The receptors located toward the center of the retina that are responsible for day and color vision
What are cones?
Minimum stimulation necessary to detect a sense 50% of the time.
What is absolute threshold?
The strength of the soundwave.
What is amplitude?
Someone who tends to be extremely sensitive to sweet and bitter tastes and spicy foods
What is a supertaster?
Where tactile receptors are located
What is skin?
Tendency to see incomplete figures as complete
What is closure?
Theory of color vision that explains complementary afterimages
What is opponent-process theory?
The perceptual process that works from big picture (general) to small details (specific).
What is top-down processing?
The three tiniest bones in your body, collectively known as the ossicles
What are the hammer, anvil, and stirrup?
The proper name for our sense of taste
What is gustatory system/gustation?
The lobe and cortex responsible for processing tactile sensory input
What is the parietal lobe; somatosensory cortex?
Tendency to group nearby objects together
What is proximity?
Visual signal that the objects are closer than the ones behind it.
What is interposition?
For people to perceive a difference, the stimuli must differ by a constant proportion/percentage.
What is Weber's Law?
The membrane in the cochlea that vibrates in response to sound waves
What is basilar membrane?
Olfactory sensory input is not routed through this brain structure before being processed in the cerebral cortex
What is the thalamus?
When senses become joined and one sort of sensation produces another.
What is synethesia?
Grouping similar objects together
What is similarity?
After the opening number, Rachel's eyes are no longer bothered by the bright stage lights (what has occurred?)
What is sensory adaptation?
Using features on the object (details) itself to build a perception (big picture).
What is bottom-up processing?
The ear structure labeled B
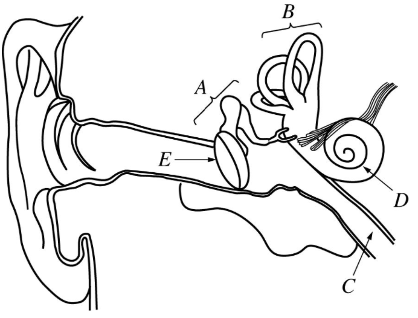
What are the semicircular canals?
We hear different pitches because different sound waves trigger activity at different areas in the cochlea.
The neurotransmitter that plays a large role in our perception of pain
What are endorphins?
Our tendency to distinguish objects from their background
What is figure-ground?
The path of a neural impulse through the retina (4 parts)
Rods/cones => Bipolar cells => Ganglion cells => Optic nerve
The detection of a stimulus depends on both the intensity of the stimulus and the psychological state of the individual.
What is a signal detection theory?
The theory that says pitch perception depends on the rate that the entire basilar membrane vibrates
What is frequency theory?
The process of converting sensory input into signals that can be processed in the brain
What is transduction?
The theory that explains why biting your tongue while getting an injection blocks your experience of pain from the needle
What is gate-control theory?
The school of psychology that studies how we organize perceptual information
What is Gestalt psychology?