giving up the change to earn money through interest (by holding cash)
What is opportunity cost (of holding cash)
Nominal - Inflation
aggregate that includes total amount of currency in circulation or on reserve by commercial banks
What is the monetary base
The United States' Central bank
What is the Federal Reserve
Reserves, Excess Reserves, and Loans are on this side of the bank balance sheet
What are assets to banks (on a bank balance sheet)
the Y axis in the money market
What is the nominal interest rate
What is expansionary monetary policy?
a hypothetical market for the money that is able to be borrowed including the market for bonds, stocks, and personal loans
What is the Loanable Funds Market
The measure of how fast an asset can be turned into cash
What is liquidity?
They type of loan banks make to ensure they maintain the same real rate of return
a Flexible interest loan
aggregate that includes demand deposits, currency in circulation, and savings accounts
What is M1
Minimum amount of cash that a bank MUST hold
what are reserve requirements /what is the required reserve rate
Demand Deposits are on this side of the bank balance sheet
What are liabilities (on a bank balance sheet)
the aggregate the money market refers to
What is M1
What is contractionary monetary policy?
additional education, skills, certifications, knowledge, health etc that makes you a better person (and more importantly better part of the labor force)
What is Human Capital
Examples include crypto, real-estate, gold/silver. and art
What are examples of least liquid assets
The expected real inflation rate when banks charge 5% interest on all loans and the expected inflation rate is 2%?
What is 3%?
Aggregate that includes money in circulation, demand deposits, savings accounts, small denomination time deposits and retail money market funds
What is M2
buying or selling government debt (though bonds)
what are open market operations
Demand Deposits / Reserves =
What is the reserve requirement (rate)
Include changes in the aggregate price level, changes in GDP, changes in technology, and changes in the ability and costs of using money substitutes (like credit cards)
What is/are (changes that result in) a shift in the demand for money
The two reasons it takes a while for the economy to respond to monetary policy changes
What are recognition lag an impact lag?
When the government is running a deficit and drives up interest rates. This leads to reduced investment spending.
What is Crowding Out?
The entity who sees a car loan as an asset
Who is the bank/lender
The actual rate of return when the bond with a 6% interest rate is met with 5% actual inflation rate.
What is 1% (rate of return)
If you move $500 from your checking account to purchase a CD, _______ is unchanged while _______ decreases.
(What is/are) M2 and M1 respectively
the interest rate banks pay the Federal Reserve when a bank needs liquid now so they can get a short term loan of cash on this discounted rate
what is the discount rate/window
This function describes the way banks create money from a single deposit
What is the money multiplier
An increase in credit card fees can cause MD to increase resulting in this effect.
The expansionary monetary policy in a limited reserve framework as a result of less money required to be in reserves.
What is the impact of a reduction in reserve rate?
The relationship between interest rates and bond values
What is an inverse relationship
The new nominal interest rate when Vern has a fixed interest CD with a nominal interest rate of 7% with no expected inflation. If inflation is now expected to be 3%
What is 7%
= $210 billion
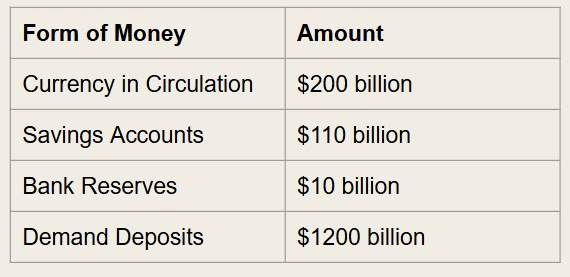
What is the monetary Base
(this isn't on the test but these 500 questions are usually easy for you so I had to throw this on here sorry)
The Chair of the Federal Reserve
Who is Jerome Powell
1/rr
What is the money multiplier formula
How will a change in the Demand for money due to a decrease in GDP affect the AD curve?
(this does not answer in a question--there's no better way to format this one)
Demand will decrease, causing NIR to decrease. NIR decreasing boosts interest based spending which increases the Consumption portion of the AD curve which shifts AD to the right (increase)
The Expansionary monetary policy that occurs in an ample reserves system.
What is a decrease in administered interest rates/ policy rate?
The rightward shift of the supply curve when there is more money entering the market to work with
What is the effect of positive inflow (net capital inflow on the loanable funds market)?