Monopolies are able to make economic profit in the long run because they have high
What barriers to entry?
For a non-price discriminating monopoly, the marginal revenue is what in relation to price
What is less than the price
When competitors collude and agree to set prices they are what type of Oligopoly
Colluding or a Cartel
If each player has chosen a strategy and no player can increase their own expected payoff by changing their strategy while the other player keeps their's unchanged, then the current set of strategy choices constitutes a ____________________________.
What is a Nash Equilibrium?
Draw a graph for a monopoly making a profit
The profit maximizing rule in a monopoly
What is MR = MC?
for monopolistically competitive firms in long run equilibrium price equals?
What is ATC
When Oligopolies collude they collectivity act as a ________________ ?
Monopoly
What is Firm 1's Dominant Stategy?
Firm 1's dominant strategy is to price high
Draw a graph for a price-discriminating monopoly and shade in the profit
Assume a monopolist is currently producing in the elastic range of their demand curve. To maximize total revenue, the monopoly should produce where MR is _________
What is ZERO?
If a non-price discriminating monopoly could suddenly start price discriminating and charge each consumer exactly what they are willing to pay then MR would be equal to
What is demand?
When one firm's actions impacts the outcomes for other firms, those firms are said to be _____________________?
Interdependent
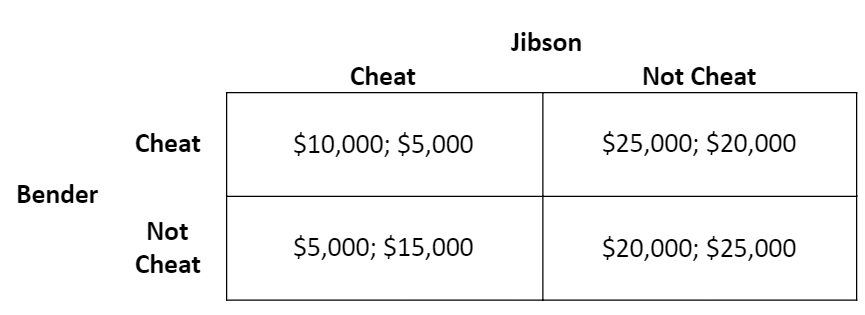 What is each firm's dominant strategy if any?
What is each firm's dominant strategy if any?
Bender’s dominant strategy is to cheat;
Jibson’s is to not cheat
Draw a graph for a monopolistically competitive firm in long-run equilibrium
What is the profit for this profit maximizing monopoly
What is $200
If a monopolistically competitive firm's variable costs increase, what will happen to QUANTITY and PRICE?
Quantity will Decrease
Price will Increase
Give 3 examples of industries which are Oligopolies
Car Manufacturers
Cereal Companies
OPEC
Railroad Companies
Tire Manufacturing
Film and TV Production Companies
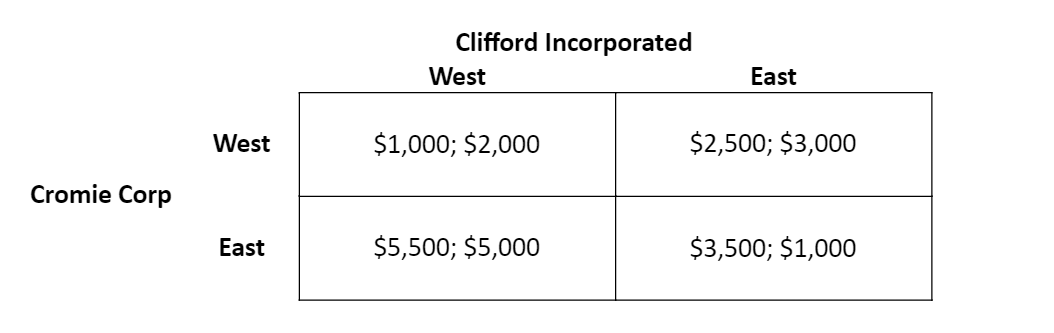 If both firms know all of the information in the payoff matrix but do not cooperate, what is their daily profit?
If both firms know all of the information in the payoff matrix but do not cooperate, what is their daily profit?
Cromie Corp = $5,500
Clifford Incorp = $5,000
Draw and label a graph for an Oligopoly

What is the consumer surplus and dead-weight loss for the monopoly.
CS = ABE
DWL = BCJ
In a monopolistically competitive market, if one firm is producing at a loss what will happen to the
1) Number of firms in the market
2) Demand
3) Marginal Revenue
4) Price
Graph It!
The economic loss causes firms to exit the market, increasing each remaining firm’s market size. That shifts the demand and marginal revenue right until the firm breaks even. Price increases.
In a Oligopoly when the ____________ is kinky, the __________ is sticky.
Demand
Price
 Is there a Nash Equilibrium? If so, what is it?
Is there a Nash Equilibrium? If so, what is it?
Yes, Paul’s will price high earning $2100 weekly profit and Sam’s will price low earning $1700 weekly profit.
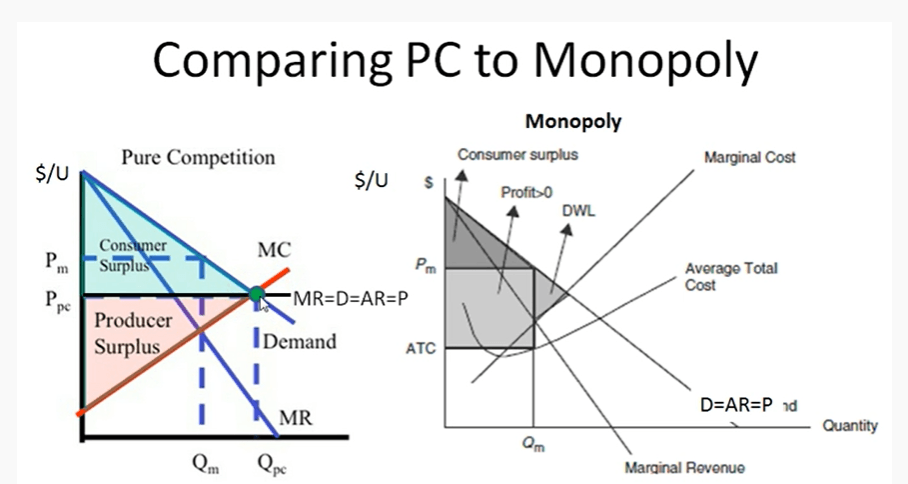
Draw side by side graphs of a perfect competition firm and a monopoly firm making profit. Label all the curves, shade DWL, CS, and PS, label the socially optimal quantity.
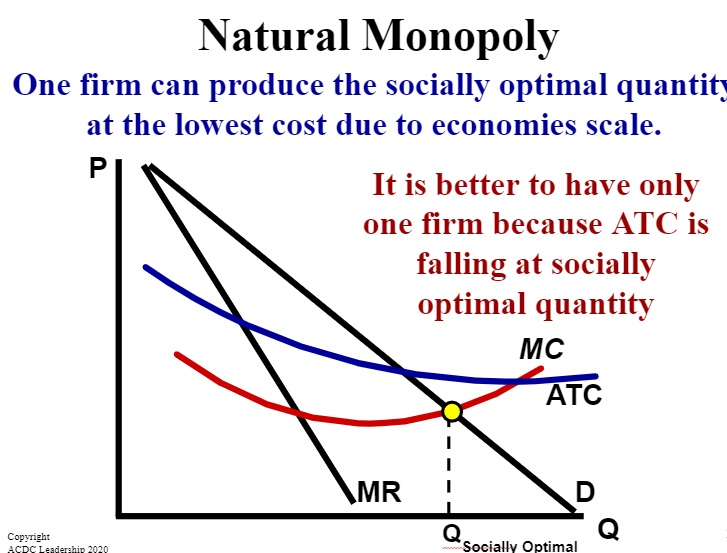
When one firm can produce the socially optimal quantity at the lowest cost due to economies scale they are a _________________ _________________.
Graph It!