this is highly folded to increase its surface area, allowing for complex neural processing and integration of information.
Cerebral Cortex
what brain structure is primarily responsible for forming and consolidating new memories - the picture is the hint
Hippocampus
are substances that alter brain function, leading to changes in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition, or behavior.
Psychoactive Drugs
What is the retina?
The light-sensitive inner surface of the eye containing photoreceptor cells that convert light into neural signals.
involves the brain's interpretation and organization of sensory information to create a meaningful experience
Perception
The state of being aware of and able to perceive one's thoughts, feelings, sensations, and surroundings.
Consciousness
chemical messengers that transmit signals between neurons, allowing for communication within the nervous system.
Neurotransmitters
It plays a critical role in increasing heart rate, blood pressure, and alertness during times of stress or danger.
Norepinephrine
What is the body's communication network called?
Nervous system
the debate on why humans act and behave the way they do - _________ vs _____________
Nature vs Nurture
refers to the brain's ability to reorganize and adapt throughout life in response to experiences, learning, and environmental changes.
Plasticity
What brain lobe is located at the front of the brain and are involved in higher-level cognitive functions, including decision-making, problem-solving, planning, and personality expression.
Frontal Lobe
region of the brain located in the parietal lobe, responsible for processing sensations from the skin, muscles, and joints.
Somatosensory Cortex
 what type of drug is this an example of?
what type of drug is this an example of?
Stimulant / Caffeine
Photoreceptor cells in the retina responsible for vision in low light conditions and detecting motion. They provide black-and-white vision and are highly sensitive to light, allowing us to see in dim environments.
Rods
The conversion of sensory stimuli into neural impulses that can be understood by the brain.
Transduction
characterized by drifting in and out of sleep, lasting only a few minutes. Brain waves slow down, muscles relax, and individuals may experience sudden muscle contractions known as hypnic jerks.
NREM Stage 1
a neurotransmitter that acts as the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. It promotes relaxation and reduces anxiety.
GABA
hormone that regulates the sleep-wake cycle and circadian rhythms in the body.
Melatonin
What is the central control system (command center) of the body?
Central Nervous System / CNS
the transmission of genetic information from biological parents to offspring.
Heredity
located in the left hemisphere of the brain, specifically in the frontal lobe, that is responsible for speech production and language processing.
Broca's Area
a region of the brain located in the frontal lobe, responsible for higher-level cognitive functions and executive functioning.
Prefrontal Cortex
a relay station in the brain that processes and relays sensory information, such as sight, sound, touch, and taste, to the cerebral cortex.
Thalmus
What are Hallucinogens?
Drugs that alter perception, mood, and cognitive processes, often causing hallucinations or profound changes in consciousness.
Photoreceptor cells in the retina responsible for color vision and detail in bright light. They enable us to perceive colors and fine visual details, such as reading text or distinguishing between different hues.
Cones
Why is pain a weird concept when it comes to sensation?
It is in fact not a sensation but an emotional response to stimuli.
characterized by light sleep, lasting about 20 minutes. Brain waves further slow down, and sleep spindles (short bursts of brain activity) and K-complexes (sudden, sharp waveforms) appear.
NREM 2
neurotransmitter that plays a vital role in regulating mood, sleep, appetite, and stress.
Serotonin
often referred to as the "love hormone" or "bonding hormone" due to its involvement in forming emotional connections, trust, and intimacy.
Oxytocin
consists of all the nerves and ganglia outside the brain and spinal cord.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
the process by which organisms with traits that are better suited to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on those advantageous traits to future generations.
Natural Selection
the phenomenon where each hemisphere of the brain controls the opposite side of the body.
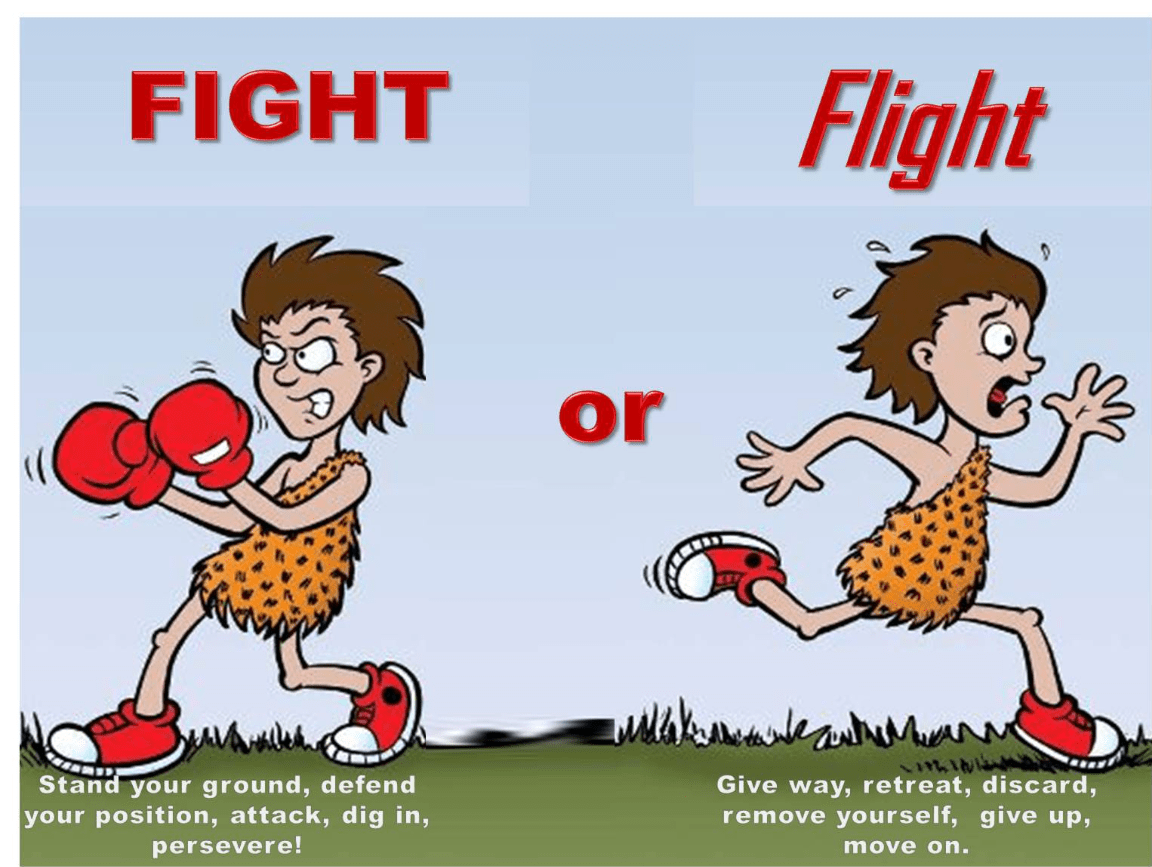
what brain structure controls this response?
Amydala
a small but powerful structure located below the thalamus, responsible for regulating various essential bodily functions, including hunger, thirst, body temperature, and the sleep-wake cycle.
Hypothalmus
Drugs that slow down neural activity and bodily functions. They induce relaxation, sedation, and can lower inhibitions
Depressants
It's a spot where vision is absent, as there are no light-sensitive cells to detect visual stimuli.
Blind Spot
Define Weber's Law
The perceived difference in a stimulus must be proportional to the original intensity of the stimulus. The bigger something is, the more you need to change it to notice a difference.
stage of sleep characterized by rapid eye movements, vivid dreams, and muscle paralysis. It is associated with increased brain activity, including dreaming, and plays a role in memory consolidation and emotional processing.
REM Sleep
neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in regulating mood, reward, motivation, and movement.
Dopamine
It is often referred to as the "hunger hormone" because its levels increase before meals and decrease after eating
Ghrelin
The sympathetic nervous system activates "fight or flight" response - what is it characterized by?
Increases heart rate, dilates airways, and redirects blood flow to essential organs, preparing the body to respond to perceived threats.
the study of how psychological traits and behaviors have evolved over time to enhance survival and reproductive success.
Evolutionary Perspective
This area helps to interpret the meaning of words and sentences, allowing individuals to comprehend and process language.
Wernicke's Area
Daily Double
this is located at the top of the brain and are primarily responsible for processing sensory information from the body, such as touch, temperature, and spatial awareness.
Parietal Lobes
What does the Medulla do?
vital structure located at the base of the brainstem, regulating essential autonomic functions such as heartbeat, breathing, and blood pressure.
Define Tolerance
A condition where increasing amounts of a psychoactive substance are needed to achieve the same effects.
Visual sensations that persist after a stimulus is removed. They occur due to temporary overstimulation of cone cells in the retina, resulting in a brief perception of an inverted or complementary image.
Afterimages
Chemical substances released by animals, including humans, that trigger social or behavioral responses in others of the same species.
Pheromones
The natural, internal process that regulates the sleep-wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours. It influences patterns of alertness, hormone release, body temperature, and other physiological processes.
Circadian Rhythm
neurotransmitters produced by the brain and central nervous system that act as natural pain relievers and mood enhancers.
Endorphins
hormone and neurotransmitter that plays a key role in the body's stress response, often referred to as the "fight or flight" response.
Adrenaline
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/neuron-anatomy-58530ffe3df78ce2c34a7350.jpg)
what is this?
What is Genetic Predisposition?
the inherited likelihood of developing specific traits or conditions due to genetic factors from biological parents.
what kind of test gives you these?
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging “fMRI” neuroimaging technique used to measure brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow and oxygen levels.
What do the Occipitol lobes do?
this lobe contains the primary visual cortex, which interprets visual stimuli and helps us perceive shapes, colors, and motion.
Limbic System
DAILY DOUBLE
The onset of symptoms when a person stops using a psychoactive substance after prolonged use.
Withdrawal
Define Monochromatism
A rare form of color blindness where an individual has only one type of functioning cone cell, or none at all. This results in the inability to perceive colors, seeing the world in shades of gray.
What is Gustation?
The sense of taste, involving receptors on the tongue that detect different flavors.
The deepest stage of non-rapid eye movement sleep characterized by the presence of predominantly delta waves.
NREM 3
the primary excitatory neurotransmitter in the CNS, playing a key role in synaptic transmission and neuronal communication. It is involved in various brain functions, including learning, memory, and neural plasticity.
Glutamate
chemicals released by neurons that increase the likelihood of an action potential occurring in the postsynaptic neuron.
Excitatory Neurotransmitters
What do sensory neurons do?
specialized nerve cells that transmit sensory information from sensory receptors, such as those in the skin, muscles, and organs, to the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). They detect various stimuli, including touch, temperature, and environmental changes, and convert these stimuli into electrical signals that can be processed by the brain.
the belief in improving the genetic quality of a human population by controlling reproduction to increase desirable traits and decrease undesirable ones.
Eugenics
What is this an example of?
Broca's Aphasia
Have difficulty producing fluent speech and forming grammatically correct sentences.
Speech may be slow, effortful, and characterized by shortened phrases or words.
these lobes are located on the sides of the brain and are involved in processing auditory information, language comprehension, and memory formation.
Temporal Lobes
often referred to as the "master gland" due to its central role in regulating hormone production and secretion throughout the body.
Pituitary Gland
psychoactive drugs that act on opioid receptors in the brain and body, producing pain relief, euphoria, and sedation.
Opioids
Transparent structure in the eye that focuses light onto the retina. It adjusts its shape to help the eye properly refract light, enabling clear vision at different distances.
Lens
What is Phantom Limb?
Sensation of pain or other feelings in a missing limb. It occurs due to the brain's continued perception of the limb, even though it's no longer there. Phantom limb sensations can range from tingling to intense pain and are thought to result from the process of plasticity in the somatosensory cortex following amputation.
Define Somnambulism
A sleep disorder commonly known as sleepwalking, characterized by walking or performing other activities while still asleep. It typically occurs during non-REM sleep stages and can result in injuries or accidents.
chemical messengers produced by glands in the endocrine system that travel through the bloodstream to target cells or organs, where they regulate various physiological processes and behaviors.
Hormones
hormone produced primarily by fat cells that regulates energy balance and appetite.
Leptin
the "support cells" of the nervous system, provide structural support, insulation, and nourishment to neurons.
Glial Cells
DAILY DOUBLE
Name 5 traits and behaviors that research suggests people may have a genetic predisposition for
Anxiety disorders, Depression, ADHD, Bipolar, Schizophrenia, Substance use disorders, Autism spectrum disorders, Intelligence, Personality traits, Aggression or impulsivity, Obesity and body weight regulation, Risk-taking behavior, Chronic pain conditions, Sleep disorders, Sensory processing sensitivity
non-invasive neuroimaging technique used to record the electrical activity of the brain
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
region of the brain located in the frontal lobe, responsible for planning, executing, and controlling voluntary movements of the body.
Motor Cortex
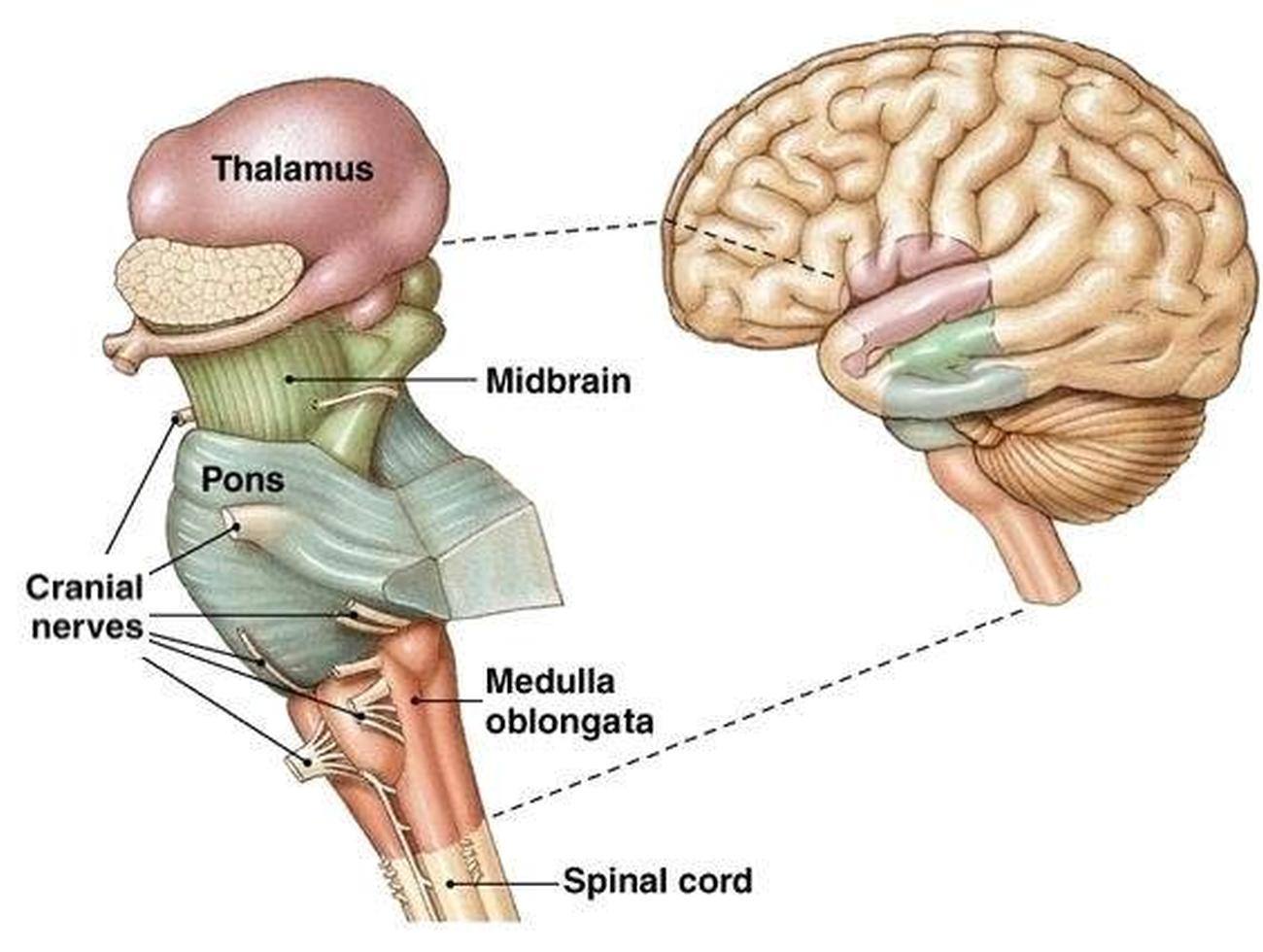
Brain Stem
A chronic brain disorder characterized by compulsive drug seeking and use, despite harmful consequences.
Addiction
Define Prosopagnosia
A neurological condition characterized by the inability to recognize familiar faces, including one's own face, despite intact vision and intellect. It's often referred to as face blindness.
Define Absolute Threshold
The minimum amount of stimulation required for a stimulus to be detected by a sensory system. It represents the point at which a stimulus becomes noticeable to an individual at least 50% of the time.
Define REM Sleep Behavior Disorder
A sleep disorder where individuals physically act out their dreams during REM sleep, potentially causing injury to themselves or others due to loss of muscle paralysis.
DAILY DOUBLE
neurotransmitter involved in transmitting pain signals in the nervous system.
Substance p
It is involved in various functions, including muscle contraction, memory, and learning.
Acetylcholine
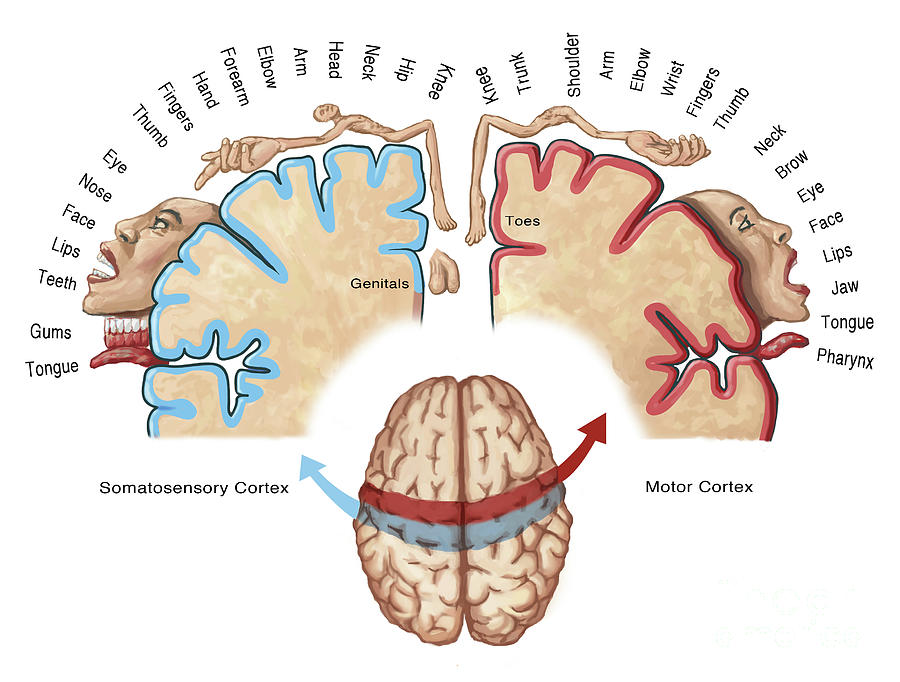
what is this and explain it
The Homunculus - the size of the associated body part is how much brain area is associated with it. your brain would think that your body looks like that, and the bigger the body part = the more sensory information / how sensitive those areas are.
Who sings the song that this category is named after?
Elton John
what is this an example of?
Wernicke's Aphasia
Exhibit fluent speech but have difficulty understanding spoken and written language, as well as producing meaningful and coherent speech.
They may use nonsensical or inappropriate words and sentences, making communication challenging.