Mrs. Garcia found the National mean score for the AP Stats exam to be a 2.89. She wants to know if the ATHS mean score on the AP Statistics exam is different than the national mean.
What is a 1-Mean T-Test/ 2:T-Test?
Two events that have no outcomes in common.
What are disjoint events?
A local TV news station has a daily poll that they ask their viewers. Every day at 5:00 PM they put up a QR code on the screen and anyone who is watching and would like to respond may do so and answer the question.
What is voluntary response bias?
What does SOCV stand for?
What is center, unusual, shape, variability? Don't forget context
This measure of center is more resistant to outliers than the mean.
What is the median?
What percentage of your score comes from FRQ 6? Describe what to expect on question 6.
The Investigative Task (#6 on the free response) is worth 25% of free response grade.
New stuff! The Investigative Task will start with content that is very familiar to you, but at some point will venture into something you have not seen before. Use your statistical thinking and reasoning skills to make your way through the rest of the question.
The Investigative Task tends to have 4 to 5 parts. Generally the first one or two parts will cover content from the course and the second or third part will start the investigative portion of the question.
The parts are scaffolded. The first few parts should be very accessible (easy) and then get progressively harder. The last part of the Investigative Task often requires you to look back holistically at all of your previous answers and summarize.
Mr. Jackson bought a jumbo bag of skittles and is curious to see if his ratio of green, red, yellow, brown and blue skittles matches the ratio described on the skittles website. He counts out the amount of each color he has and decides to run a ________ Test to see if it matches the historical ratio.
What is a Chi Squared Goodness of Fit Test?
The effects of two variables on the response cannot be distinguished from each other.
What is confounding?
An airline company wants to survey its customers one day, so they randomly select 5 flights that day and survey every passenger on those flights.
What type of sample is this?
What is a cluster random sample?
What does DUFS stand for? Where is it used?
What is form, unusual, direction, strength? discussing 2 variable data
Stem plots, histograms, box plots, bar graphs, dot plots and scatter plots can be used to display this kind of data.
What is quantitative data?
How to ensure to maximumize your points.
Don’t leave any blank. Even if you aren't sure how to solve a question, write down what you do know or think might be part of the solution.
Make up an answer. Suppose you know that the answer from part (a) is needed to answer part (b), but you have no clue how to answer part (a). Make up an answer! Then use that answer to work through part (b). AP Exam graders are trained to grade each part based on student work from the previous part.
Always use context. Context shows up on AP Exam rubrics over and over and over again. You might even be able to get some partial credit for using context even if some of your other calculations are totally incorrect.
40 Multiple choice questions. Answer all questions: # correct *1.25 points
A hospital reported 5 c-section births out of 89 patients under the age of 38. The same hospital reported 9 c-section births out of 56 patients over the age of 38. What test should be used to see if there is a difference between the 2 groups?
What is a 2 proportion Z Test/ 6:2-PropZTest?
P(A)=P(A|B) and P(B)=P(B|A)
What are independent events?
A television reporter wants to determine if Maryland residents would be interested in renovating Camden Yards, Baltimore's baseball field. The reporter asks baseball game attendees at Camden Yards if they support the idea.
What is convenience sampling?
You have a normal distribution; this many standard deviations is what 95% of the values lie within.
What are two standard deviations?
This rule helps to determine if data is normally distributed by checking the number of observations within 1, 2, and 3 standard deviations away from the mean.
What is the Empirical Rule (68-95-99.7 Rule)?
Types of Bias. What is bias
Nonresponse – selected people do not respond Undercoverage – systematically excluding people from being able to be selected
Response bias – providing inaccurate responses (on purpose or by accident)
Wording Issues – confusing wording or question is slanted towards a particular response
Bias is the systematic tendency to overestimate or underestimate the true population parameter.
ATHS track Coach Hawkins wants to see if her training is leading to improvement in her sprinter. She has them all run a 100m at the beginning of the year and records their times. Then, after a full season of training, she has them run the 100m again in the same conditions (same track, same weather, etc.). She then records their new times. She runs a test to see if there is a statistically significant difference between their times at the beginning of the season, pre-training, and at the end of the season.
What is a Matched Pairs T-Test/ 2:T-Test? (must say matched pairs to get credit)
What is the difference between geometric and binomial distributions? What must you do on both?
*Define your variable* include name, p (geometric) n (binomial)
GEOMETRIC RANDOM VARIABLE 1. Binary: two outcomes for each trial (success or failure) 2. Independent: Each trial is independent of the next 3. Trials UNTIL a success (not fixed number) 4. Same probability of success for each trial (p) Remember: Keep going until a success
BINOMIAL RANDOM VARIABLE 1. Binary: two outcomes for each trial (success or failure) 2. Independent: Each trial is independent of the next 3. Number of trials is a fixed number (n) 4. Same probability of success for each trial (p) Remember: Fixed number of trials.
What is a randomized Block Design?
For a randomized block design, treatments are assigned completely at random within each block. For each block, individuals are similar to each other with respect to at least one blocking variable. The purpose of blocking is: • to reduce the variability of results within each treatment group • to eliminate the possibility of the blocking variable as a confounding variable.
This is the expected value equation.
What is E(X) = ∑(x)*P(x)?
How can you find whether or not a data point is an outlier mathematically?
What is
> Q3 + 1.5(IQR)
< Q1 - 1.5(IQR)
What is Coefficient of Determination, how find r, sentence frame?
r2: About r2% of the variation in y-context can be explained by the linear relationship with x-context.
Example: About 87.3% of variation in electricity production is explained by the linear relationship with wind speed.
take r2 and square root, on a table it is the r-sqr value
Mr. Paulson has noticed that a couple of his students are taking AP Calculus BC at the same time as they are taking AP Statistics. He wonders if there is a correlation between taking BC Calculus at the same time and good performance on the AP Statistics tests. He separates students into 3 groups: Students taking AB Cal and Statistics, students taking BC Calc and statistics, and students only taking Statistics. Then he looks at how many students in each group have a grade of A or B, C or D, and finally E and below. Based on the results of his test, he will be able to determine whether the proportion of students who perform well in the class differs between which/how many math courses they are taking.
What is Chi Squared Test for Independence?
An airport screens bags for forbidden items, and an alarm is supposed to be triggered when a forbidden item is detected. Suppose 5% of bags contain forbidden items. If a bag contains a forbidden item, there is a 98% chance that it triggers the alarm. If a bag does not contain a forbidden item, there is an 8% chance that it triggers the alarm.
Given a randomly chosen bag triggers the alarm, what is the probability that it contains a forbidden item?
What is 0.392?
A truck manufacturer selects 3 trucks at random from each of 6 models for safety testing. What type of sample is this?
What is a stratified random sample?
What are the conditions and formula for a 2 sample z test for p1 - p2?
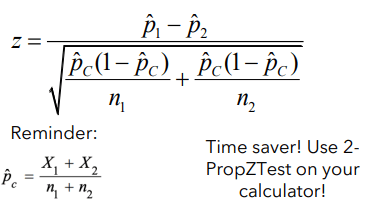
-Random indpendent 2 samples
- 10% on both (unless it is an experiment)
-Large counts for both **must use pc combined
Write the conclusion for a 95% confidence interval (-4.25,-1.33) for the average drop in MP3 grades.
What is "We are 95% confident that the true drop of MP3 grades is between -4.25 and -1.33"?
What are some major things to include on FRQ's?
1. Context
2. Work
3. If normal curve - picture, direction, work, answer
4. On z, u tests - work or calculator speak
5. chi-square - expected counts values/matrix
6. Tests - df (chi square means), p-value, t or z value