treatment for Phenylketonuria?
Avoiding foods containing phenylalanine.
Which of the following assessments is indicative for use of an automated external defibrillator (a strong electrical shock to restart the heart)?
A. A patient with an extremely erratic heart rhythm.
B. A patient with severe tachycardia (very high pulse rate)
C. A patient experiencing asystole (complete absence of heart rhythm)
D. A patient with a palpable heart rhythm who is complaining of severe chest pain
A. A patient with an extremely erratic heart rhythm.
What are the long-term effects of prolonged inactivity or bed rest on the skeletal system? What causes these effects?
bone loss (osteopenia), decreased bone density, and increased risk of fractures are all acceptable answers.
Bones rely on mechanical stress, such as weight-bearing activities and muscle contractions, to stimulate bone remodeling and maintain density
A stroke occurs when blood flow to part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, leading to neuronal cell death. Despite this, 10 percent of stroke patients recover almost completely,and 25 percent of patients recover with only minor impairments. Explain how this is possible even when parts of the brain are damaged due to stroke.
Neuroplasticity
The brain can reorganize itself and form new neural pathways, enabling healthy parts of the brain to compensate for damaged areas, which can help restore lost functions.
The left side of the heart receives blood from the lungs and sends it across the entire body. The right side of the heart receives blood from the body and sends it to the lungs. A patient experiencing pulmonary edema (fluid in the lungs) is most likely experiencing heart failure on which side? EXPLAIN your answer
Left side; the left side of the heart fails to effectively pump blood, causing fluid to back up into the lungs.
The "fight or flight" response is the body's automatic reaction to a perceived threat, preparing it to either confront or flee from danger by releasing stress hormones like adrenaline. List 3 effects adrenaline can have on the body and explain how these can help in "flight or fight" situations.
Possible answers:
- Increases heart rate
- Boosts blood pressure
- Expands airways for better oxygen intake
- Increases blood flow to muscles
- Dilates pupils for improved vision
- Triggers the release of glucose for more energy
- Reduces blood flow to non-essential systems like digestion
- Heightens alertness and focus
- Enhances the body’s ability to respond to stress
- Inhibits fatigue during stressful situations
Explain how the air flows into the lungs.
Diaphragm contraction and chest cavity expansion. Increase in chest cavity volume causes the pressure inside the lungs to drop below the atmospheric pressure outside the body.Due to this pressure difference, air flows from the higher pressure outside the body to the lower pressure inside the lungs (to equalize the pressure) through the nose or mouth.
List 2 functions of the microbiome (gut bacteria) in digestion and overall health. How can an imbalance in gut bacteria affect digestive health?
Possible answers:
breaking down complex carbohydrates
producing essential vitamins
supporting the immune system
Dysbiosis causes poor nutrient absorption and inflammatory disorders.
Metabolic syndrome is characterized by a combination of conditions, including high blood pressure, high blood sugar levels, excess body fat around the waist, and abnormal cholesterol levels, which together increase the risk of heart disease and diabetes. How does excess abdominal fat contribute to metabolic syndrome?
(HINT: WHAT DOES EXCESS FAT SECRETE?)
Excess abdominal fat contributes to metabolic syndrome by producing inflammatory substances and hormones that disrupt normal metabolic processes.
In general, how does chronic inflammation contribute to the development of diseases such as atherosclerosis, cancer, and autoimmune disorders?
Continuous immune response. Constant release of inflammatory cytokines, free radicals, and other mediators that promote cellular dysfunction, DNA damage, and disruption of normal tissue repair processes.