acronym we use to describe data distributions and what each letter tells us to do
Shape
Outliers
Center
Spread
define response and explanatory variables
an explanatory variable explains or predicts changes in the response variable, and the response variable measures the outcome of a study
treatment
What does this formula help you find?
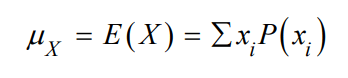
when do you use z-test and when do you use t-tests?
z-test for proportions t-test for means
command to find the z-scores given area
the value with p percent of observations less than te value itself
how do you classify weak, moderate, or strong correlation?
weak is less than .3, moderate is between .3 and .7, strong is more than .7 in either the positive or negative direction.
what are stratified and cluster sampling?
stratified: levels
cluster: groups
when working with random variables, doing this changes measures of but does not change measures of spread
What is adding a contant?
what do we say when we interpret confidence intervals?
we are 95% confident that the true population proportion mean of whatever lies within lower bound and upper bound
command to find the critical value for a t-distribution
inverset
what does the standard deviation measure?
the typical distance of the values in a distribution from the mean
acronym we use to describe linear relationships, and what each letter stands for
DOFS
Direction
outliers
form
strength
difference between random sampling and simple random sampling?
random sampling means every individual has an equal chance. Simple random sampling means every group and individual have an equal chance of being chosen as part of that group.
when working with random variables, doing this changes both measures of center and spread.
what is multiplying by a contant?
what do we say when we interpret confidence levels?
if you have to find a 90% confidence interval for a population mean, what area do you type for the inverse t function?
divide the area in the tails by 2 and add it to the confidence level
What is the 5 number summary and how do you find each value?
Min
Q1
Median
Q3
Max
How do you know if an observation is an outlier or an influential observation?
stratified is same within different between
cluster is different within same between
What are the formulas to check if events A and B are independent?
P(A|B)=P(A) and P(B|A)=P(B)
when do you reject the null hypothesis?
when your p-value is lower than the alpha value
how do you find degrees of freedom for t-distribution?
n-1
Describe how you can tell if a distribution if left skewed, right skewed, or symmetric using these two measures?
mean equals median it is symmetric
mean is higher than median then it is right skewed
mean is lower than median then it is left skewed
the mean follows the tail
how do we interpret slope in context?
when the explanatory variable increases by one unit, the response variable is predicted to increase/decrease by these many units.
difference between a blind and double blind experiment
blind experiment only the individuals do not know
double blind neither the individuals nor the researchers know who gets the treatment or placebo.
In words describe
what is the mean of the sum of 2 or more random variables,
what is the mean of the difference of 2 or more random variables
what is the variance of the sum of 2 or more random variables
what is the variance of the difference of 2 or more random variables
and what is special about the standard deviation of the variance of the sum or difference of 2 or more random variables?
the mean of the sum is the sum of the means
the mean of the difference is the difference of the means
the variance of the sum is the sum of the variances
the variance of the difference is the sum of the variances
the standard deviation is the square root of the sum in both cases of the sum or difference.
what is more dangerous a Type I or a Type II error?
depends on the situation
difference between, population, sample, and sampling distribution.
population is all the individuals
sample is one a sub sample of individuals
sampling is a distribution of the mean (or other statistic) of many samples drawn from the population.