priority intervention of pt suspected to have meningococcal meningitis 
Initiate droplet precaution
define apnea
temporary cessation of breathing
ATP production
Phosphate
What is a shearing force? When does it occur?
applied force that causes a downward and forward pressure on the tissue beneath the skin. occurs when pt slides down a chair, bedclothes, pulled beneath pt, or slid to head of bead without lifting the body.
gives clues about inflammatory condition
erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
Intervention with rooming a pt with TB
pt needs to be placed in a negative pressure room
LOC, Vital Signs, Respiratory effort, Ability to communicated, vision and hearing ability, condition of skin, prosthetic or assistive devices, other health problems
Ca range
8.4-10.6
Hazards of improper alignment & positioning
1. circulation interference; pressure ulcers
2. Muscle cramps; possible contractures
3. Fluid collection in the lungs
Explain the long-period urinalysis specimen collection

collected over 12-24 hr period, kept on ice & has some form of preservative, used to determine kidney function and glomerulonephritis
Organism that is a normal flora
Escherichia coli in intestines
Shallow for two or three breaths with a period of variable apnea
Biot's respirations
Signs and Symptoms of Dehydration

thirst, weak, dizzy, postural hypotension, decreased urine production, concentrated uine, dry lips/skin/ membranes, thick saliva, poor tissue turgo, flat neck vein, increased pulse, weak/thready pulse, increased temp
Nutritional therapy in HIV pts are aimed at
1. Replacing fluids & electrolytes 2. Wt gain 3. replacing lost muscle mass 4. Maintaining the immune system
A pt undergoing a colonoscopy must withheld
iron medication, aspirin, anti inflammatory drugs for 3 days.
An employee is receiving a Hepatitis B shot. This is what type of immunity
Artificially acquired immunity
Nia comes to the OBGYN clinic for a 12 week check up. Nia's pulse is slightly higher than baseline. The priority of the nurse is to
signs of fluid overload
weight gain, crackles in lungs (wet), slow bounding pulse, increased BP, edema
Before administering TPN the nurse should
check pt drug allergies, ensure solution is clear and free from floating material, gently squeeze the bad or check the container for leaks, check the insertion site for leakage and signs of infection
what is a angiography used for? How is it done?
Located lesions, occluded vessels, tumors, malformed blood vessels; contrast medium injected into an artery and x-rays tken of tthe dye spreading through the vessels; dx problems in arteries anywhere in body:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Angiogram-TestPurposeandProcessFromStarttoEnd-7c9f3b63702f4b40b2c5f1a8d164a53a.jpg)
The 5 methods of sterilization are 
1. Steam/moist heat
2. Dry heat/hot air
3. Ethylene Oxide
4. Low temp gas plasma
5. Radiation
Nurse J's pt is having a fever. What interventions should be done?
Increase patient’s fluid intake, Lower room temperature, Increase the rate of circulating air, Remove excessive clothing or bed covers, Control or reduce the amount of body activity, Provide sponge bath or cooling blanket, Antipyretics (ASA, acetaminophen)
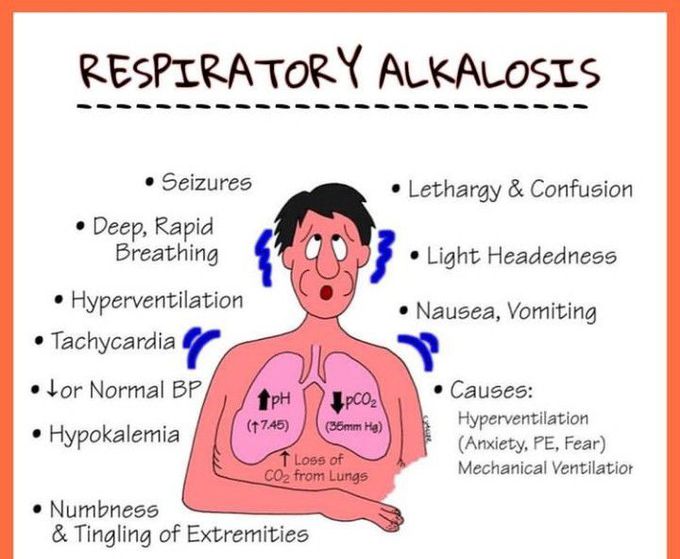
Causes of respiratory alkalosis
anxiety, high fever, hyperventilation, salicylate poisoning, encephalitis
Tina reports noticing her infant has swelling, changes in her skin, slow growth, and a distended abdomen. Tina reports being 10 months post c-section, back working and is no longer breastfeeding. The nurse would suspect
Kwashiorkor 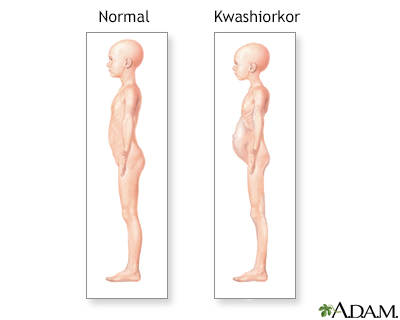
The nurse must ensure that the pt undergoing a fine-needle aspiration cytology study of the liver will
remain still during the procedure