Physiology
Physiology
Anatomy
Physiology
Anatomy
What is the function of red bone marrow?
Produce blood cells and platelets
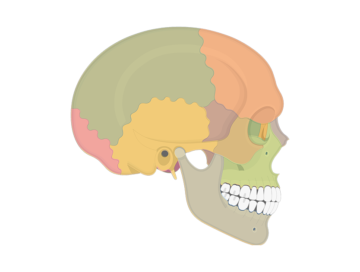 List 4 bones are pictured here?
List 4 bones are pictured here?
Parietal, frontal, temporal, zygomatic, mandible
What is the difference between asynarthrosis and diarthrosis joint?
A synarthrosis is an immobile or nearly immobile joint. A diarthrosis is a freely moveable joint.
What is a motor unit?
One motor neuron + multiple muscle fibers.
Name the three hamstring muscles.
Semitendinosus, semimembranosus, biceps femoris
How does the skeleton assist in producing movement?
Muscles attach to bones. Bones are what muscles move to produce body movement. Bones are light enough that muscles can move them.
 What bone is pictured here?
What bone is pictured here?
tibia
This type of joint allows you to use your thumb to grab things with your hand in a way that you can’t with your foot.
What is saddle joint?
Explain how muscles help regulate body temperature.
When body heat falls below optimal levels, the skeletal muscles increase their activity to make heat. Increased muscle contractions means increased cellular respiration which is an exothermic, or heat producing, reaction.
Name the four rotator cuff muscles
Supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis, teres minor
Describe longitudinal growth.
Cartilage within the epiphyseal plates begins to replicate. The side of the epiphyseal plate closest to the diaphysis begins to solidify and bone is created, allowing bone to lengthen.
What are 4 of the 6 main functions of the skeletal system?
Support/framework, protect organs, aid movement, storage of minerals, blood cell formation, hormone production
What is the difference between a pivot and hinge joints? Give an example of each.
Hinge joint permits motion in one direction, that is, backward and forward. ex: the ankle and knee joints.
Pivot joint allows rotation of a bone over the other. ex: between the radius and ulna, or atlas and axis in the neck.
What is a muscle insertion?
The distal attachment, attached to more moveable end
The _________________ muscle acts to shrug the shoulders.
upper trapezius
What is ossification?
The process of bone formation. By way of osteoblasts and osteoclasts
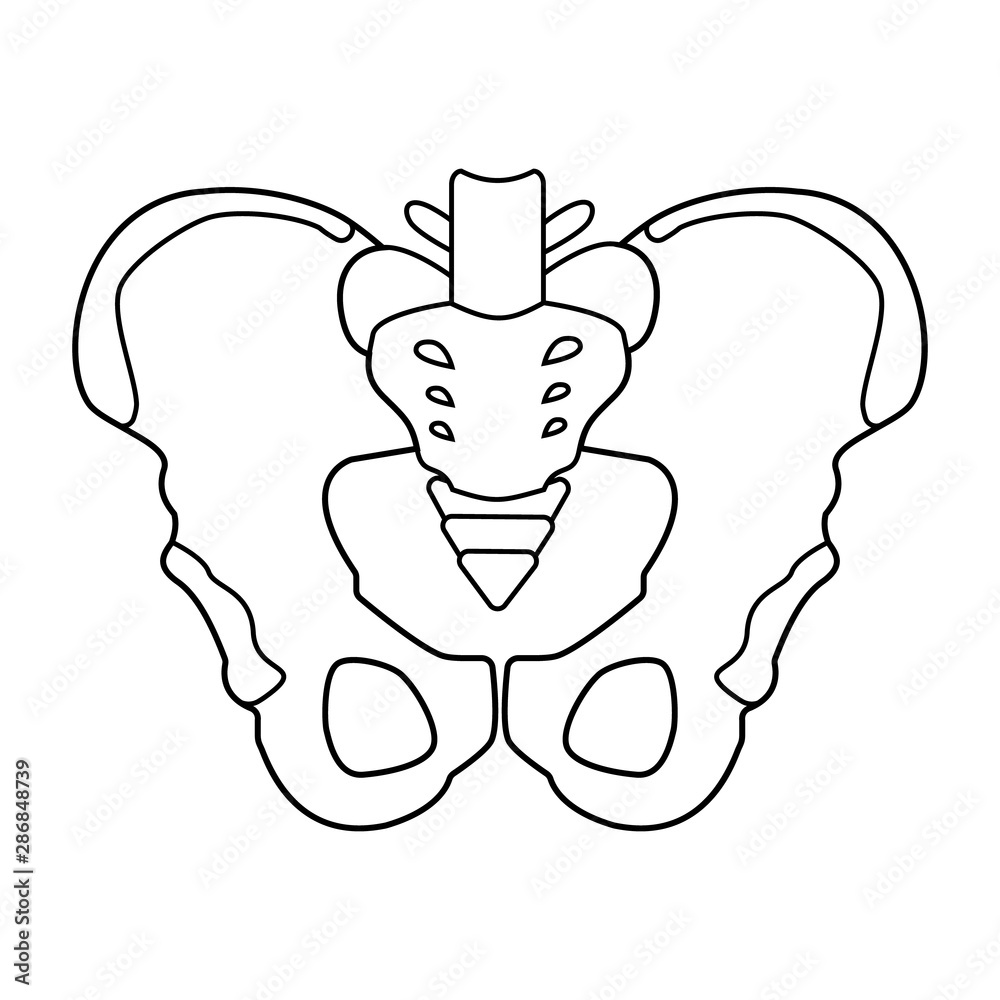 Identify the bones in this picture.
Identify the bones in this picture.
Sacrum, coccyx, ilium, ishium, pubis
What is a fibrous joint? Give an example.
Fibrous joints connect adjacent bones by fibrous connective tissue especially collagen fibers. Ex: The sutures are present between the bones of the skull or teeth connected to the maxilla or mandible.
What is acetylcholine and why is it important for muscle contraction?
Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter. i.e. released by neurons. It is used at the neuromuscular junctions, triggering the firing of motor neurons and affecting voluntary movements.
What muscles are pictured here? 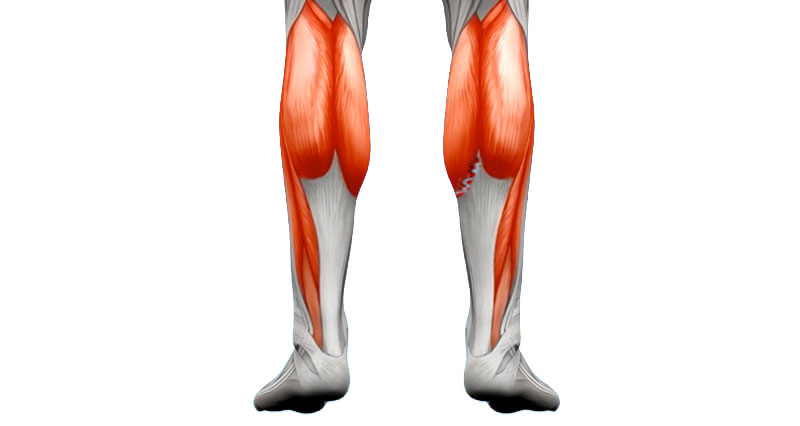
gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris
What is the name for a bone cell?
osteocyte
What are the sections of the vertebral column? How many vertebrae per section?
Cervical - 7
Thoracic - 12
Lumbar - 5
Sacrum - 5 (fused)
Coccyx - 4 (fused)
What are the major differences between synovial and cartilaginous joints?
Cartilaginous joints contain cartilage and allow very little movement. Synovial joints are the only joints that have a space (a synovial cavity filled with fluid) between the adjoining bones.
Describe the sliding filament model of muscle contraction. Use the words: sacromere, myosin heads, actin filaments, H zone
Muscles contract because sarcomeres contract. Sarcomeres contract when the heads of myosin filaments grab the thinner actin filaments and pull them to slide past each other. This causes the filaments to overlap more (disappearing H zone) and the sarcomere to shorten
 What muscle is pictured here?
What muscle is pictured here?
Sartorius