These are the 3 kinds of imperfect markets
What are monopolies, monopolistic competition, and oligopolies?
This is why monopolies are not allocatively efficient
What is that they set price higher than marginal cost?
This is the definition of price discrimination
This is a characteristic of monopolistic competition
What is low barriers to entry, many firms, differentiated products, lots of advertising, inefficiency?
This is a characteristic of oligopolies.
What are a few large firms, mutual interdependence, control over price, high barriers to entry, inefficiency?
This is a type of imperfectly competitive market that has many firms with low barriers to entry.
What is monopolistic competition.
What are high start-up costs, patents, access to raw materials, or geography?
This is the definition of perfect price discrimination
What is when producers charge the maximum price a consumer would be willing to pay for a good.
This is why firms use advertising in monopolistically competitive markets.
What is to make demand more inelastic OR increase demand?
This is why collusion among cartels is typically ineffective.
What is because firms have incentive to cheat on agreements?
This is what imperfectly competitive firms have to do to sell more units of output.
What is lower their prices?
This is true of the average total cost curve of a natural monopoly.
These are the type of consumers who are charged higher prices under a price-discriminating firm (Hint: The answer will be those with inelastic demand or those with elastic demand).
What are consumers with more inelastic demand.
This is true of economic profit in the long-run for monopolistically competitive firms.
What is that economic profit equals 0
This is what would happen if both firms colluded in the payoff matrix below:
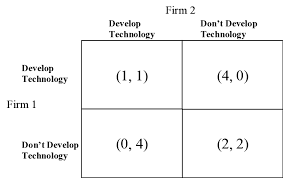
What is both firms don't develop technology?
This is the relationship between demand and marginal revenue in imperfectly competitive markets.
What is that Demand>Marginal Revenue?
This is a graph of a monopoly earning a loss.
This is what happens to consumer surplus with a perfectly price discriminating firm.
What is that it shrinks to 0?
This is why economic profit equals 0 in the long-run for perfectly competitive markets.
What is because firms can enter or exit the market, impacting the demand curve?
This is the dominant strategy for firm 1 in the payoff matrix below.

What is developing technology?
This is a graph of an imperfectly competitive firm (specifically a monopoly or monopolistically competitive firm in the short run) earning economic profit.
What is:

This is a monopoly graph with deadweight loss & consumer surplus shaded in.

This is what a perfectly price discriminating firm graph looks like with marginal cost, marginal revenue, and demand labeled.
What is:

This is what a graph for a monopolistically competitive firm looks like in the long-run with D, MR, P, Q, and ATC labeled.
What is:

This is the Nash Equilibrium in the payoff matrix below.

What is Firm 1 Developing Technology & Firm 2 Developing Technology?