What are the 3 major components/structures of a long bone?
Epiphysis, metaphysis, and diaphysis!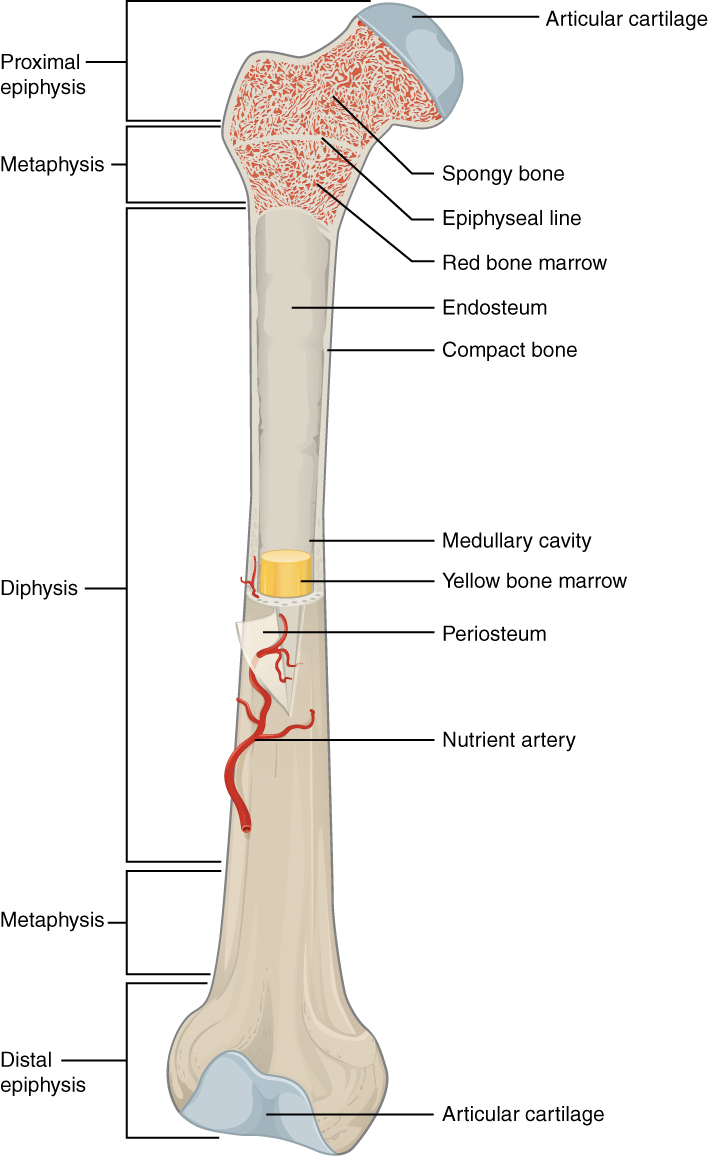
What is the functional unit of a muscle fiber?
Sarcomere!

The CNS and PNS consist of?
CNS: brain and spinal cord
PNS: everything except brain and spinal cord
What area of the brain is responsible for motor and speech?
Broca’s area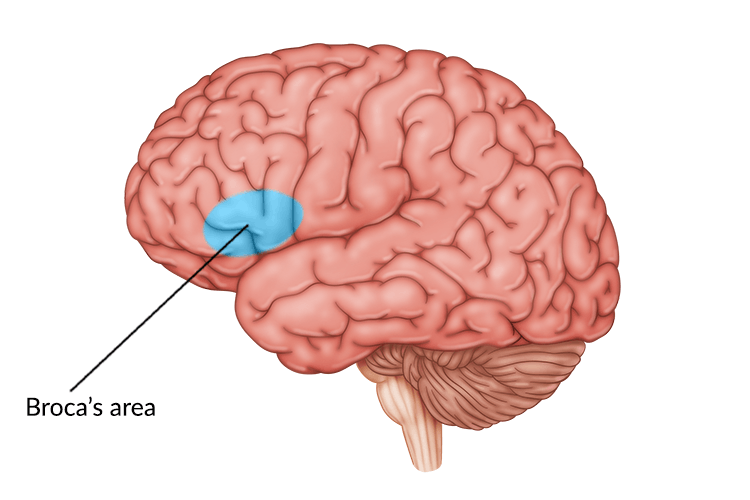
What is the main purpose of negative feedback?
Maintain homeostasis!!
What are the 5 main functions of the skeletal system?
Support, movement, protection, production of RBC, and storage of minerals!
The dense layer of connective tissue that surrounds an ENTIRE skeletal muscle is the ________!
Epimysium!
E-P-E --> Epi-Peri-Endo
entire muscle-fascicles-muscle fibers!

What is the junction between neurons or between a neuron and an effector called?
Synapse!
The brain stem consists of these 3 parts, which are _______!
Midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata!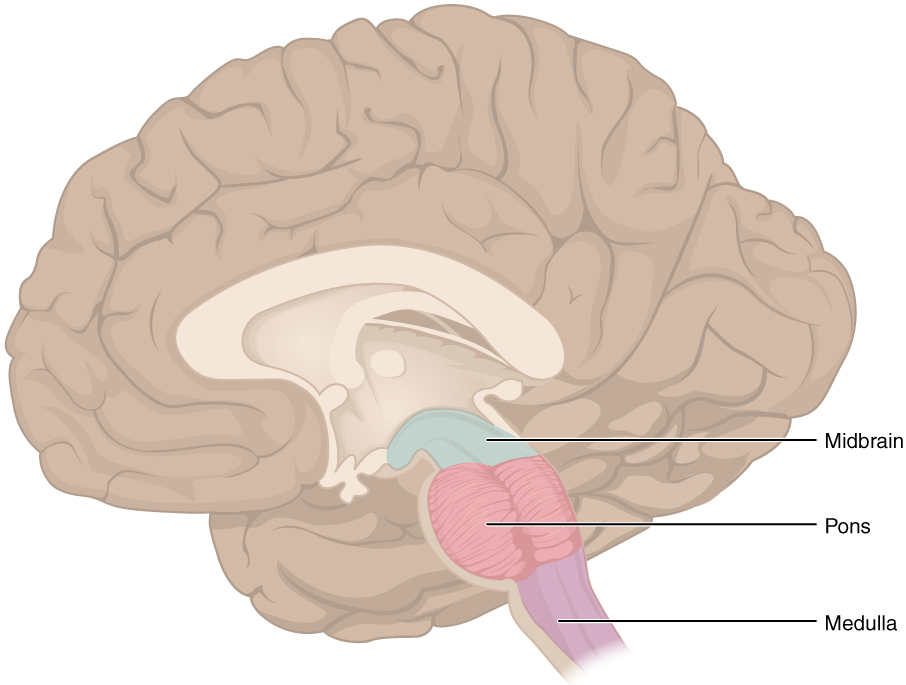
What is atrophy and hypertrophy?
Atrophy: decrease in muscle size
Hypertrophy: increase in muscle size

What are the 4 major cell types of bone tissue?
Osteoprogenitor cells, osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts!

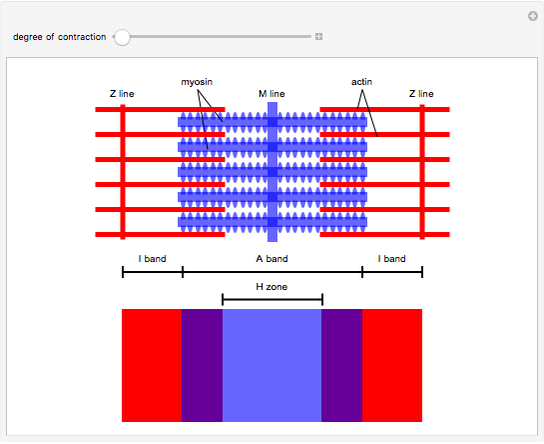
The specific protein that is found in the I band is _____ and the specific protein that is found in the A band is _______!
The specific protein that is found in the I band is ACTIN and the specific protein that is found in the A band is MYOSIN!
I band = ActIn, lIght, thIn
A band = Myosin, dArk, thick
Which two types of neuroglia cells (glial cells) form myelin sheaths? (CNS and PNS)
Oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells.
CNS: Oligodendrocytes form the myelin sheath.
PNS: Schwann cells form the myelin sheath.
This part of the brain controls balance and equilibrium
Cerebellum!
What are the 3 types of Muscular Tissue? & state 1 feature for each! (location, voluntary/involuntary, or fibers/appearance)
Cardiac, Skeletal, and Smooth!

What are the two types of bone ossification?
Intramembranous and endochondral!
Intramembranous: Occurs in flat bones (eg. Skull) when a connective tissue membrane is replaced by bone
Endochondral: Ossification that replaces cartilage with bone in the developing embryo and fetus (occurs in womb); happens in epiphyseal plates of long bones as they grow in length (during child development)
What blocks the binding site of actin?
Tropomyosin!
Tropomyosin is the rope like structure that is controlled by troponin!
What 3 factors affect propagation speed? (action potential traveling across the neuron)
Axon diameter: Larger diameter axons propagate APs faster
Amount of myelination: Myelin increases speed of AP propagation
Temperature: Higher temperature increases speed of AP propagation
The medulla oblongata is responsible for regulating ?
Heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, and digestion!
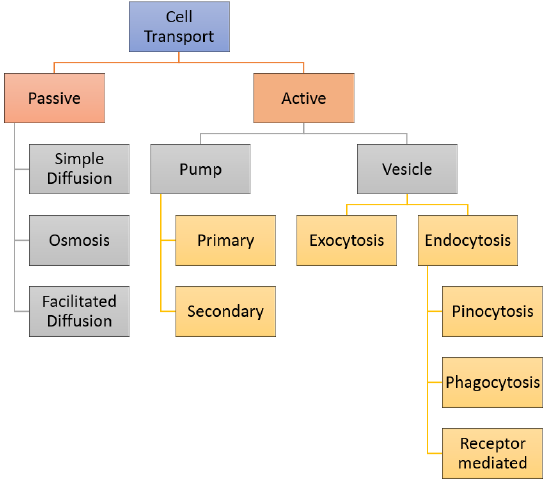
Process that requires cellular energy to move a substance AGAINST its concentration gradient is called _______
Active transport! Moving against needs ENERGY (ATP REQUIRED)
What 3 hormones play a role in calcium homeostasis of the body?
PTH, calcitonin, and calcitriol!

Synaptic cleft or NMJ (neuromuscular junction)
This subdivision of the PNS regulates the activity of the heart and smooth muscle, and of glands; it is also called the involuntary nervous system:
Autonomic nervous system!
________ is a liquid fluid that protects the brain and spinal cord against chemical and physical injuries!
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)! 
What two systems work together to maintain homeostasis in the body?
Nervous and endocrine systems!
