Brain Parts
Brain Parts
Neurons
Controlling voluntary movements of the body
What is the Motor Cortex?
Number 48 can be identified as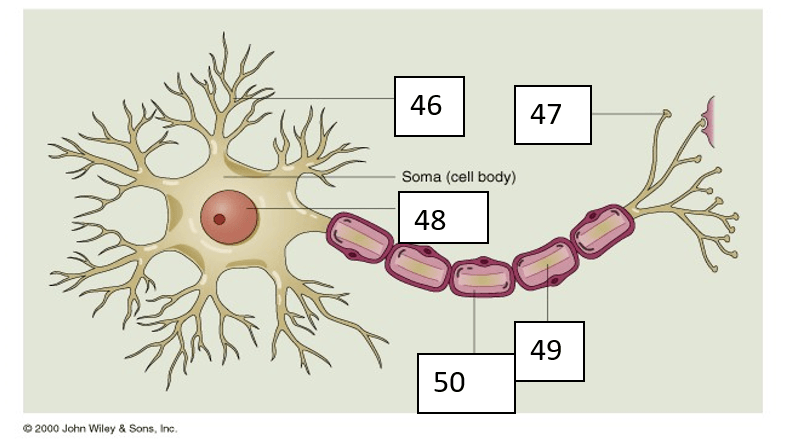
What is the nucleus?
What is the yellow (51) part of the brain?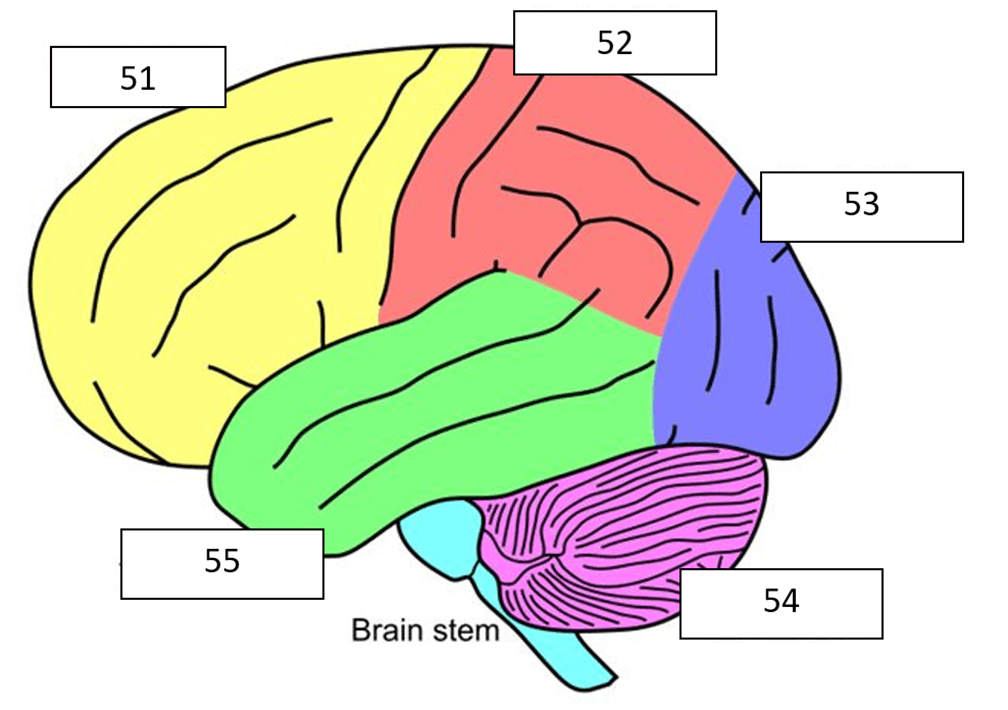
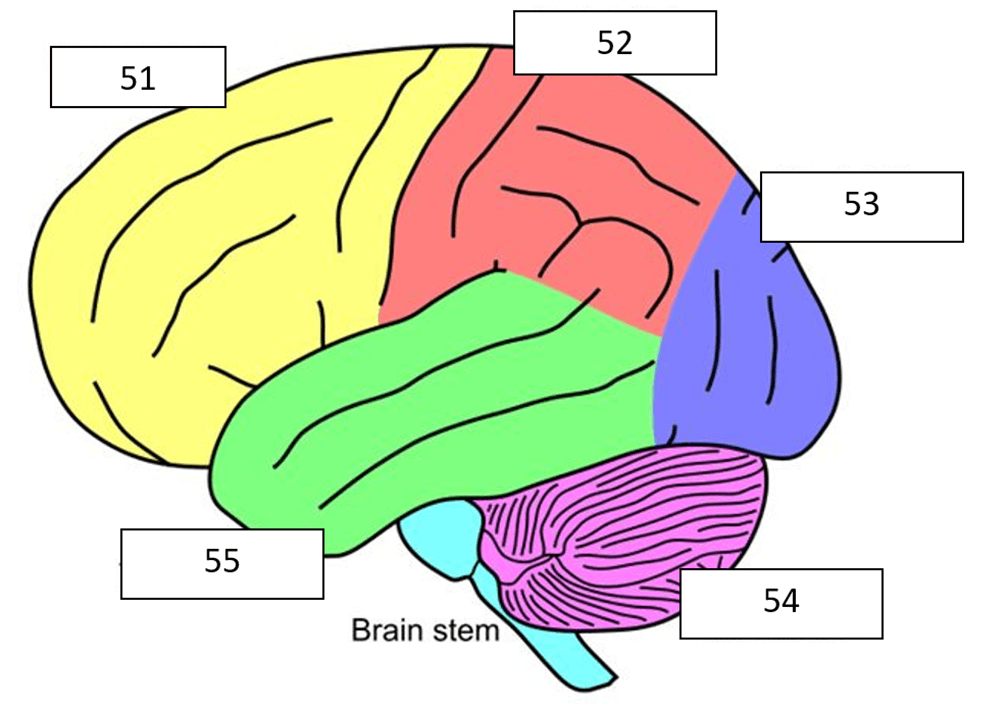
What is frontal lobe?
Information Processing that analyzes raw stimuli through various systems
What is bottom up processing?
_____ is Interpreting sensory information based on the larger context, prior knowledge, and expectations.
What is Top-Down Processing?
This part of the brain regulates someone's sense of fear
What is amygdala?
Number 49 can be identified as
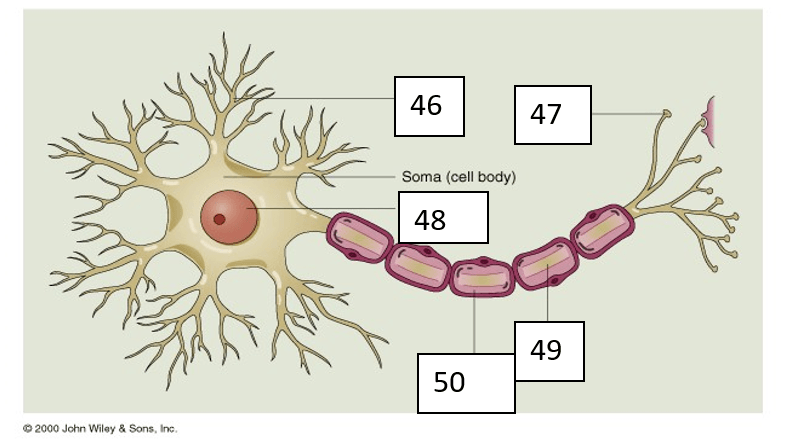
What is Axon?
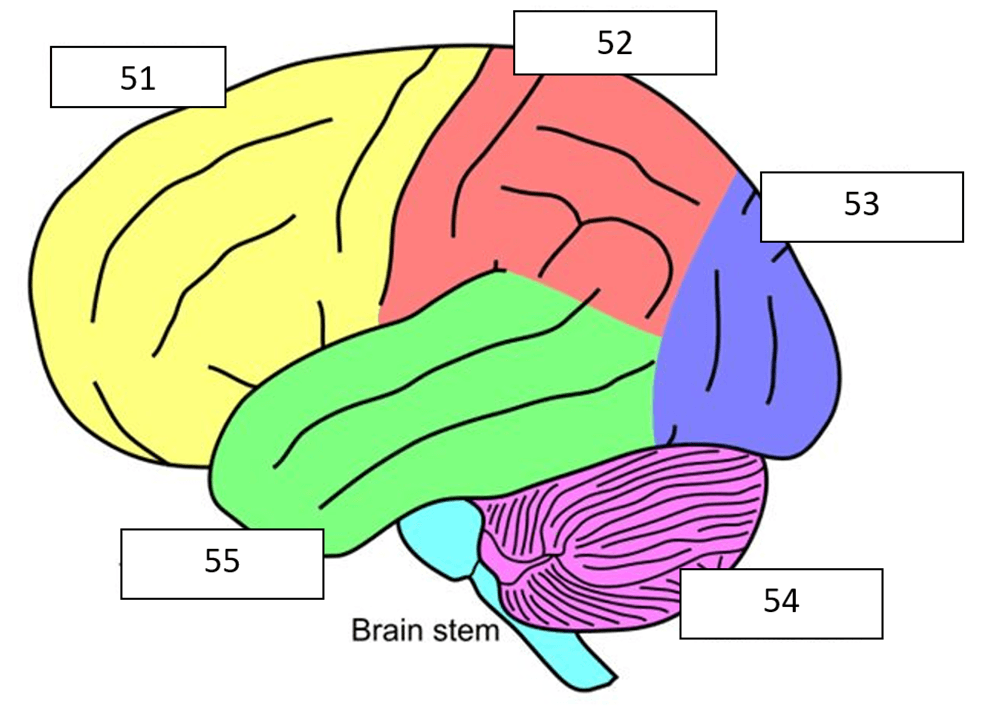
What is the purple (54) part of the brain?
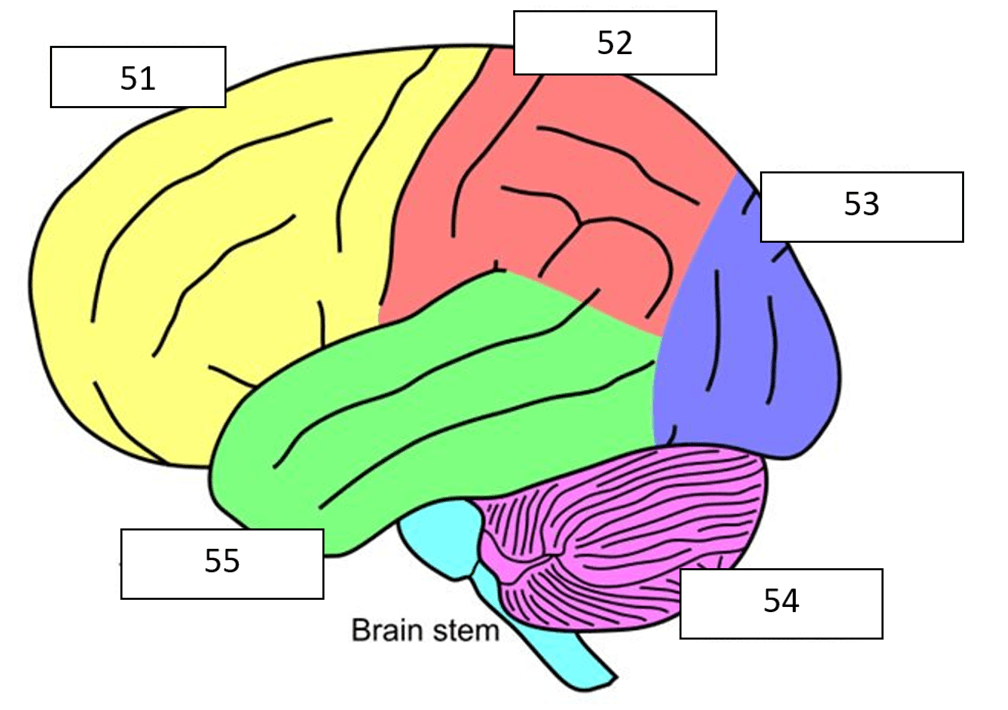
What is cerebellum?
Walking into a person's home for the first time, you notice a peculiar smell, when you mention it to the owner, they don't seem to notice, this is known as
What is sensory adaptation?
when our eyes move inward toward each other to focus on a close object.
What is the convergence?
Brain part that stores long term memories
What is hippocampus?
The term for chemicals that travel from one neuron to another, affecting nearby neurons.
What is neurotransmitters?
What is the green part of the brain?
What is temporal lobe?
The minimum amount of stimulation required for a stimulus to be detected by a sensory system.
What is absolute threshold?
short-term memory used for temporarily holding and manipulating information. Short-term and long-term memories combine.
What is working memory?
Injury to this part of the brain is likely to cause someone to have great difficulty maintaining their balance and coordinating their movements
What is cerebellum?
The central control system of the body
What is the Central Nervous System (CNS)
What is the blue (53) part of the brain?
What is occipital lobe?
This ________ can open to allow pain signals to be transmitted to the brain or close to block them.
What is Gate Control Theory?
the possibility that a third, unmeasured variable may be influencing the relationship between the two variables of interest.
what is third variable problem?
The _____ side of the brain is responsible for recognizing faces and the _____ side of the brain is responsible for language
What is the right side and the left side?
The "Support Cells" of the nervous system
What are Glial Cells?
What is the red (52) part of the brain?
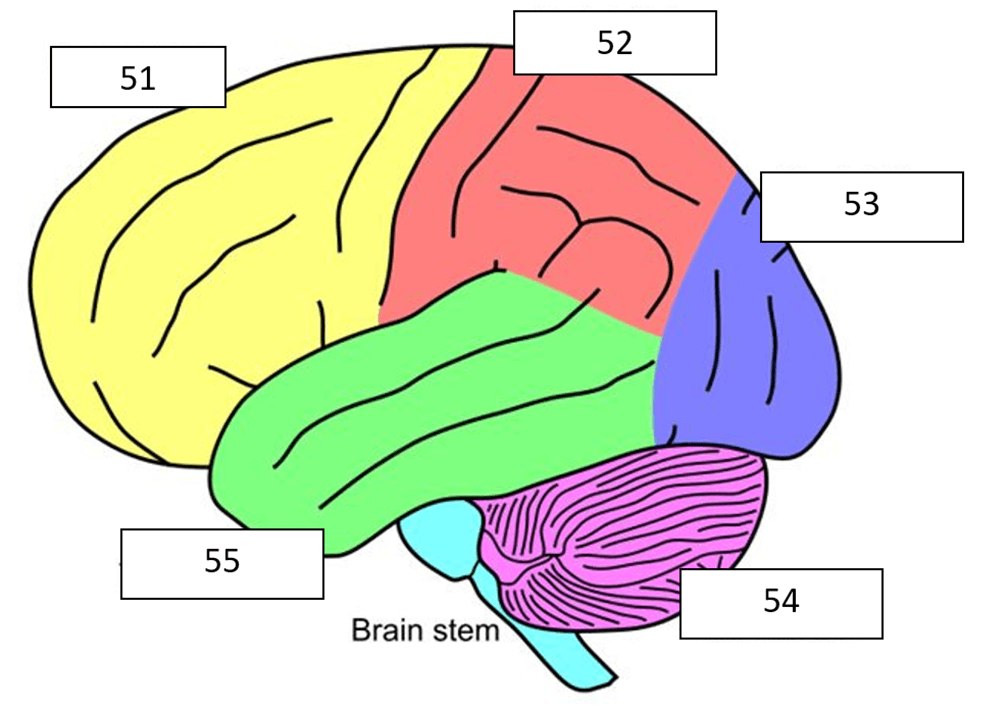
What is parietal lobe?
A theory proposing that color vision is based on three types of cone receptors, each sensitive to different wavelengths of light (red, green, and blue). The brain combines signals from these cones to create the perception of a wide range of colors.
what is Trichromatic Theory?
During this sleep stage, your brain experiences sleep spindles and you can still be awakened without difficulty
What is NREM stage 2?
Number 46 can be identified as
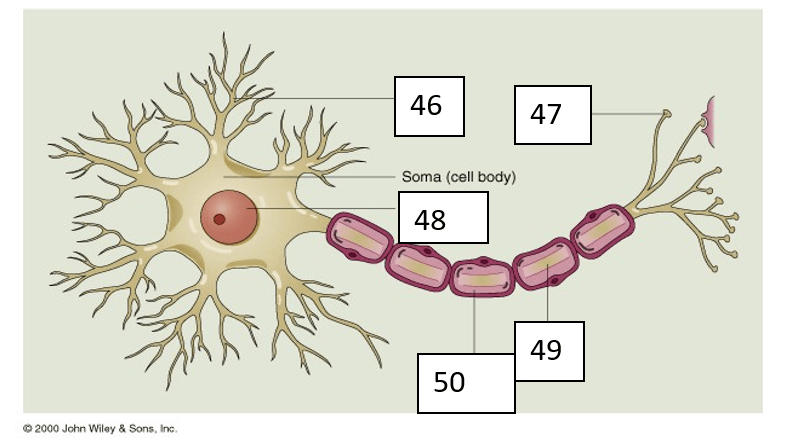
What is dendrite?
Explain how the case study of Phineas Gage impacted what psychologists know about certain regions of the brain
When Gage's frontal lobe was destroyed, psychologists were able to determine it plays a major role in personality and executive functioning
The sense of body movement and position, including the awareness of muscle and joint sensations.
What is Kinesthesis
people tend to look for, interpret, or remember information in a way that confirms what they already believe.
What is your conformation bias?