The purpose of CSF.
Cushion and protect the brain.
The term for the 3 layers that help protect the brain.
Meninges
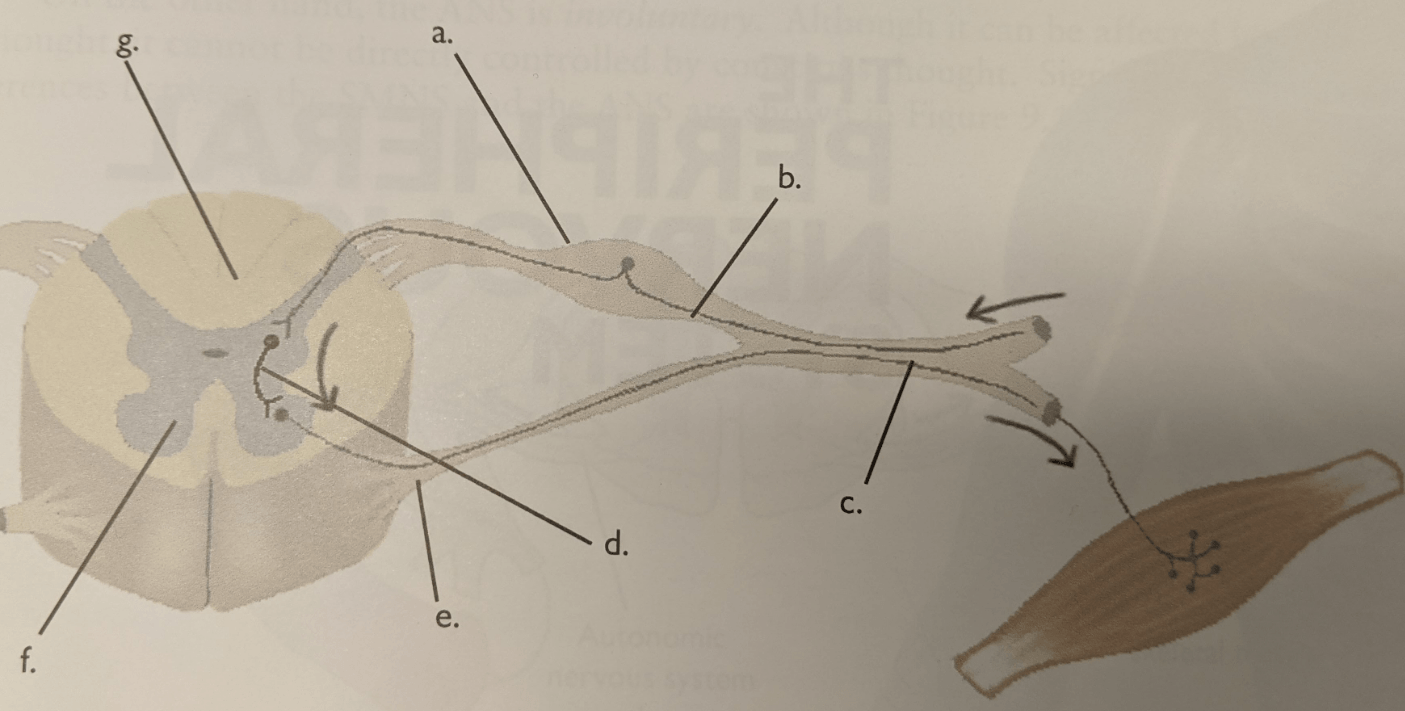
Letter g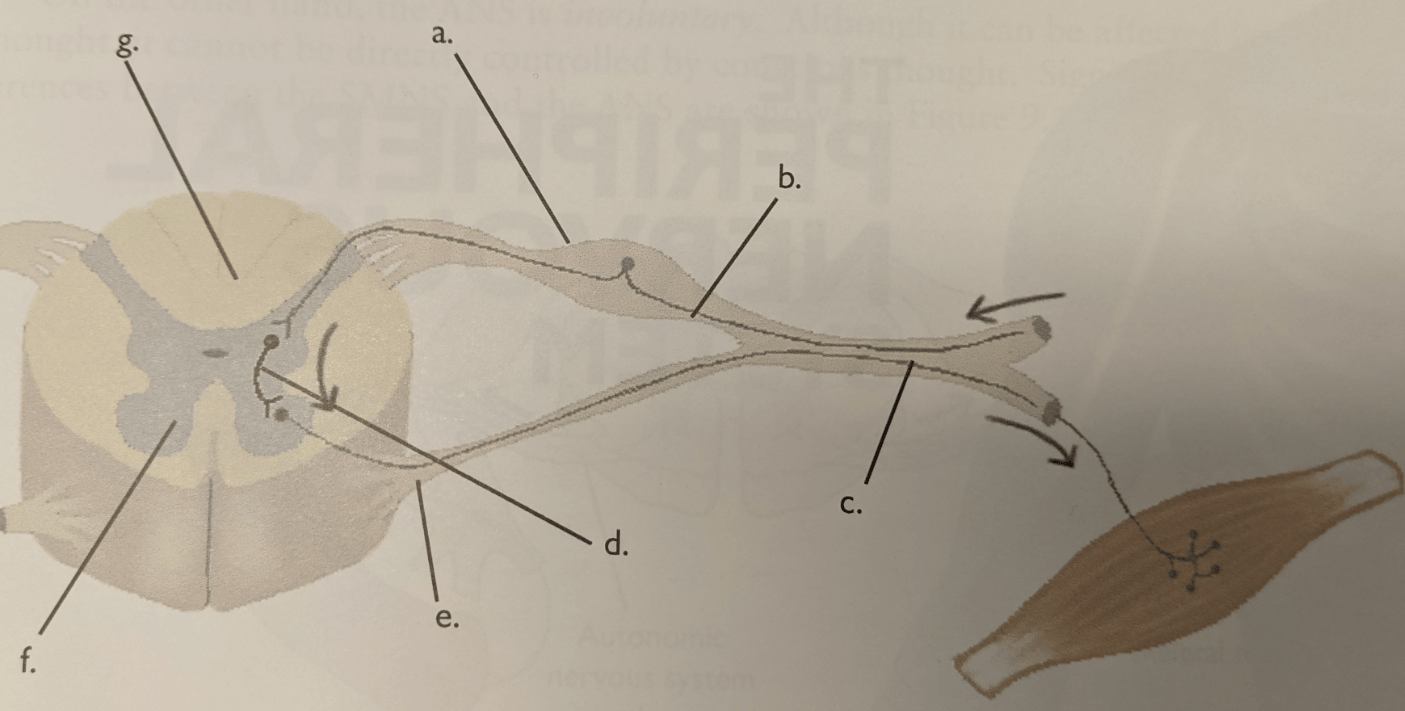
White matter
Where can you find the association neuron in the reflex arc?
In the spinal cord.
Letter E.
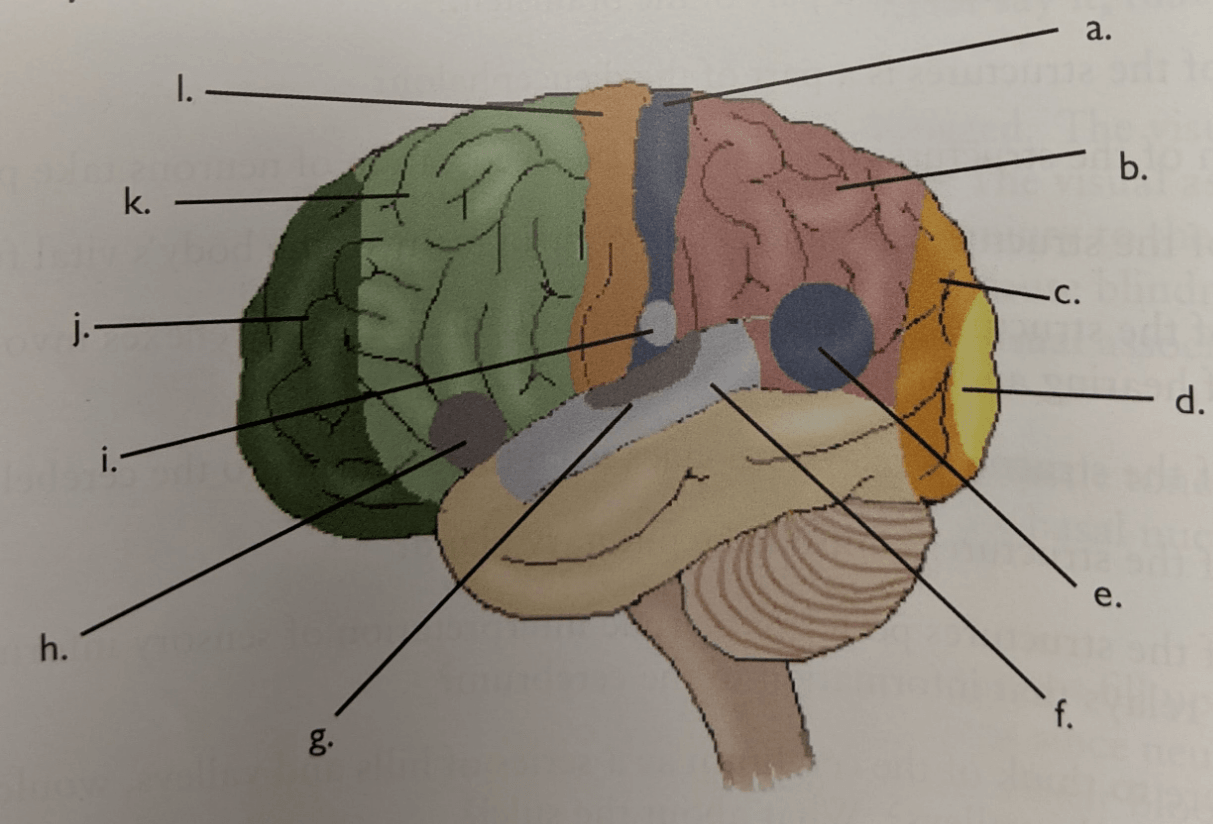
Wernicke's area.
Area that receives sensory input from all over the body.
Primary somatic sensory area.
Where CSF is located.
Skull and spine
Innermost meninx
Pia mater
Letter f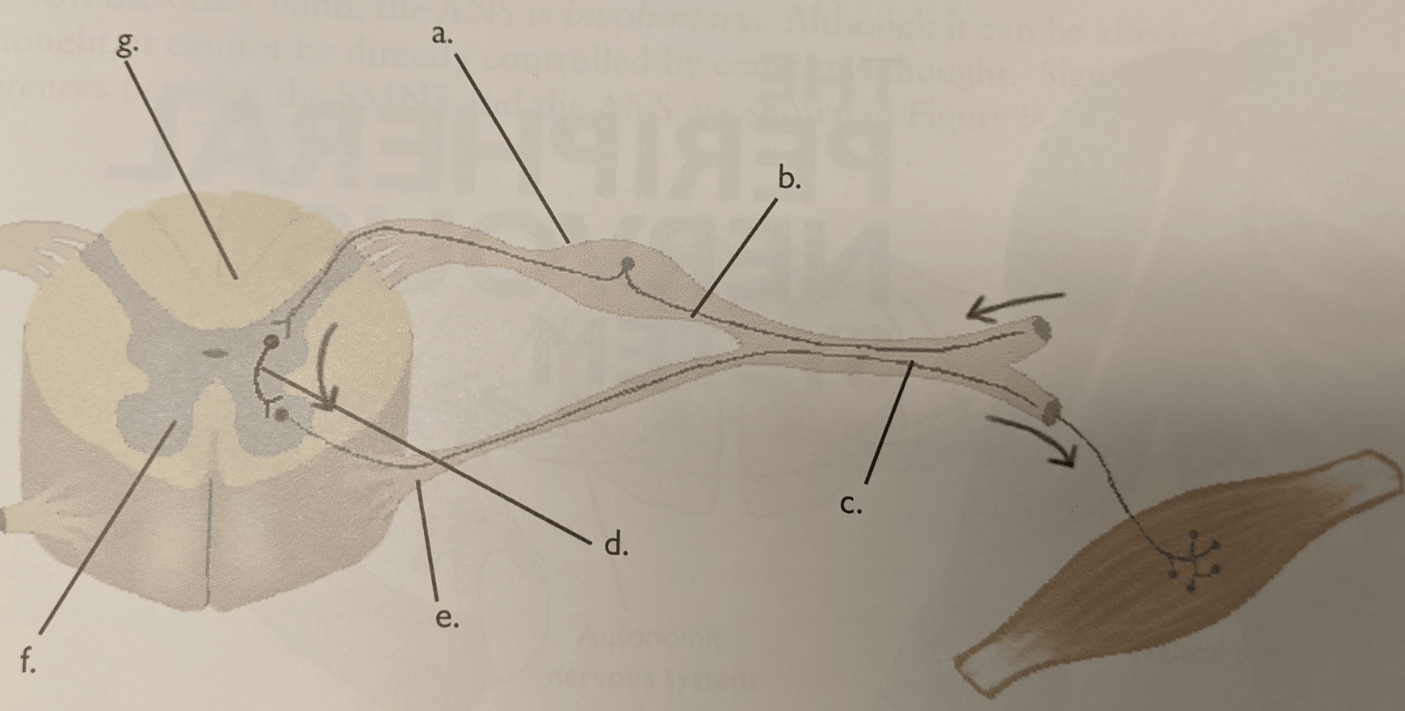
gray matter
What neuron is activated last in reflex arc?
Efferent (motor) neuron
Letter j.

Prefrontal area
Area that determines the meaning of the sensory touch received.
Somatic sensory association area.
This is where the majority of the cerebrospinal fluid is produced.
Lateral ventircles
Outermost mininx
Dura mater
Letter d
Association neuron
What neuron is activated first in reflex arc?
Afferent (sensory) neuron
Letter d.

Area that receives basic shapes and colors from vision.
Visual cortex.
This is where a small portion of CSF is made.
The third and fourth ventricles.
Meninx that is spider-web like in appearance.
Arachnoid mater
Letter e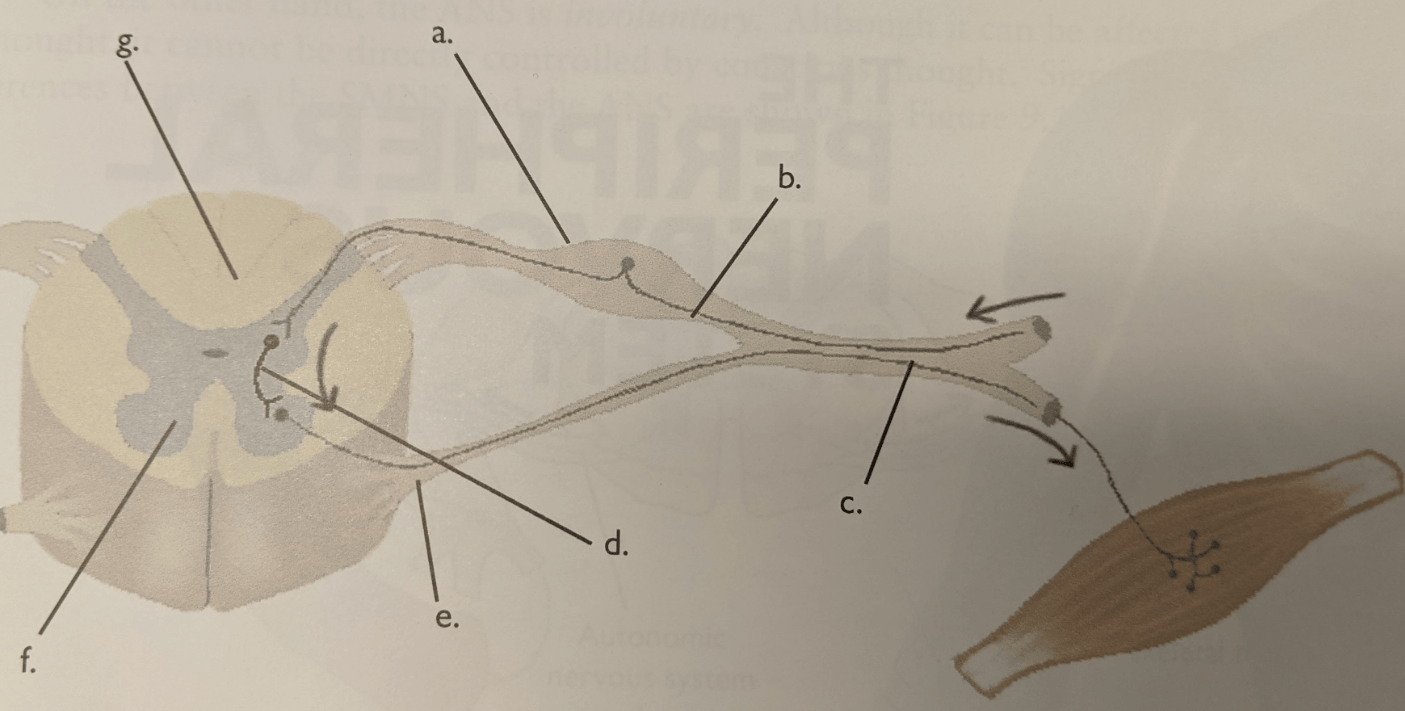
Ventral root
What type of circuit is formed by the afferent neuron in the reflex arc?
Diverging circuit.
Letter g

Primary auditory area
Area that gives visual shapes and colors meaning
Visual association area.
CSF is in this layer of the mininges.
What is dura mater.
Extensions of arachnoid mater that help return CSF to blood
Arachnoid granulation
Letter b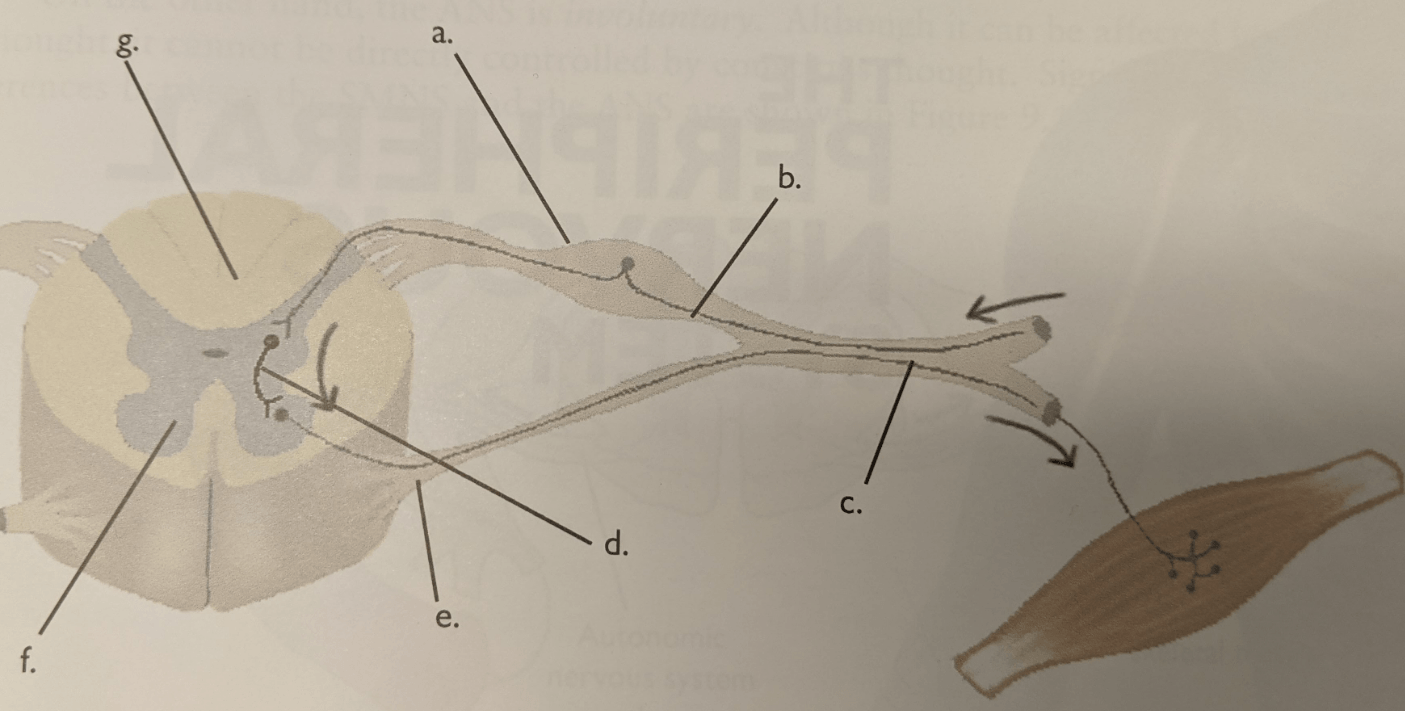
Afferent (sensory) neuron
What type of circuit is formed by the efferent neuron in the reflex arc?
Converging Circuit
Letter a.

Primary somatic sensory area
Area that processes sounds into language.
Wernicke's area.