What are the two primary divisions of the nervous system?
Central nervous system
Peripheral nervous system
BONUS: What does each system consist of?
What is the function of neuroglia cells? Give an example of a type of neuroglia cell in the CNS.
Neuroglia cells support and protect neurons. Astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglial cells, ependymal cells
BONUS: What are neuroglial cells incapable of doing?
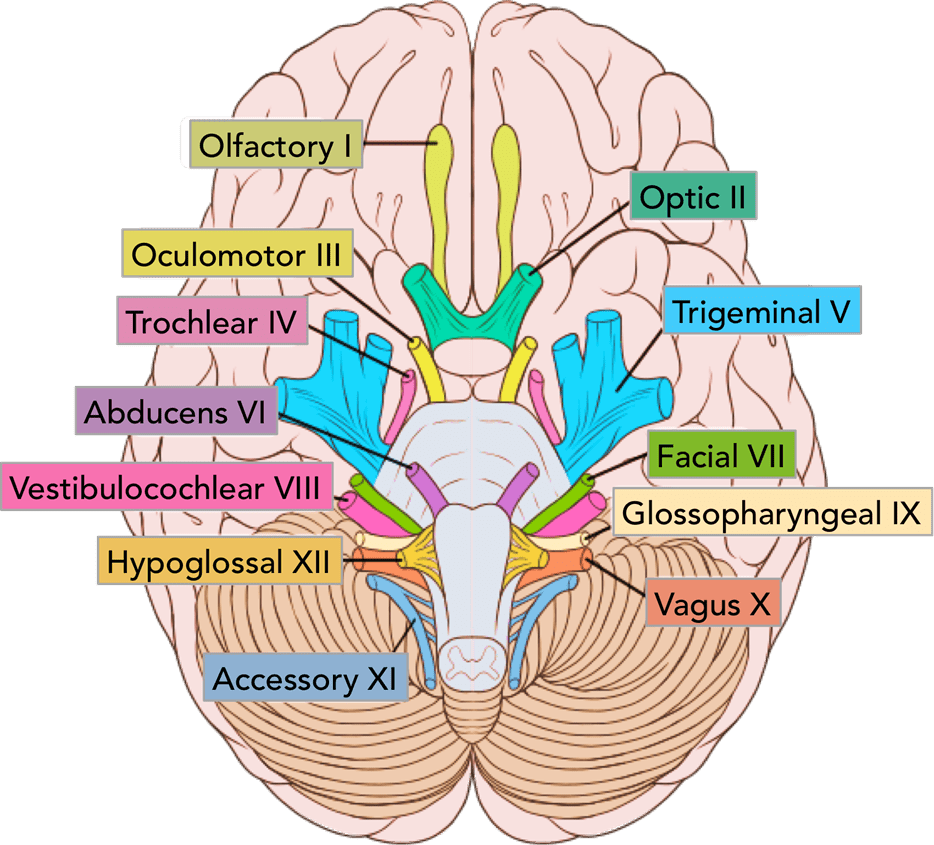
What is the trick used to remember the 12 cranial nerves? (HINT: It has to do with a truck)
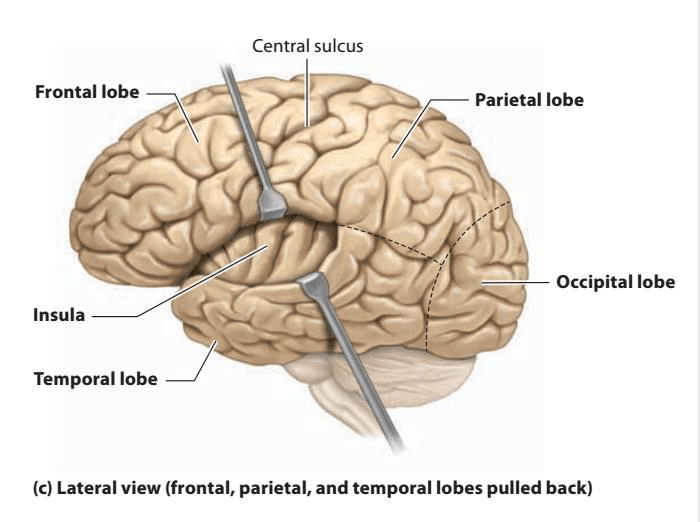
What are the five lobes of the brain?
Frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, insula
BONUS: Which lobe cannot be seen from the surface?
What are the clusters of neuronal cell bodies called in the CNS and the PNS?
CNS: Nuclei
PNS: Ganglia
What is are bundles of axons called in the CNS and PNS?
CNS: Tracts
PNS: Nerves
Where is the Node of Ranvier and the myelin sheath in this picture?
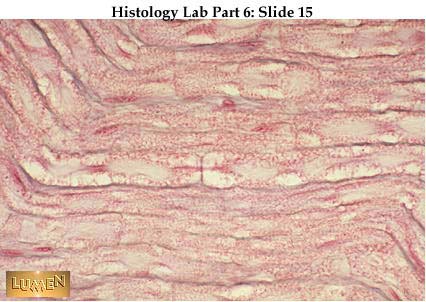
What does the lateral sulcus divide?
The temporal lobe from the parietal lobe
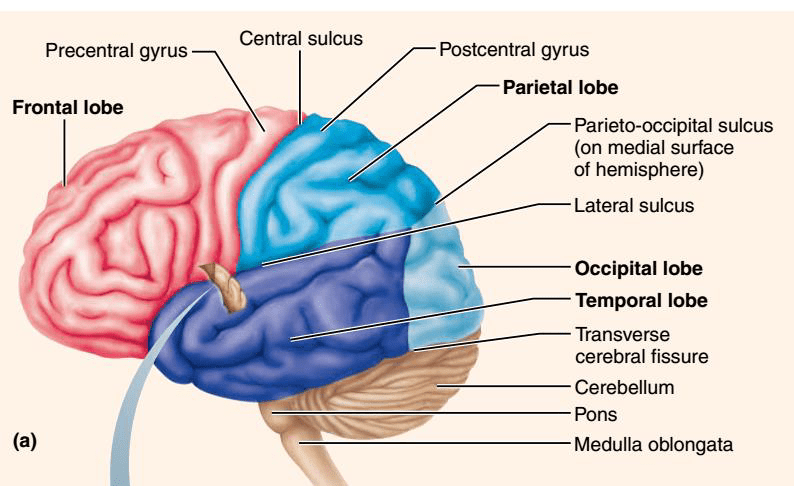
Fill in the blanks. Neurons can have ______ dendrites, and ______ axon. (HINT: The answers refer to numbers).
Many; one
Most neurons in the CNS have this type of structural classification.
Multipolar neurons.
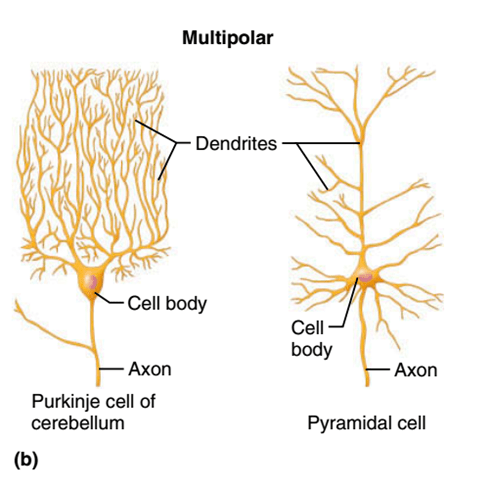
Explain the difference between axons and dendrites.
Dendrites: Receptive regions that bear receptors for NTMs released by the axon terminals of other neurons
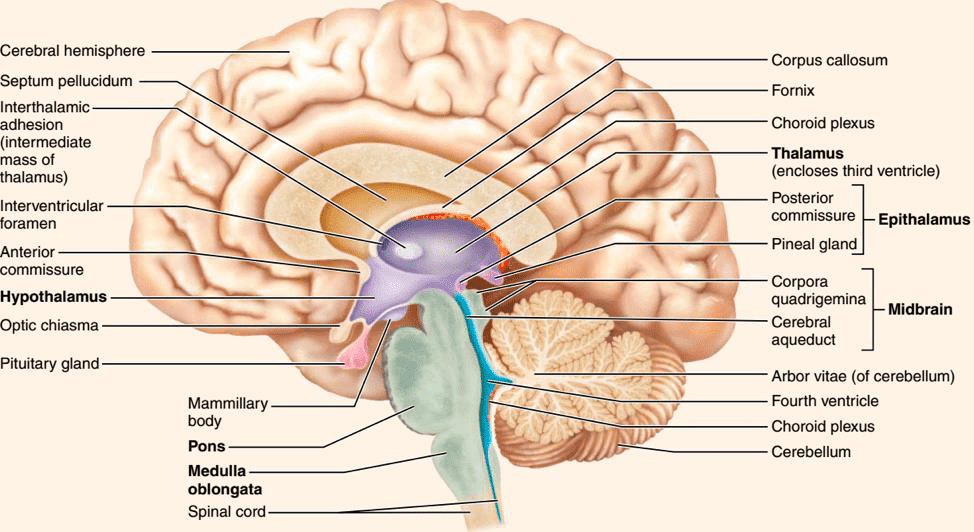
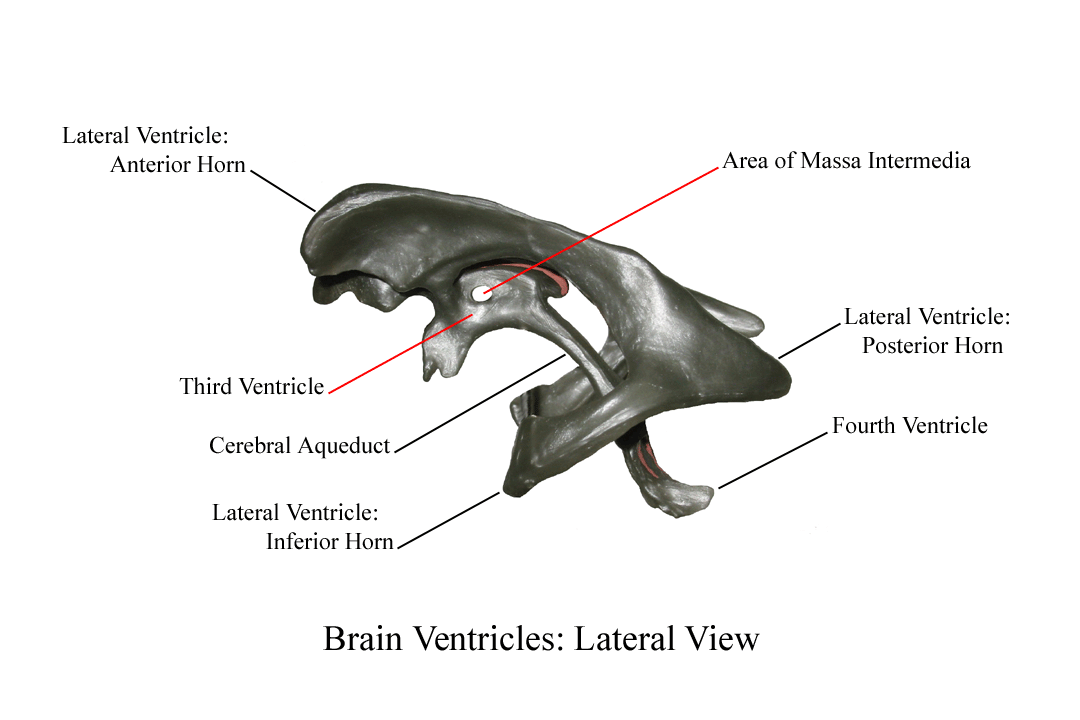
What are the four major internal structures of the diancephalon?
The thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus, subthalamus
Cranial Nerve VIII: Vestibulocochlear Nerve
What type of functional classification do motor neurons have and why?
Most motor neurons are multipolar neurons. This allows them to receive and integrate a large amount of information from various sources. The multiple dendrites enable the neuron to integrate signals from different parts of the nervous system, making it effective in coordinating complex movements.
BONUS: What is another name for motor neurons?
What are the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system?
Parasympathetic and sympathetic
Where in the body are the most ependymal cells found and why?
The ventricles of the brain and the cantral canal of the spinal cord. This is becuase they play a crucial role in producing and regulating cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Which part of the body is the most heavily myelinated, and what are the reasons for its extensive myelination?
The brain. Myelin sheaths insulate nerve fibers, allowing electrical signals to travel rapidly along axons. This ensures quick communication between neurons, which is essential for functions like sensory perception, motor coordination, and cognitive processes.
BONUS: There are two types of matter in the brain. Which one is more myelinated?
Which internal brain structure is known as the control center of the brain and why?
The hypothalamus. This is due to controling crucial functions such as regulating temperature, hunger, thirst, sleep-wake cycles. It also helps to manage the autonomic nervous system which affects heart rate, blood pressure, and digestive functions
A patient presented with difficulties in language, memory, and hearing. Which lobe of the brain is likely to be affected?
Temporal lobe
A patient hit the back of his head and is presenting with sleep disorders, vision disturbances, and hydrocephalus. Which brain structure is most likely affected?
The epithalamus
BONUS: Which specific structure in the epithalamus might be affected if the patient presents with insomnia?