A group of people who share a common culture, history, and homeland
Examples: Japanese, Russians, Irish, Koreans, etc.
Nation
_____________boundaries are drawn using straight lines. (latitude or longitude lines)
Examples: Border between U.S. and Canada - 49 parallel
Geometric Boundary
Organization of three or more states to promote shared objectives AND provide an example
supranational organizations (UN, EU, NATO, ASEAN, OPEC, etc.)
A strong feeling of pride in and devotion to one's country
Nationalism
A supranational organization that was created to promote world peace and prevent another world war. (Hint–replaced the League of Nations after WW2)
United Nations (UN)
What is the name of this empire that balkanized into 15 independent states in 1991? 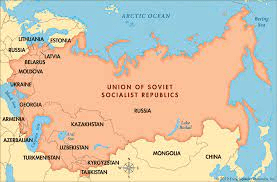
Process of redrawing legislative boundaries for the purpose of benefiting the party in power.
gerrymandering
A territory with defined boundaries, population, government, sovereignty, and recognition.
State
A ___________ boundary is one that no longer functions but can still be detected on the cultural landscape
Example: Berlin Wall
Relic Boundary
In the 1990s and into the 2000s, Yugoslavia went through a process where the state fragmented into multiple nation-states due to conflicts among its ethnicities. This process is known as...
Balkanization
Ability of a state to govern its territory free from control of its internal affairs by other states.
Sovereignty
Formed in 1993 to reduce trade barriers and increase cooperation and unity between members
• Monetary Union allowing for free flow of people and goods
– Single currency
– Very few restrictions on movement of people
EU (European Union)
The Berlin Conference reshaped the contemporary borders of...
Name one country that had its borders changed
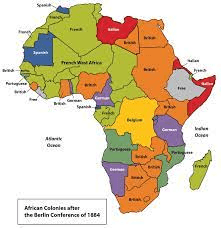
Africa
Provide a pro and a con of supranational organizations
Pros–Promote peace and cooperation, environmental sustainability, economies of scale, collective defense
Cons– Challenges state sovereignty, membership costs, the free-rider problem
A homogenous country (i.e. a country of mostly one ethnic group)
Example: Japan, Iceland (no true examples)
Nation-State
_____________ boundaries existed before people settled there. These are often based on landforms, such as mountains.
Example: Andes Mountains, Rio Grande River
Antecedent Boundary
Forces that tend to unify people and enhance support for a state. Provide an example
Centripetal Force (Common language, religion, ethnicity, even development, etc.)
government systems that divide the powers between the national government and state or provincial governments
Federal System
Military alliance created in 1949 to provide mutual protection to members
– Originally meant to counter the threat of the Soviet Union and Warsaw Pact
(NATO) North Atlantic Treaty Organization
The Treaty of Versailles reshaped the border of...
Name ONE empire's borders that were changed as a result.
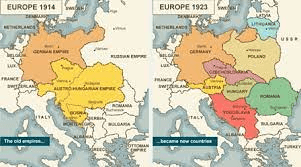
Europe and the Middle East
Exclusive economic zone extends ________ miles from land; a conflict between many Southeast Asian countries over the exclusive economic zone is currently happening in the ___________________ Sea
200; South China
A group of people with a history of self-determination, but doesn't have a recognized state.
ALSO
Name 2 examples
Stateless Nation
Kurds & Palestine
_________________boundaries are drawn on an area by a conquering or colonizing power that ignores existing cultural patterns.
Example: Berlin Conference created these boundaries
Superimposed Boundaries
Forces that divide people and countries. Provide an example
Centrifugal Forces
A policy in which a strong nation seeks to dominate other countries politically, socially, and economically.
Imperialism
Coordination of oil production to ensure the stability of the market
– Promotes economic and regular supply of oil to customers
– Ensures a steady income to producers
– Promotes fair return on investments
OPEC (Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries)
The image below refers to the historical era in which many countries in Asia, Africa, and the Caribbean gained independence from their European colonial rulers. This process took place primarily between the end of World War II in 1945 and the 1970s, although some countries gained independence earlier or later than this time frame.
What process is being described in this picture?

Decolonization
The process where a majority ethnic group wants to claim territory from a neighboring state due to a shared culture with the people residing across the border. (I.e. Reunification of multistate nations.)
Ex: Russians in Ukraine
Irredentism
A heterogenous
Example: USA, Russia, China (technically every country in the world)
Multinational State
______________ boundaries are established after the settlement in an area. It changes as the cultural landscape changes and is drawn to accommodate developments due to a certain event, such as a war.
Example: Former Yugoslavia
Subsequent Boundaries
A region of a state that operates under different rules than the rest of the state.
Ex: tribal lands
Autonomous/Semi-autonomous region
States must concede (share) some power to autonomous regions or subnational political units to avoid conflict
Devolution
Helping to promote stability and development in Africa – Encourages democratic governance – Increased cooperation and communication • Building of Infrastructure – Increase living standard of all
African Union
A driving force behind decolonization and the formation of new states. It has also been a source of conflict, as groups seek to break away from existing states and form their own nations (e.g. Catalonia, Scotland, and Tibet). These groups are seeking...
Self-determination (i.e. independence, autonomy)
Provide at least 2 examples of challenges to state sovereignty
Examples–Devolution, Advances in communication technology, Supranationalism, Democratization
When a cultural group lives in a few different countries
Example: Koreans in North and South Korea
Multistate Nation
_____________ boundaries are drawn in order to separate groups based on ethnic, linguistic, religious, or economic differences.
Example: India separated because of different religious group in the country (Hindu and Muslim)
Consequent Boundaries
A state in which most political power exists at the national level (highly centralized), with limited local authority
Unitary System
the drawing of new electoral district boundary lines in response to population changes and how often does this take place
redistricting & 10 years
Promotes trade cooperation between Canada, Mexico, and the United States
– Removal of some tariffs
– Has increased trade among the three
(USMCA) United States Mexico Canada Agreement/ used to be (NAFTA) North America Free Trade Association
This force has been both a unifying and divisive force in world history. It has led to the formation of nation-states and the creation of shared identities. However, it has also been a source of conflict, as groups with different national identities compete for power and resources. It can take different forms (i.e. ethnic, civic, patriotism)
Nationalism
Name 4 of the 6 factors that lead to the devolution of states
Factors that can lead to the devolution of states include the division of groups by physical geography, ethnic separatism, ethnic cleansing, terrorism, economic and social problems,
and irredentism.