The number of individuals in a given area is a population's
Density
What causes a population to increase?
Births and Immigration
If the population of rabbits in an ecosystem grows at a rate of approximately 4% per year, the number of years required for the rabbit population to double is...?
70/4 = 17.5 years
The greatest rate of population growth takes place in this phase.
Transitional
(death rates lower but birth rates still high)
What claim can we make about trends in population size over time that would be supported by the data?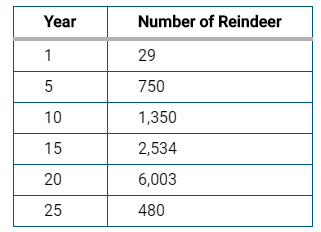
The Population exceeded the carrying capacity
Occurs when there are many Organisms in an area
High Population Density
What causes a population to decrease?
Deaths and Emigration
If a country has a crude birth rate of 24 per 1,000 and a crude death rate of 8 per 1,000, the natural annual percent increase of its population is:
1.6%
Explain why a country may have a declining death rate in stage 2. (why is there a longer life expectancy)
improvements in public health, sanitation, and access to food
A population was 1,000,000 and now is 600,000. What is the percent decrease?
40%
What distribution patter is shown?

Uniform
What shape represents an exponential growth curve?
J-shaped
Compare the population growth rate of India and that of China.
India has a higher population growth rate than China and Australia

The rate of population growth starts to slow down at which phase?
The beginning of Phase III
what type of growth curve is shown?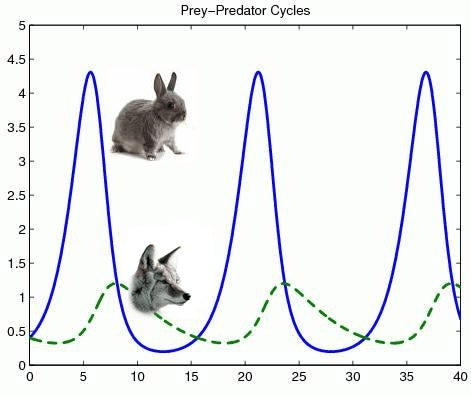
Cyclic
What distribution pattern is shown?
Random
The maximum population size that a given environment can sustain
Carrying Capacity
How does replacement level fertility differ among developed and developing countries?
Hint* The TFR required to offset the average number of deaths in a population so that current population size remains stable.
It is lower in developed countries and higher in developing countries.

What is the most likely cause of high death rates in phase I?
Infant and childhood mortality
what type of growth curve is shown?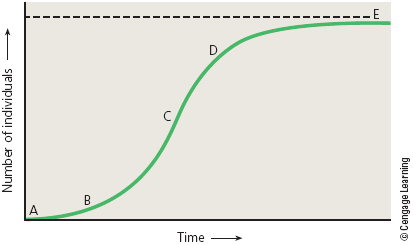
Logistic
What distribution pattern is shown?

Clumped
Name two things that separate r-selected and k-selected species
level of parental care
life span
# of offspring
reproductive maturity age
population regulation
size of offspring
What is doubling time and why can’t we predict it with certainty? What is the rule of 70?
Doubling time is the number of years it takes for a population to double.
We can never determine a country’s doubling time with certainty because growth rates may change in future years. We can calculate it if we know the growth rate of a population and assume the growth rate is constant.
The rule of 70 can be used to approximate doubling time. Doubling time (years) = 70/growth rate (expressed in %).

Zero population growth is associated with which phases?
Phases I and IV
Label the following as density dependent (DD) or density independent (DI) factors
1. A tornado
2. amount of food available
3. availability of water
4. climate change
5. predation
DI
DD
DD
DI
DD