It's a point against which motion is measured.
What is a reference point?
This is the rate at which an object is moving at a given moment in time.
What is instantaneous speed?
What is extrapolation?
It's the change in velocity over time.
What is acceleration?
This represents the object's magnitude of acceleration.
What is the slope of a line on a speed-time graph.
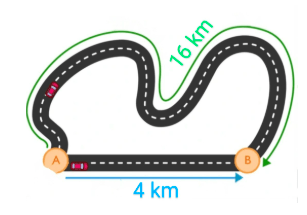 The green path represents _____ and blue path represent ______.
The green path represents _____ and blue path represent ______.
What are distance and displacement.
Green path: distance; Blue path: displacement
This tells you how quickly and in what direction the object is moving in relation to a reference point.
What is velocity?
It's the steepness of a graph line and it represents speed on a distance-time graph. The steeper line indicates a greater speed.
What is slope?
Explain why the term deceleration is NOT acceptable in physics.
This shows the acceleration on a speed-time graph.
What is the slope of a line?
 Describe at least two frames of references for the photo.
Describe at least two frames of references for the photo.
What are:
The riders aren't moving relative to each other
AND
The people riding are moving relative to someone watching from the ground.
What is ANSWER THE QUESTION?
A flat, horizontal line indicates this speed.
Give the equation for acceleration in words.
What is acceleration of an object equals final velocity minus initial velocity divided by the time it takes for the object to accelerate.
a=Vf -Vi /t
This looks like a CURVE rather than a straight line on a distance-time graph.
What is acceleration?
This is the difference between vector and scalar quantity.
What is direction?
Give the mathematical equation for speed in words.
What is speed equals distance divided by the time to travel that distance? (v=d/t)
Complete the following problem on the board:
Find the speed of a car if it traveled 340 miles in 20 seconds.
Show all steps.
What is:
1. d=340 m; 20s; v=? in m/s
2. v=d/t
3. v=340m/20s
4. v=340m/20s = 17 m/s
5. The speed of a car was 17 miles per second.
What are:
1. if the object speeds up
2. if the object slows down
3. if the object changes direction
A biker that slows to a stop is an example of this kind of acceleration.
What is negative acceleration?
The 5K class took 45 minutes to run a 5 kilometer loop around the church ending where they began. This was their total displacement.
What is zero?
Complete the following question on the board, showing all FIVE steps in your answer:
What is the average speed of an object that travels 800 miles in 4 hours? Put your answer in units of miles per hour.
What is:
Step 1: d=800 mi; t=4 hours; v= ? in mi/h
Step 2: v=d/t
Step 3: v=800 mi/4h
Step 4: 800mi/4h =200 mi/h
Step 5: The average speed of an object that travels 800 miles in 4 hours is 200 mi/h.
 Draw and label the following diagram on the board to show the formulas for how to calculate time, distance and speed. Write out the formula for each.
Draw and label the following diagram on the board to show the formulas for how to calculate time, distance and speed. Write out the formula for each.
What is: 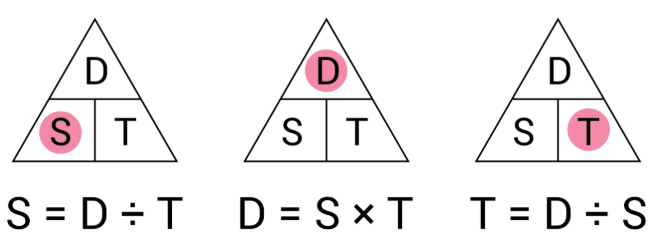
Complete the mnemonic device for helping you divide by fractions:
When dividing by fractions, don't ask why, just _____ the bottom and _________.
Hint: See the units for acceleration.
What is:
When dividing by fractions, don't ask why, just FLIP the bottom and MULTIPLY.
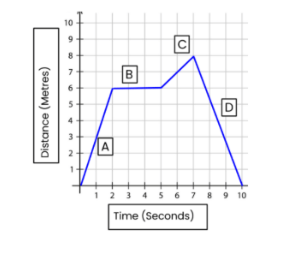 Give a description of what's happening in section B.
Give a description of what's happening in section B.
What is no acceleration?