The central nervous system is made up of 2 parts: What are they?
Brain and spinal cord
Which part of the brain communicates with pituitary gland which in turn controls the endocrine system?
Hypothalmus
When people use drugs, it stops neurotransmitters from reaching this section between.
Synapse
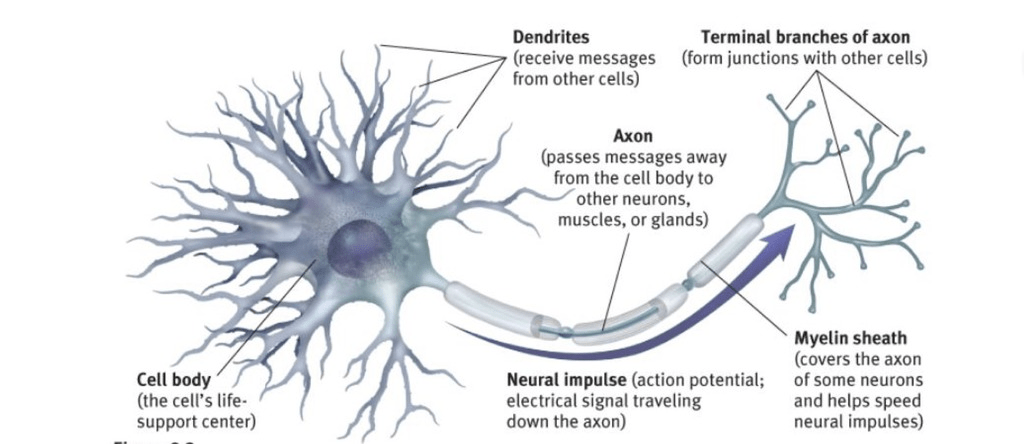
What part of the neuron receives messages?
Dendrites
This bundle of nerves connects the left and right hemisphere.
Corpus callosum
The CNS is connected to the PNS? Tell me what PNS stands for and what is the purpose in the body?
Peripheral Nervous System....Outer parts of the body....Signals back and forth
The job of hormones are ___________ that are released into the ____________.
Chemical messengers - Bloodstream
Which neurotransmitters affects sleep, mood, hunger, and arousal. Undersupply of this can lead to depression.
Serotonin
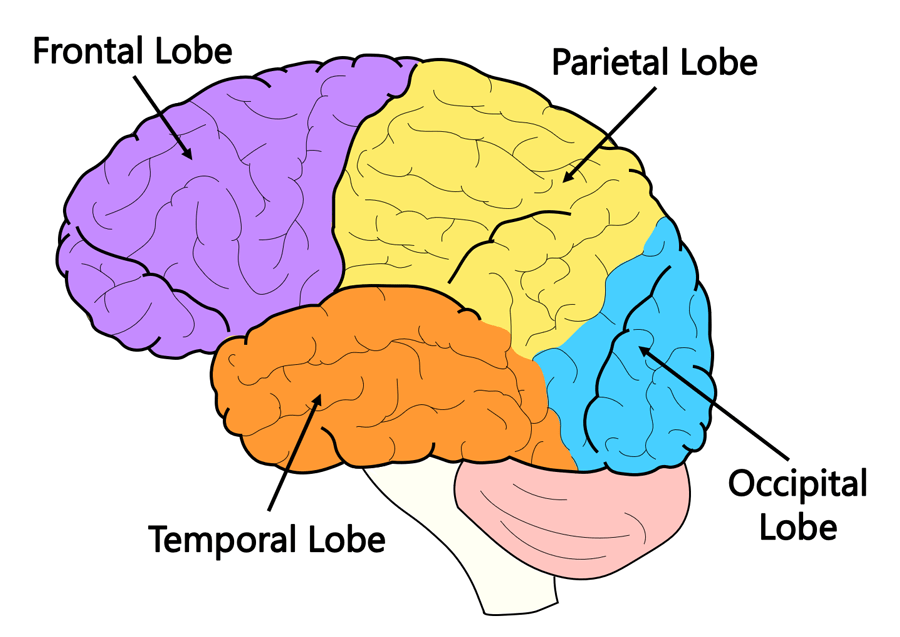
2 parts: The structure of the brain is essential for forming long-term memories... (Which lobe is it in?)
Hint: Who's got a great memory?
Hippocampus - in the temporal lobe
This lobe of the brain controls coordination vision, perception and visual memory.
Occipital lobe.
1. Which nervous system is responsible to respond to stress or danger?
2. What other way can we describe this reaction?
"_______ or _______ "
Sympathetic Nervous System
"Fight or Flight"
After consuming a banana split, which hormones would be expected to increase? Hint: Balances sugar
Insulin
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for motor functions?
Frontal lobe
How does dopamine affect your body?
(Name 2 of the 4 functions)
Influences movement, learning, attention and emotion.
What are the functions of the temporal lobe? (Give 2 of the 3
Short term memory, equilibrium, and emotion
The Autonomic Nervous is broken into 2 parts.
What is the function of the Sympathetic Nervous System and Parasympathetic Nervous System?
Sympathetic - Increases heart rate, blood pressure. The arousing part of the NS
Parasympathetic - Regulates the body - Tries to reach homeostasis... Slows heart rate and drops BP.
Part 1 - Why is the pituitary gland called the master gland?
Part 2 - What functions does it control?
Controls the functions of other glands. Growth , metabolism and sexual development.
Explain what each part of the frontal & temporal lobe does:
Broca's area:
Wernicke area:
Broca - Speech production
Wernicke - Understanding spoken language
MS or multiple sclerosis is a result of generation in the this part of the neuron?
Hint: Brrrr its cold....I need a coat
Myelin sheath
Name the 4 lobes of the brain
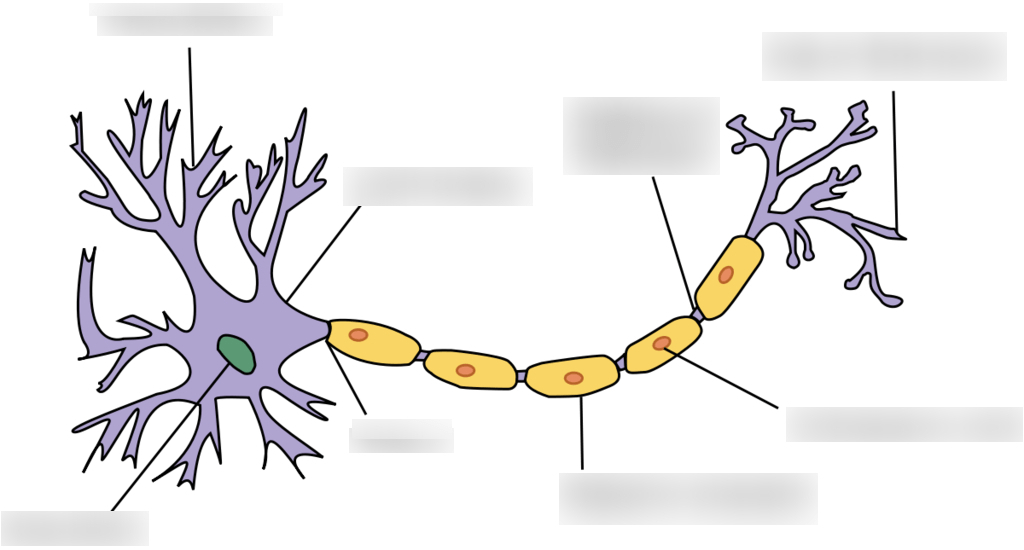
Explain the difference between a sensory neuron and a motor neuron.
A sensory neuron carries signals from the body's sensory receptors towards the central nervous system (CNS), while a motor neuron carries signals from the CNS to muscles and glands, causing movement; essentially, sensory neurons receive information from the environment, while motor neurons initiate actions based on that information
Epinephrine and norepinephrine increase energy and are released by the ___________ glands.
What is the purpose of the ________ glands.
Adrenal
Produce hormones - Stress response - metabolism - immune system - water / salt balance.
What is the purpose of the brain stem? Explain
The brainstem serves as the control center for many vital bodily functions, including breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, consciousness, and swallowing, by relaying information between the brain and the rest of the body, essentially acting as a bridge between the spinal cord and the cerebrum; it is responsible for regulating these functions automatically, without conscious thought.
Label 4 of the parts of the diagram
Name 2 scans of the brain that shows structure.
Name 2 scans of the brain that shows function.
Structure - MRI (Magnetic resonance imaging) CT (Computer tomography)
Function - fMRI , PET and EEG (Electroencephalogram)
(Positron Emission Tomography)