What is the axial skeleton composed of?
What is appendicular skeleton composed of?
Axial: skull, face, thorax, and vertebral column.
Appendicular: upper extremities, pelvis, lower extremities
The area of the brain where critical life functions are coordinated
What is the brainstem?
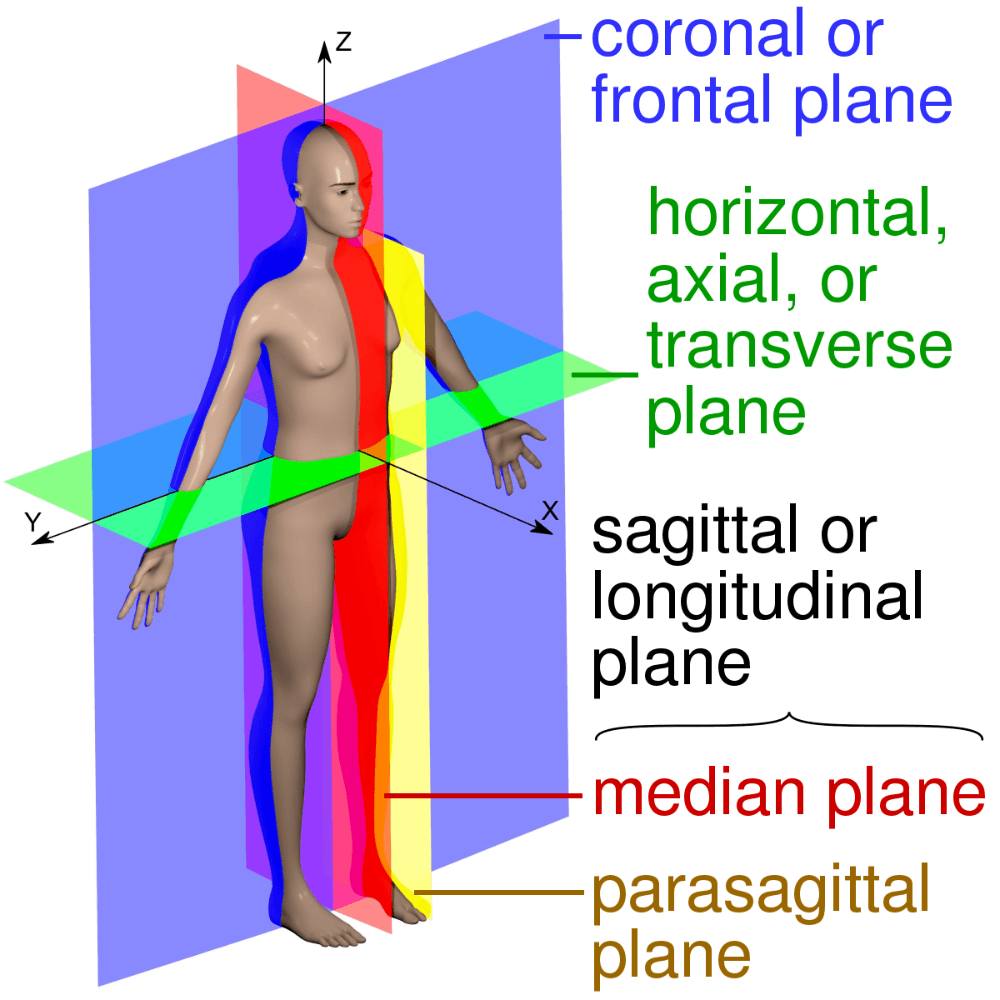
Please describe or the draw the plans of the body.
Frontal, lateral, midline, axial AKA
coronal, sagittal, midsagittal, transverse.
The nose & belly button lie on what plane of the body?
List some differences in the airway of a pediatric patient versus an adult patient.
Flexible trachea, occiput is proportionally larger
During adolescence, teenagers are becoming adults. What does this entail?
A. The development of secondary sexual characteristics
B. The endocrine and reproductive system mature
This age range begins at __ and ends at 40 years old. Lifelong habits are solidified.
What group is this? Average pulse & range?
This group is the young adult group. It ranges from 19-40, the average pulse is 70, but the range is 60-100. This is a generally stable period of life.
Carpals form the _____.
Tarsals form the ______.
Phalanges form the ____.
Carpals form the wrist.
Tarsals form the ankle.
Phalanges form the fingers.
What does the central nervous system contain?
What does the peripheral nervous system contain?
What is the difference between their functions?
Central Nervous system= brain and spinal cord.
Peripheral are the nerves found elsewhere in the body. Somatic(voluntary) & Autonomic(involuntary).
Bonus(50 points): what is the difference between sensory and motor nerves?
List the composition of blood.
List the functions of blood.
1. Plasma-liquid portion of blood.
2.RBC(erythrocytes)-contains hemoglobin
3.WBC(leukocytes)-immune defense to fight infection
4.Platelets-essential in formation of a blood clot
Fight infection, transport O2, transport CO2, controlling pH, transporting wastes/nutrients, coagulation.
How do newborns and infants differ as far as their communication/interaction with strangers?
Newborns(birth to 1 month)-may be uncaring of your presence due to inability to recognize caregiver
Infants(1 month to 1 year)- 2 months can recognize familiar faces, 6 months sit up right/coo and babbles, separation anxiety is common in older infants
School age = 6 to 12 years old.
A. Preconventional: children act purely to avoid punishment
B. Conventional: children look for approval from their peers and society
C. Postconventional: children make decisions guided by their conscience
While vital signs remain the same, middle adults are vulnerable to ____, _____, cardiovascular issues, and ______.
While vital signs remain the same, middle adults are vulnerable to hearing loss, vision loss, cardiovascular issues, and financial concerns.
(100pts) Why do financial concerns become a big issue?
They are preparing for retirement but still must manage everyday finances.
Name the 3 pain muscle types and give a location of each.
1. Skeletal-attached to the bones and forms major muscle mass of body. Sometimes called VOLUNTARY muscle.
2. Smooth-found within blood vessels, urinary system,& intestines(INVOLUNTARY).
3. Cardiac-muscle is only found within the heart.(again, INVOLUNTARY). The NAME of the muscle tissue of the heart is called the MYOCARDIUM.
Other functions of muscle(general): contract/relax to make it possible to move and manipulate the environment, protect structures under them, produce heat(by shivering) when you get cold.
What is the difference between respiration and ventilation?
Respiration is the gas exchange(oxygen and carbon dioxide) in the alveoli/tissues of the body.
Ventilation is the movement of air between lungs and the environment.
Name 3 common pulse points.
The aorta.
Carotid, brachial, femoral, radial, pulse.
Give 5 examples of goals toddlers reach. (Ages 1-3).
Toddlers- trust v. mistrust up until 18 months, usually will know name, begin walking around 1 year, toilet training complete, cause and effect is learned, by 3 basic language is mastered, children learn to recognize gender differences by observing role models
Adolescents and their family appear to be in a constant struggle for control. What are some reasons for this?
A. Privacy becomes an issue
B. Self-consciousness increases(fixated on public image)
C. Code of ethics is developing, lots of input from peers, smoking and drug use increases,
What are some internal changes we may see inside of an older adult?
Decrease in elasticity of the lungs, decrease in metabolism, stiffening of blood vessels, decrease in cardiac output, bones become more fragile, shrinkage in brain size (10to20%) by 80 years old
Give the name and number of each group of vertebrae.
7-Cervical
12-Thoracic
5-lumbar
5-sacrum
4-coccyx(fused together)
The process by which gas exchange occurs within the lungs
What is diffusion?
BONUS(100points)...Where does the exchange of oxygen and nutrients for waste products occur?
On a tissue/organ/organ system level, what does moderate blood loss do to your circulatory system?
Vascular constriction and tachycardia
A neonate is born with 300 bones.
An adult has 206. How are these bones disappearing?
In neonates specifically, fontanelles are present. The posterior fontanelle fuses by 3 months, anterior between 9 and 18. Sunken in fontanelle may indicate dehydration. Bulging may indicate an increase in intracranial pressure.

Infants receive antibodies via breastfeeding which bolsters their immune system. What does does this "passive immunity" fade off?
During toddler/preschool age is the period when passive immunity is lost. Toddlers & preschoolers are at risk for respiratory issues due to an under developed lung musculature.
This age centers on work, family, and stress. This age group is attempting to create a place for themselves in the world or settle down.
Young adults-->body is working at peak efficiency at beginning, but effects of aging gradually become evident.
Please give a few key hormones of the sympathetic nervous system.
Epinephrine and norepinephrine.
Lets talk about breathing.
1.What is the amount of air that remains in lungs JUST keep them open?
2.What is the portion of the respiratory system that has NO ALVEOLI and little to no gas exchange?
3.What is tidal volume?
2. Dead space is the portion of respiratory system with no alveoli.
3.The amount of air that is moved in our out of the lung in a single breath(about 500mL in an adult).
Where are the lungs located?
Retroperitoneal space.
Thoracic cavity.
A neonate is born with certain reflexes..
Name AND explain all 4 of them.
1. Moro: if a neonate is startled, it opens its arms wide, spreads fingers, tries to grab at things.
2. Palmar: occurs when an object is placed into neonate's palm.
3. Rooting: when something touches a neonate's cheek, it will turn head toward the touch
4. Sucking: occurs when neonates lips are stroked, will turn head over
Teenagers are developing a lot with the increase of different hormones. Which body system is responsible for this change?
The endocrine system.
Upon responding to an 80 year old complaining of a fall(hitting head & hip hurting), it is important to be aware of....
1. Risk of bleeding in skull because of decrease of brain mass
2. Patient may be LESS able to compensate during blood loss from a severe injury