This type of diversity explains that ecosystems that have a larger number of species are more likely to recover from disruptions.
What is species diversity?
Something that is produced by an ecosystem and can be used by humans.
What is a provisioning service?
Islands that are large and this tend to have the most migration from the mainland.
What is close?
The peak conditions that a species can exist in.
What are the optimum conditions?
The term for human-caused disturbances.
What are anthropogenic?
The community that is more diverse.
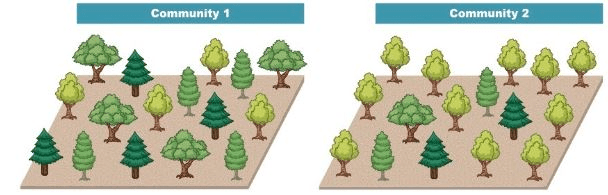
What is community 1?
Services of particular personal value to humans
What are culutural services?
Islands that are this and far from the mainland tend to have the least biodiversity.
What is far?
This is an intolerent zone.
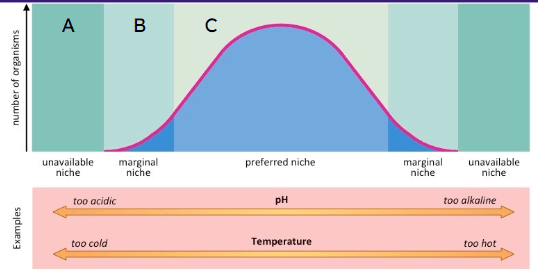
What is Zone A?
The number of different species in a specific area, such as a landscape, ecological community, or region
What is species richness?
Ecotourism
What is a cultural service?
This graph represents this island biogeography concept.
What is the island equilibrium model?
This zone is known for physiological stress.
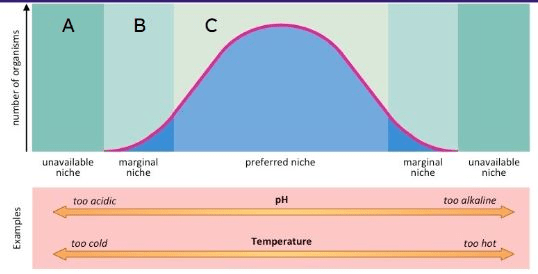
What is Zone B?
Disturbances that occur at repeated intervals
What are periodic?
This type of diversity allows a particular species to have a good chance of surviving a natural disruption IF the diversity is high.
What is genetic diversity?
Trees provide shade/lower local temperatures.
What is a regulating service?
Organisms that exist only on a specific island.
What are endemic species.
An organism that can signal changes in its environment, and can be used to help assess the health of an ecosystem
What is an indicator species?
Disturbances occurring occasionally and at irregular intervals
What are episodic?
Renewable commodities.
What are provisioning services?
Conditions such as temperature, pH, salinity, etc. that determine an organisms tolerance range.
What are abiotic factors?
This is the largest cause of tree-cover loss in Africa.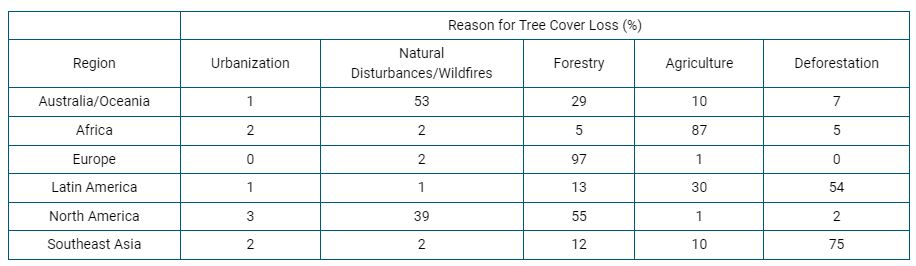
What is agriculture?
This is a dramatic reduction in the size of a population, often caused by a catastrophic event like a natural disaster, disease outbreak, or human activity, which leads to a significant decrease in genetic diversity within that population as only a small number of individuals survive to reproduce, passing on a limited gene pool to future generations.
What is a population bottleneck?
Habitats
Photosynthesis
Nutrient cycling
Soil formation
Water cycle
Genetic diversity
What are supporting services?
The concept that explains why Darwin's finches all evolved different beak sizes/shapes to fulfill different niches on the Galapagos Islands.
What is adaptive radiation?
The collection of all genes, including different variations (alleles), present within a specific breeding population of a species at a given time; if this is low, a species is vulnerable to collapse.
What is a gene pool?
Mangroves mitigate storm damages along coastlines.
What are regulating services?
A measure of how quickly the ecosystem can “bounce back” from the disturbance.
What is resilience?