Perfect Competition
The study that focuses on firms, households, and individuals is known as
What is microeconomics?
In order to have Demand, these two aspects must exist for a Consumer
What is Willing and Able
market in which buyers and sellers are numerous and well informed that all elements of monopoly are absent.
What is perfect competition?
MR=D=AR=P stands for
What is Marginal Revenue, Demand, Average Revenue and Price
The formula for Total Costs
What is FC + VC
"Other things being equal."
What is Ceteris Paribus?
The point where the demand and supply curve intersect
Market Equilibrium
Long Run Profit is what kind of Efficiency
What is Allocative and Productive
Firms do these two things in the Long Run
What is Enter or Exit the Market?
As you add more of a variable input to a fixed input, the addtl output you get will eventually decrease is known as
what is the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
An economic system where the government has total control
What is Command Economy?
The relationship between Price and Qty on the Demand Curve
What is inverse
The Marginal Cost Curve Above Min AVC
What is PC Supply Curve?
The Market that most approximates a Perfectly Competitive Industry
What is Agriculture
The cost advantages that arise when a company increases its production volume leading to lower average costs per unit
What are Economies of Scale
Land, Labor, Capital, and entrepreneurship is also known as the...
What is the four factors of production
the Cross-Price Elasticity of these two goods is negative
What are Complement Goods?
Short run shutdown rule
Long run exit rule
P<AVC
The fall in total surplus that results from a market distortion, such as a tax, and is a loss of economic efficiency
What is Deadweight
What kind of profit is calculated when we subtract both Implicit and Explicit Costs from TR?
What is Economic Profit?
As the production of one good increases, producers must sacrifice ever-increasing amounts of the other goods because factors of production are not perfectly interchangeable between the production of both goods
What is Law of Increasing Opportunity Costs?
The Elasticity of Demand = 1
What is Unit Elastic?
A tax that is a fixed amount, no matter the change
What is a lump sum tax
The Socially Optimal Price is _____ on a Perfect Competition graph
P=MC
The Long Run Point on the graph as shown is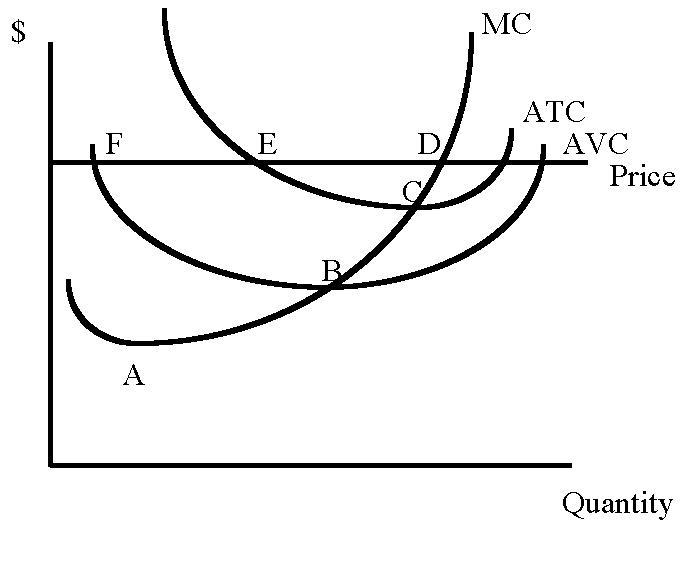
What is Point C?