What separates the primary somatic sensory cortex from the primary motor cortex?
The central sulcus
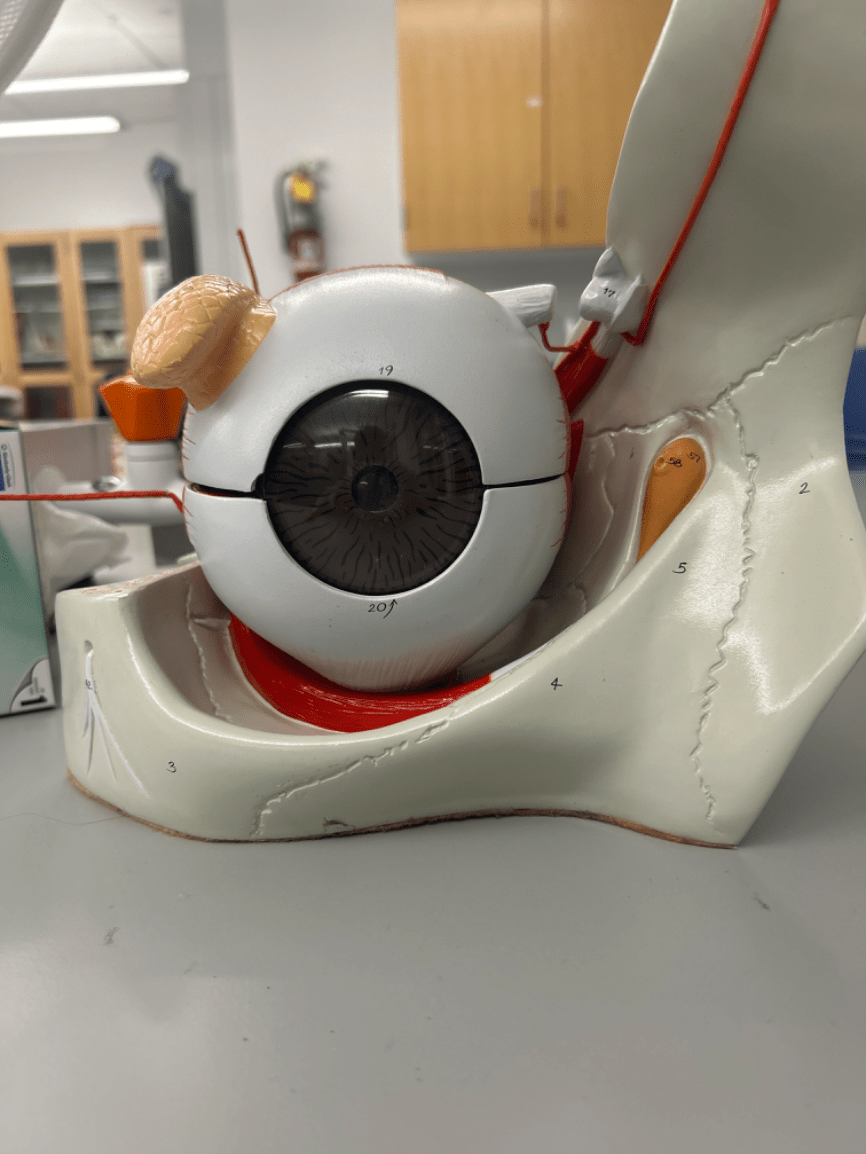
What structure is labeled by #20?
Cornea
What cell carries oxygen?
Red blood cell
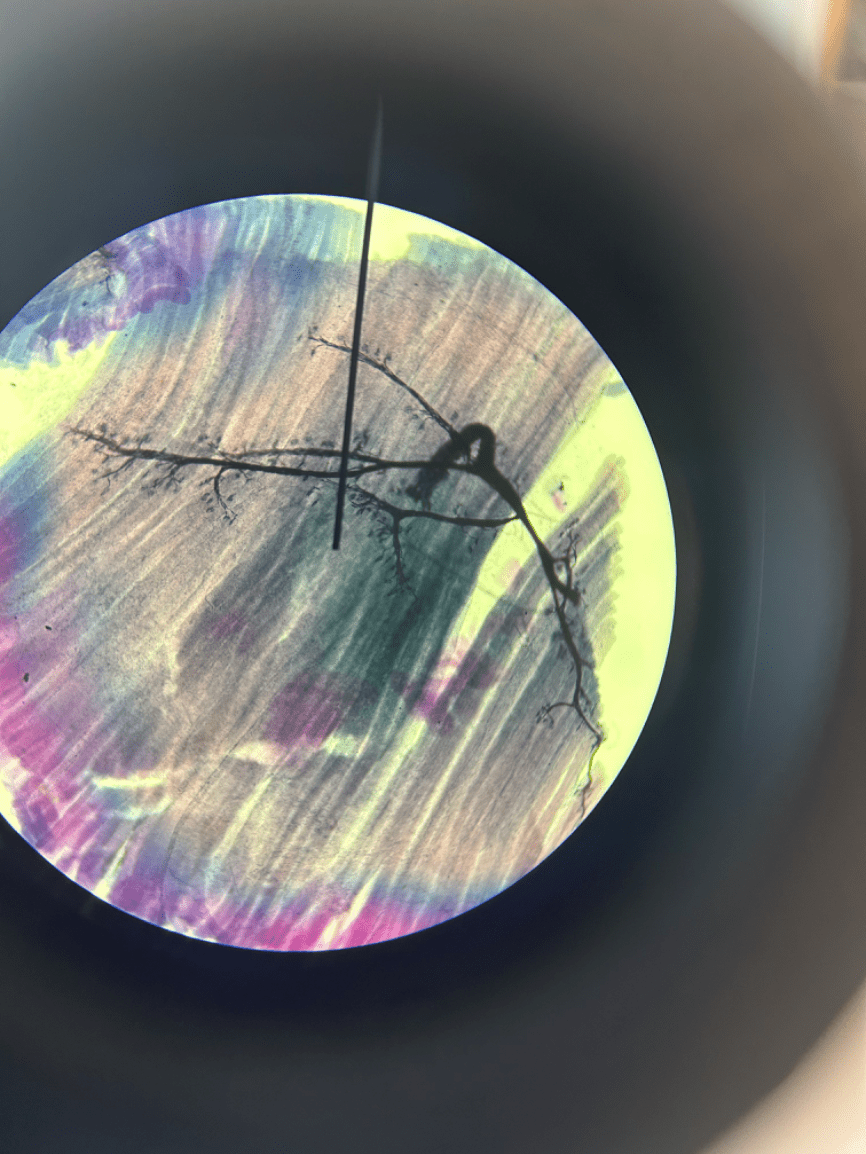
What is this?
The motor nerve end plate
What part of the NS houses spinal nerves? How are they named?
This final nerves are located in the peripheral nervous system. They are named based on the vertebrae above their location.
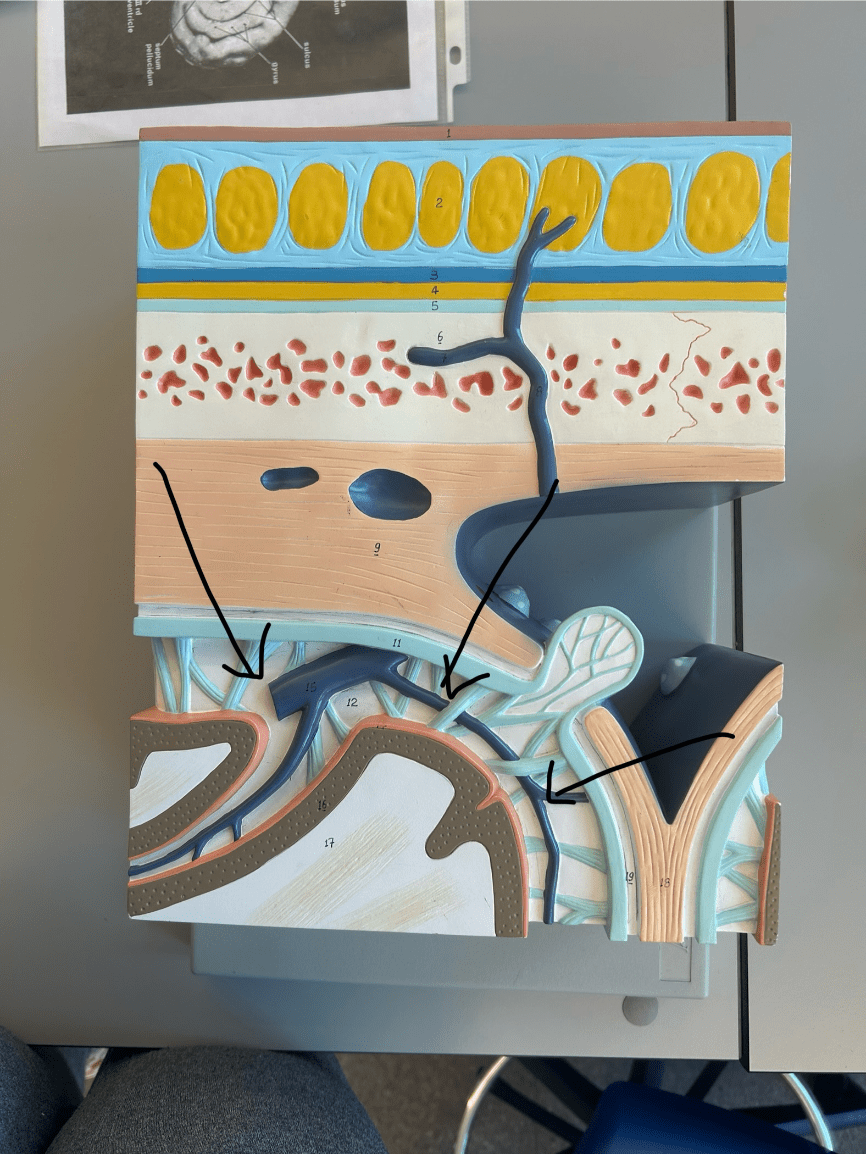
What structure is this?
This is the subarachnoid space
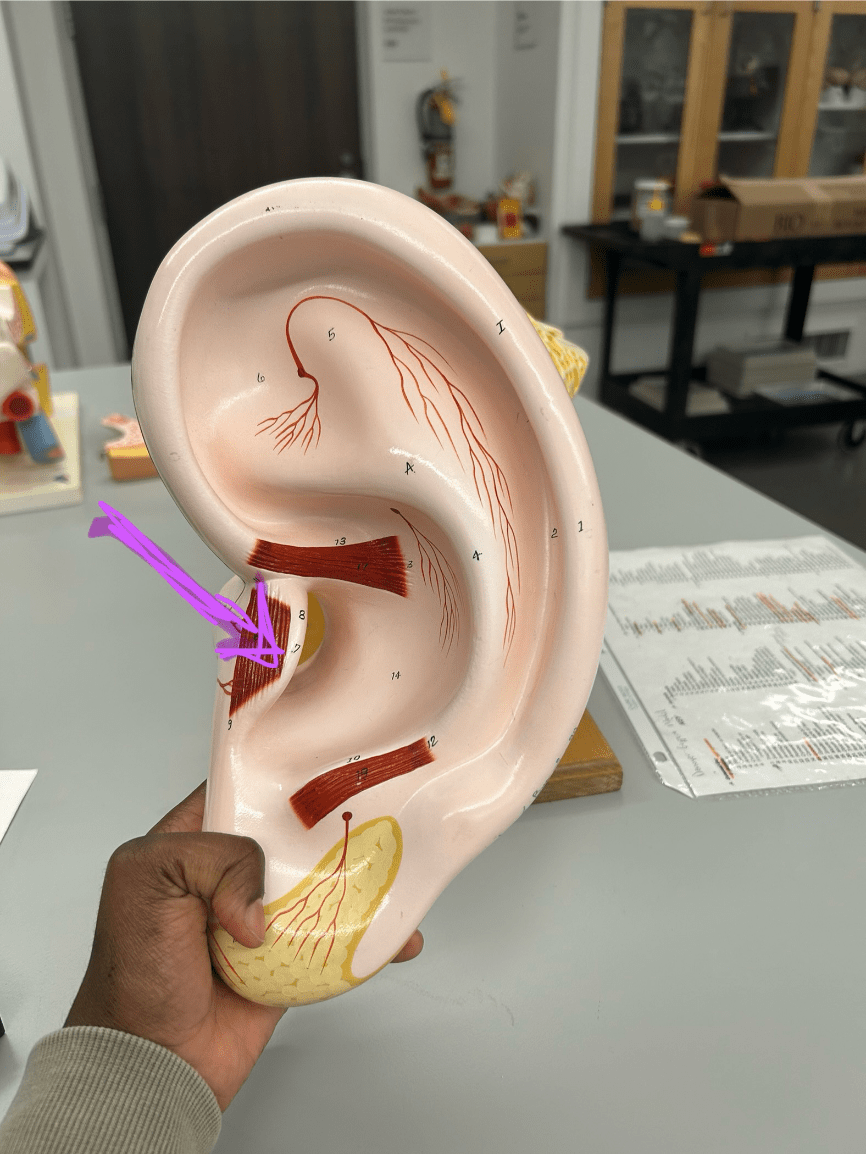
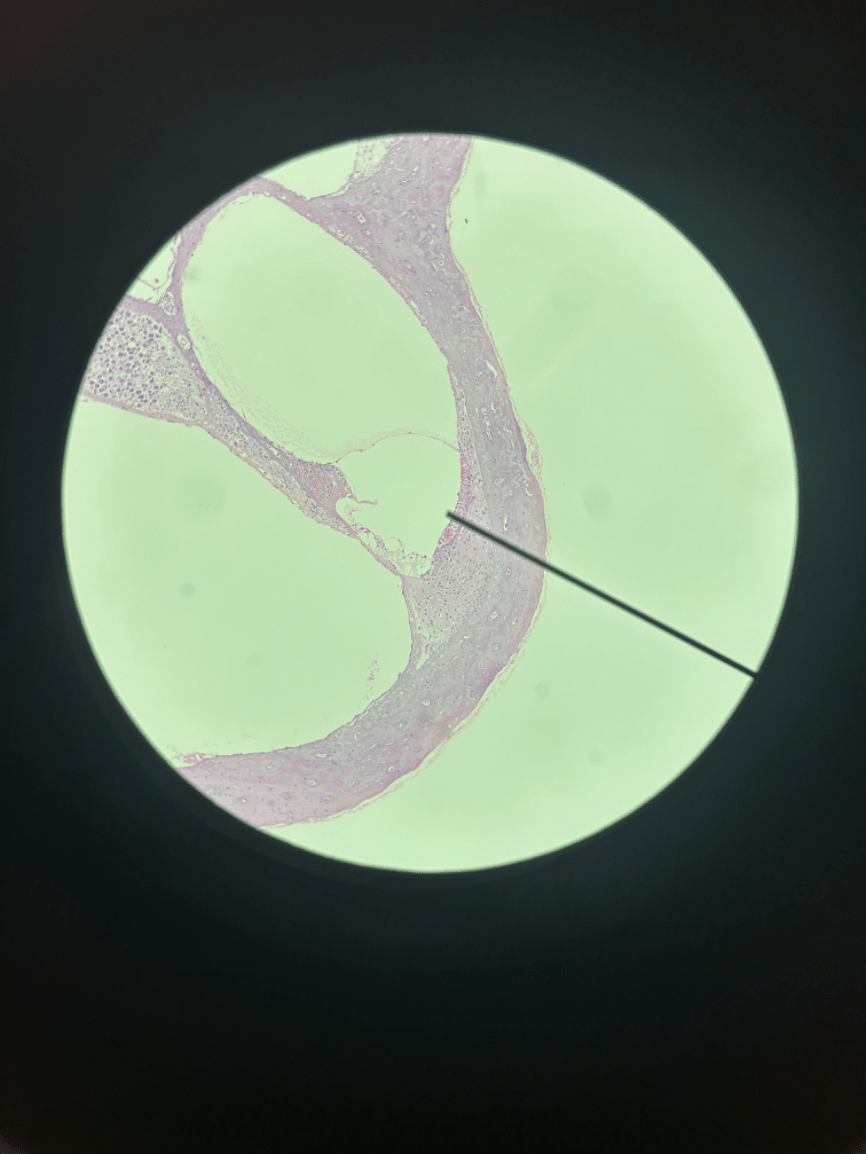
What structure is being shown by the purple arrow in the image?
Tragus
Name the five leukocytes and their normal ranges
Neutrophils, Basophils, eosinophils, monocytes, lymphocytes
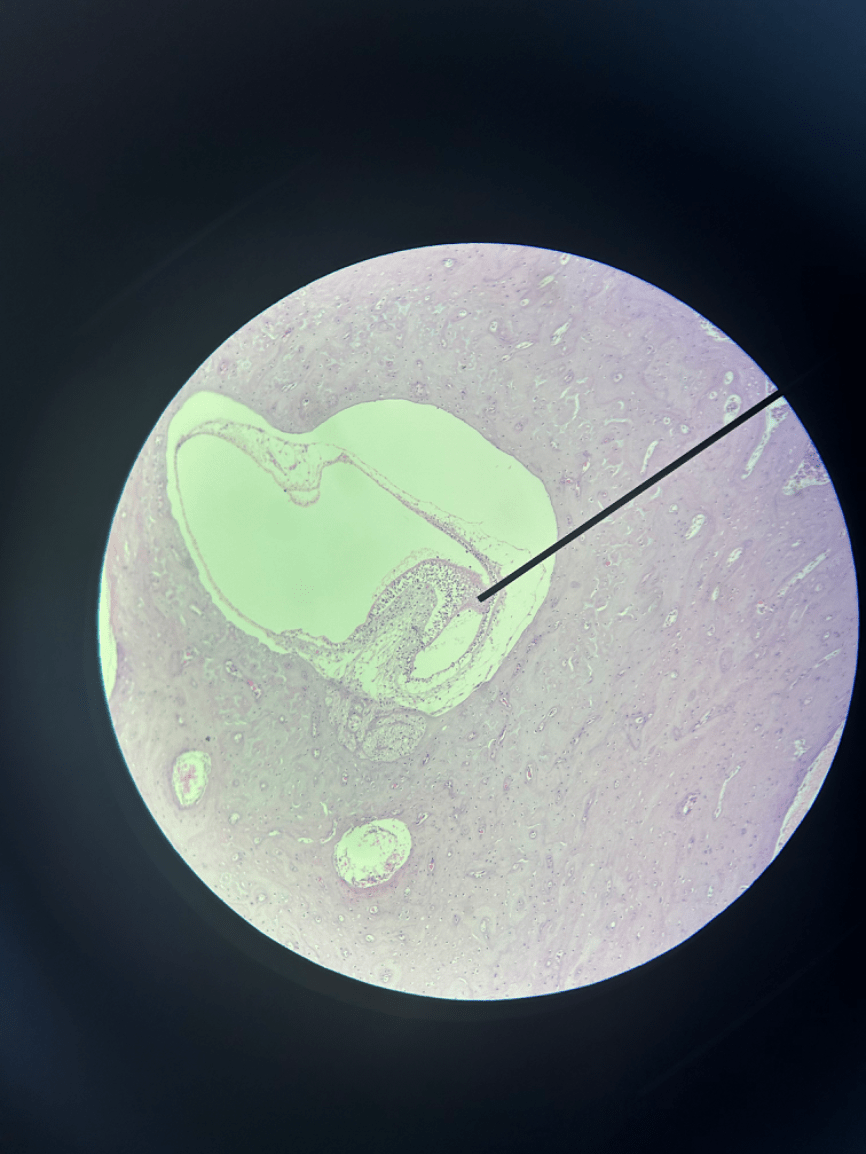
What structure in the cochlea is this analogous to?
The tectoral membrane
What test is used to detect hearing loss?
Webers and Rinne Test.
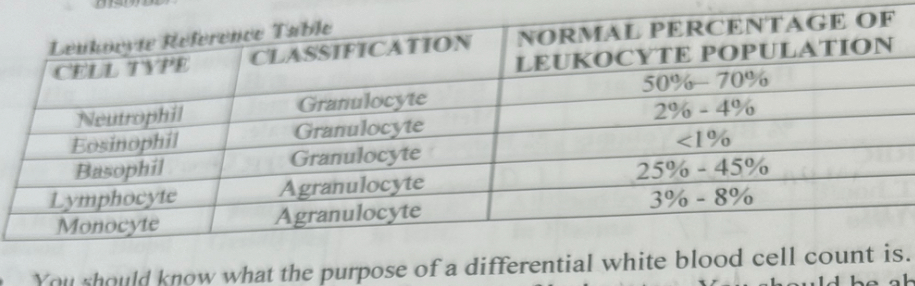
What is the appointed structure? And what structural and functional neurons are found here?
This is the dorsal route ganglion. Here you’ll find the somas unipolar sensory neurons.
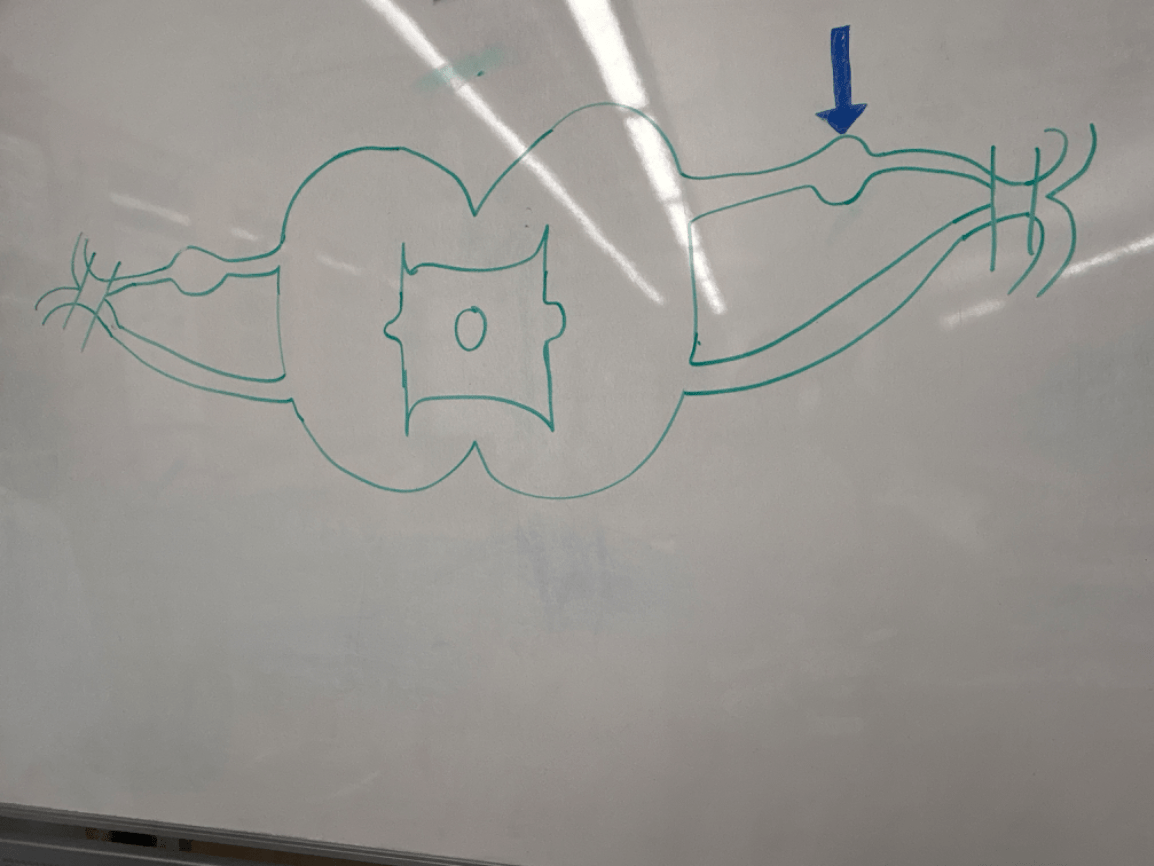
Where layer of the cochlea is the pointer located? What kind of fluid can be found in this region?
Scala Media. Endolymph fluid
What is hematocrit?
What is the normal range for females?
Hematocrit is the percentage value of red blood cells that make up the total blood volume.
Females: 42 (+ or -) 5
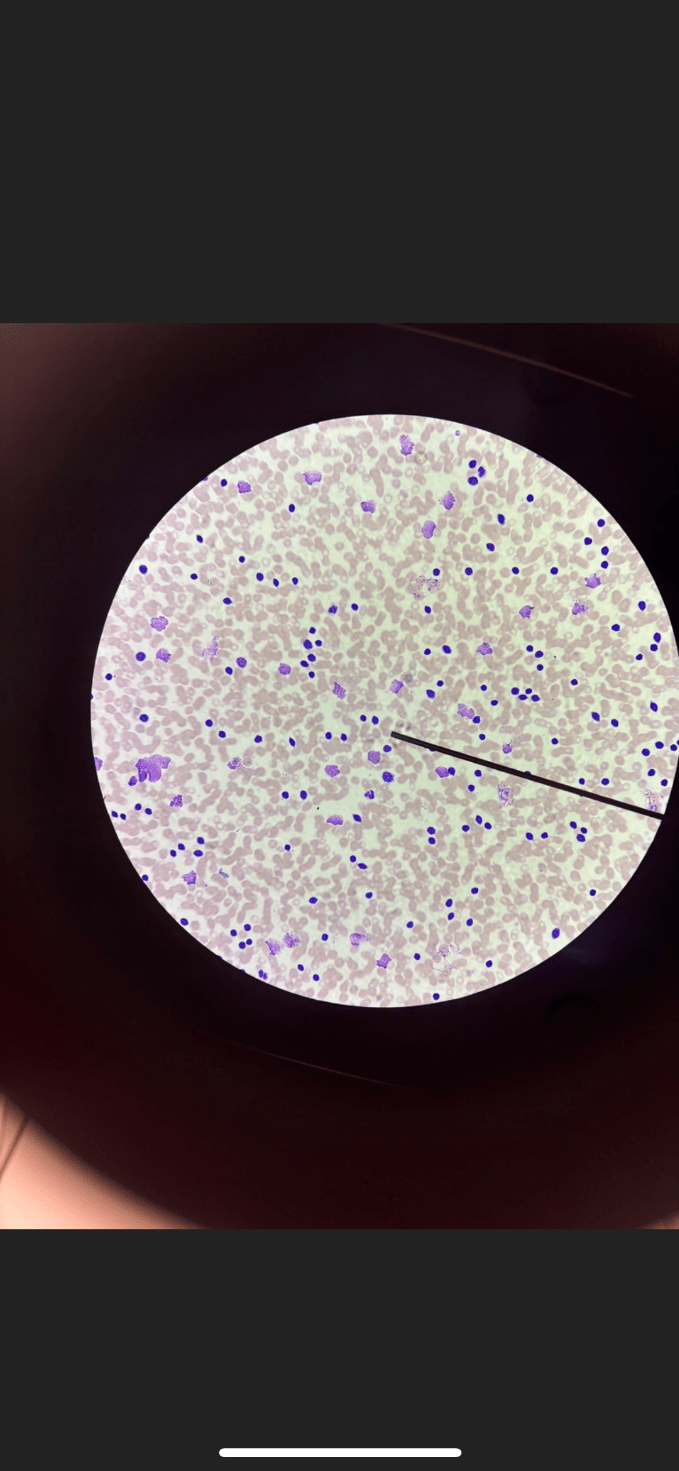
What disease is depicted on the histology slide? What is occurring in the body?
Chronic lymphocytic Leukemia. This is an auto immune disease characterized by an increased production of immature, white blood cells.
What is sickle cell disease and how is it different from thalassemia?
Sickle cell disease is an inherited disorder that is characterized by a mutation in one of the amino acid, causing abnormal structure of the hemoglobin. Thalassemia is characterized by an imbalance in the production of the alpha beta sheets, making up the hemoglobin.
What is the function of cranial nerve lX? And how is it tested?
mixed nerve
somatic motor, fibers serving pharyngeal muscles parasympathetic fibers serving salivary gland
sensory fibers carrying impulses from the posterior tongue chemo receptors
This nerve is tested by using a tongue depressor to check for the position of the uvula, gag and swallowing reflexes, speaking and coughing, and testing for taste in the posterior third of the tongue.
What equipment is required for testing of cranial nerve ll?
Pen light, smelled eye chart, ophthalmoscope, near point of vision chart
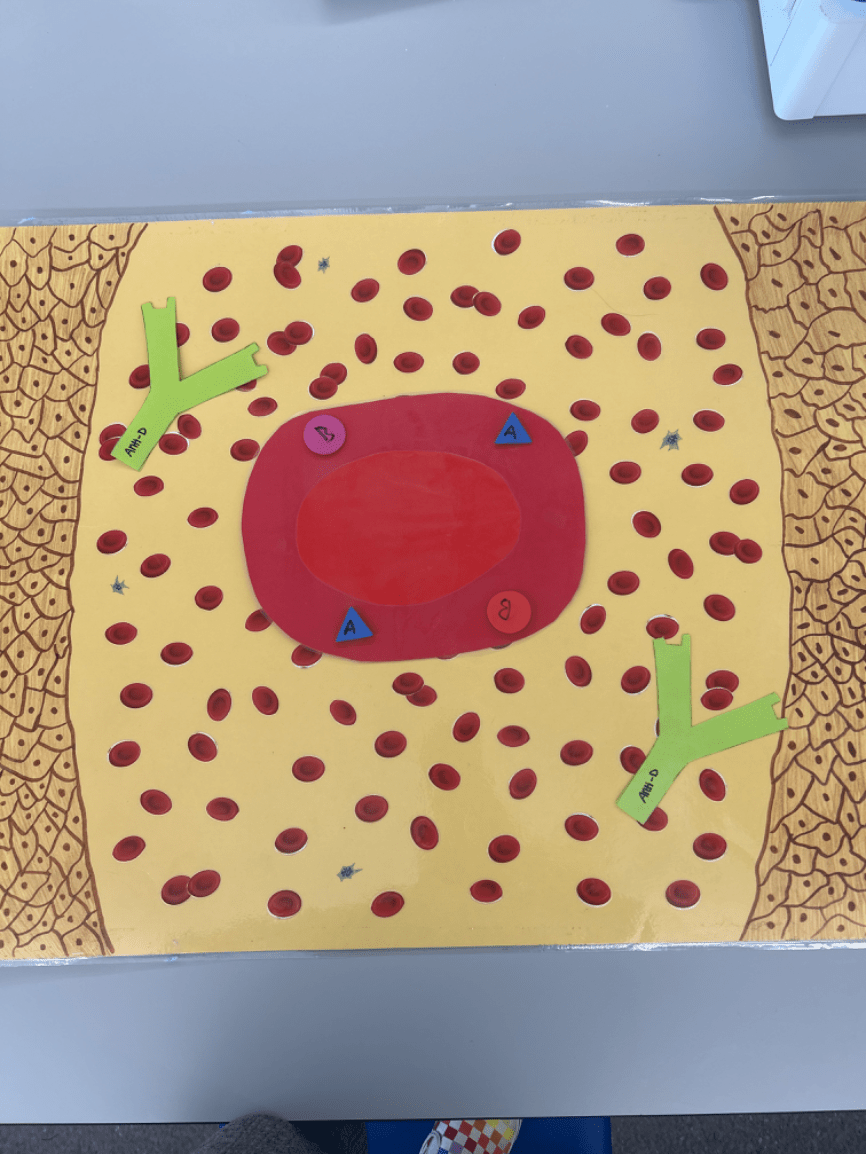
What blood type is depicted in this image? And who can a person with this blood type receipt blood from?
This is AB type blood and a person with this blood can receive blood from any blood type.
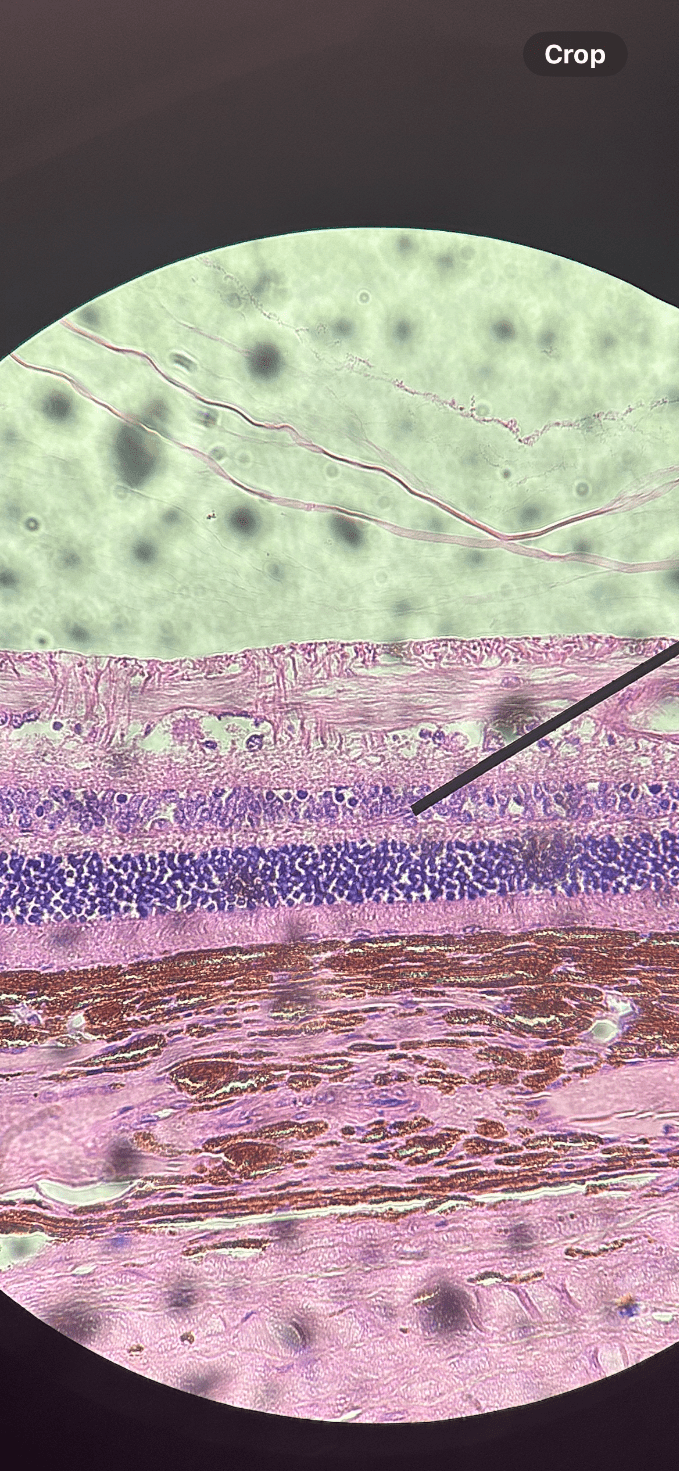
What organ is depicted in this slide and what cells are found in the appointed region?
The eye. Ganglionic cells can be found in this structure.
Describe the flow chart of cerebral spinal fluid starting from the choroid plexus.
Choroid plexus located in each lateral ventricle—> 3rd ventricle —> cerebral aqueduct—> 4th ventricle—> lateral and medial apertures and the spinal cord—> subarachnoid space and into the subarachnoid villi—> transportation into the venous blood of the dura—> superior sagittal sinus—>repeat
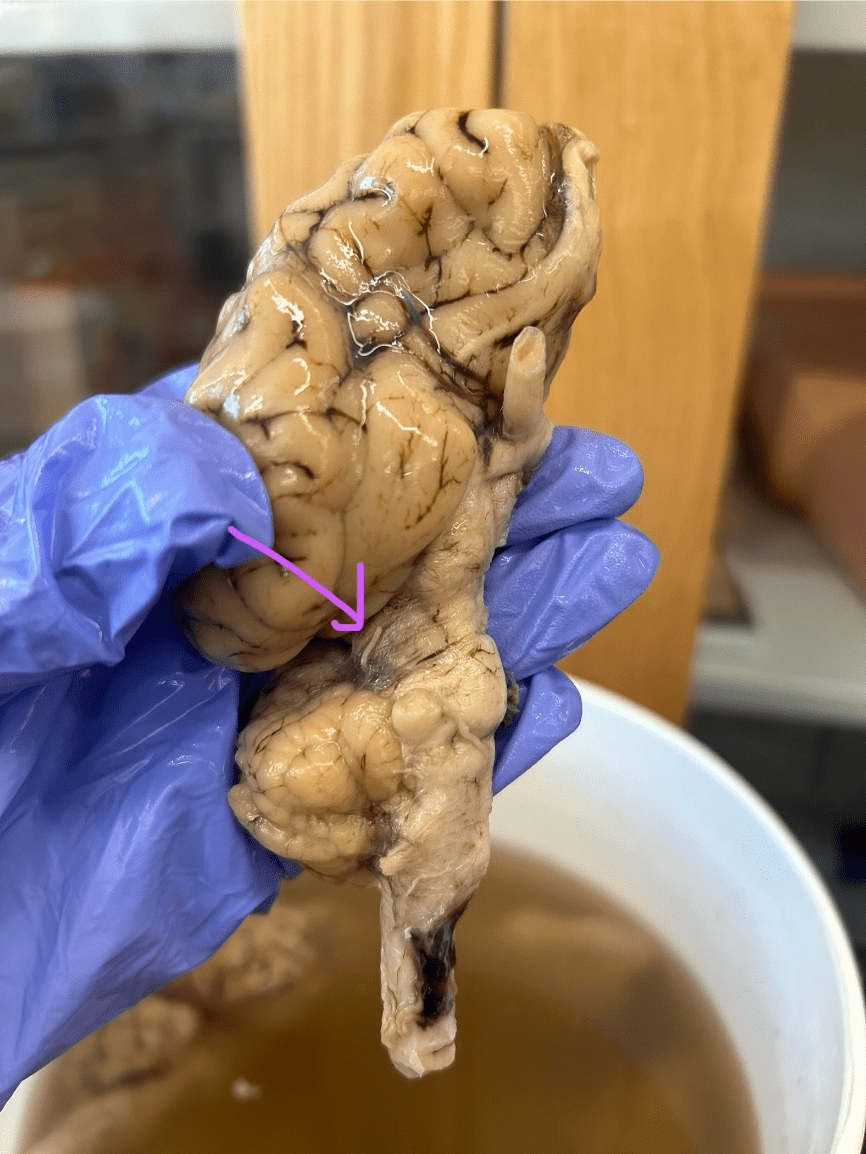
What nerve is being depicted on the sheet brain?
Trochlear nerve
Name the three tunics of the eye and one structure located in each tunic.
Fibrous ( sclera, cornea)
vascular ( choroid, ciliary bodies, iris blood vessels)
sensory ( retina, optic nerve)
Sally was admitted to the hospital yesterday on October 13. She appeared at the emergency department feeling unwell. As per protocol, the doctor ordered a complete blood count along with a basic metabolic panel. The results were as followed.

As the healthcare provider, taking care of Sally, what do you suspect she is experiencing? What symptoms do you expect to see with this disorder?
Sally is most likely experiencing anaphylactic shock. This is demonstrated by her high eosinophil levels. it is suspected that she will be presenting with wheezing, excessive itching, and generalized edema due to extreme vasodilation.
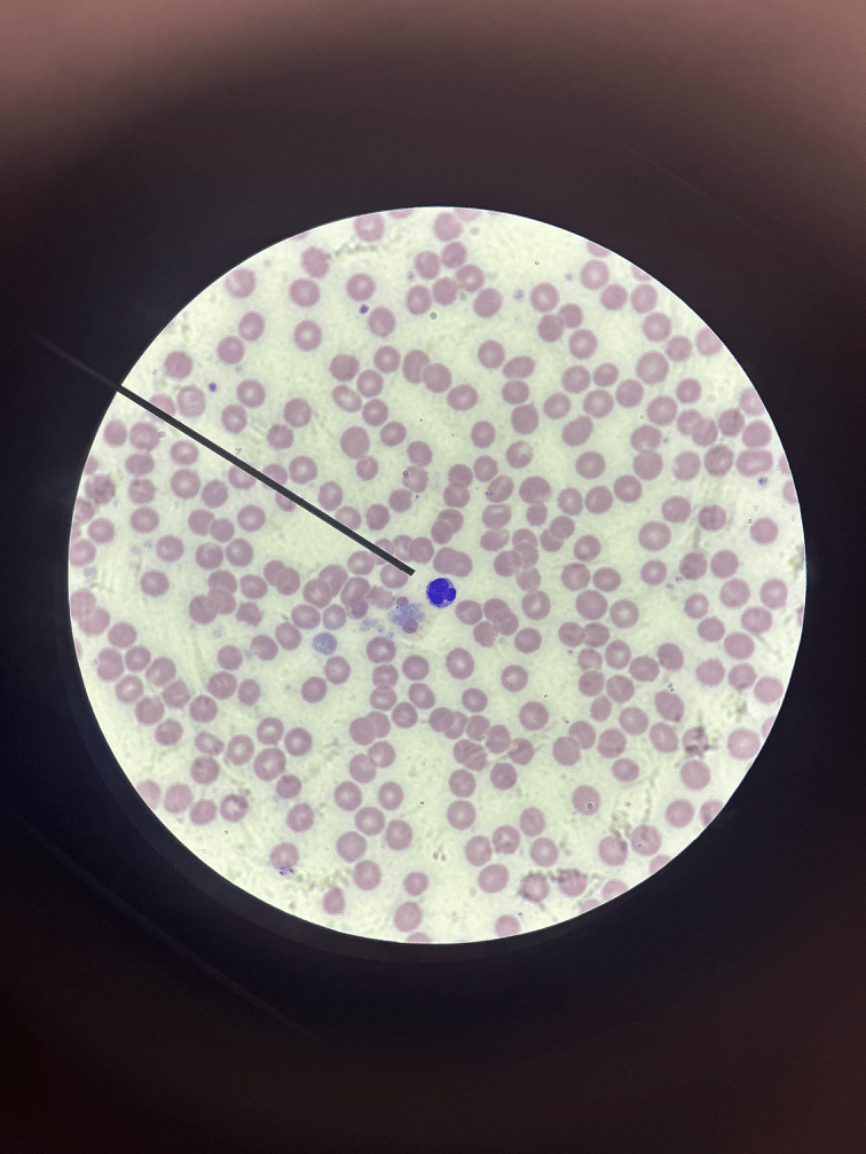
What cell is depicted? And in what conditions are the levels increased?
This is a monocyte. an increased percentage in this cell means that patient is likely experiencing a chronic bacterial infection or viral infection.
What nerve is being appointed? What plexuses is it derived from
This is the operator nerve and it is derived from the sacral plexus