Publications
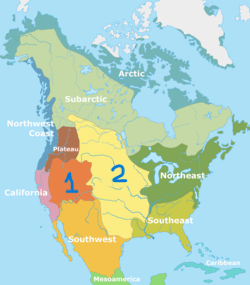
Name the two regions depicted on the map.
Great Basin and Great Plains
A business model used for large-scale ventures like colonization, where multiple investors pooled their money by purchasing shares to fund the enterprise.
Joint-stock company
Benjamin Franklin's proposal for a unified colonial government to manage defense, trade, and Indian relations during the French and Indian War.
Albany Plan of Union
Political philosophy of Thomas Jefferson and his supporters, emphasizing agrarianism, states' rights, a strict interpretation of the Constitution, and a limited federal government.
Jeffersonian Democracy
Proposed by General Winfield Scott, this Union strategy involved a naval blockade of Southern ports and taking control of the Mississippi River to 'suffocate' the Confederacy, much like its namesake snake.
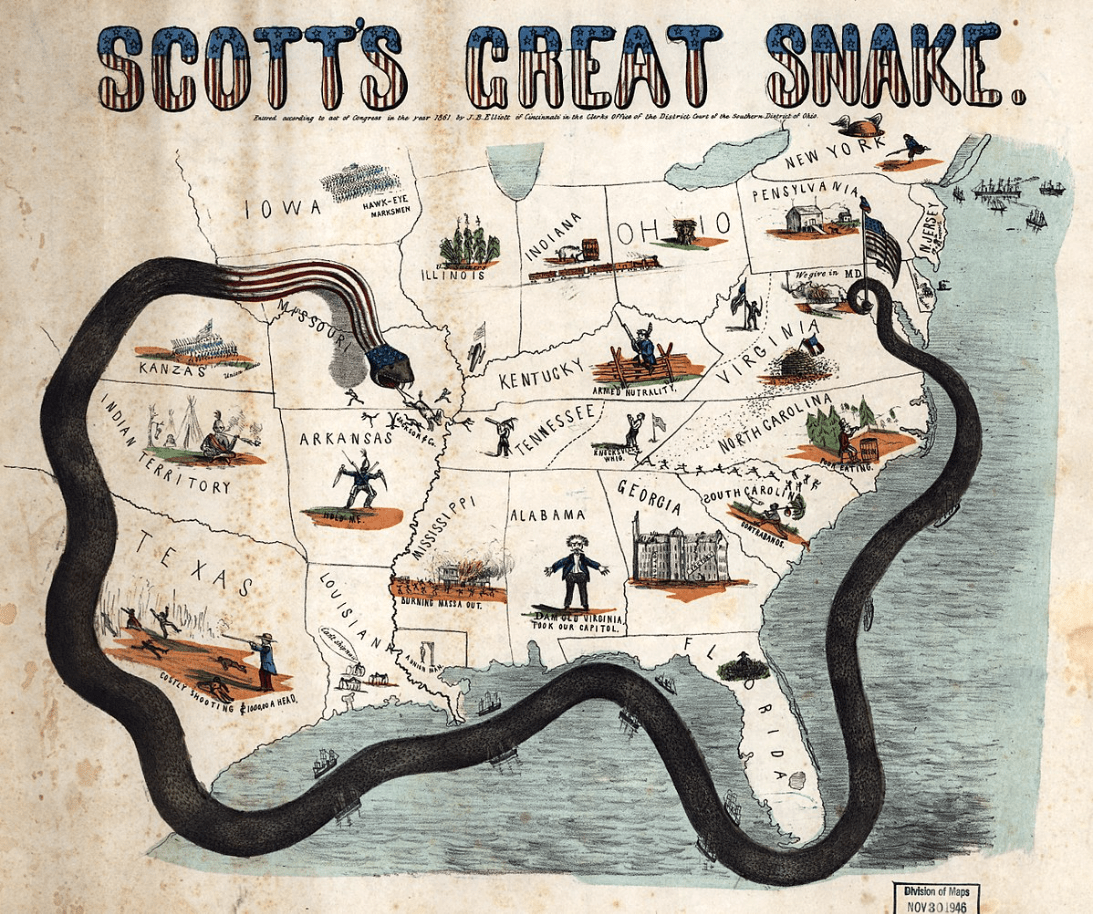
Anaconda Plan
First self-governing document for the Plymouth Colony, establishing rules for the settlers (Pilgrims and "strangers") outside Virginia's jurisdiction.
Mayflower Compact
Passed by a Republican-controlled Congress in 1862 during the Civil War, this act provided vast federal land grants and government bonds to the Union Pacific and Central Pacific companies to construct the first transcontinental railroad.
Pacific Railway Act
Its cultivation spurred economic development, settlement, and social diversification, enabling the development of sophisticated agricultural systems like the "three-sister" method and complex irrigation networks in regions like the American Southwest.
Maize
Jamestown settler known for cultivating the first profitable tobacco crop in Virginia, which became a crucial export. Also married Pocahontas which helped create a period of peace with the Powhatan people.
John Rolfe
British law that prohibited colonists from settling west of the Appalachian Mountains after the French and Indian War. Seen as an overreach of British authority, leading to resentment that led to the American Revolution.
Proclamation Line of 1763
Supreme Court case where Chief Justice John Marshall established Judicial Review, the principle that the Supreme Court can declare an act of Congress unconstitutional, effectively making the judiciary a co-equal branch with the legislative and executive.
Marbury v. Madison
Southern whites used this term to highlight its difference from other labor systems and to defend it as a divinely ordained, benevolent, or essential part of their way of life, despite growing abolitionist criticism.
"Peculiar institution"
Thomas Paine's 1776 pamphlet that argued for American independence from British rule, using plain language to advocate for a republican government based on Enlightenment ideals like natural rights.
Common Sense
U.S. foreign policy warning European powers against further colonization or interference in the Western Hemisphere, asserting American dominance in the region while pledging U.S. neutrality in European affairs.
Monroe Doctrine
The massive transfer of plants, animals, diseases, culture, and people between the Old World (Europe, Africa, Asia) and the New World (the Americas) after 1492.
Columbian Exchange
Puritan belief in a divine mission to create a society based on religious ideals and moral integrity. Also, John Winthrop's phrase from a 1630 sermon.
"City upon a Hill"
British laws passed in 1774 to punish Massachusetts for the Boston Tea Party, which united the colonies and led to the First Continental Congress.
Intolerable Acts
Henry Clay's economic plan to strengthen the U.S. by unifying it with three parts: a protective tariff to boost domestic industry, a national bank for stable currency, and internal improvements linking regional markets.
American System
This 1848 land acquisition, which included present-day California, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, and New Mexico, was ceded to the U.S. by Mexico following the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo.
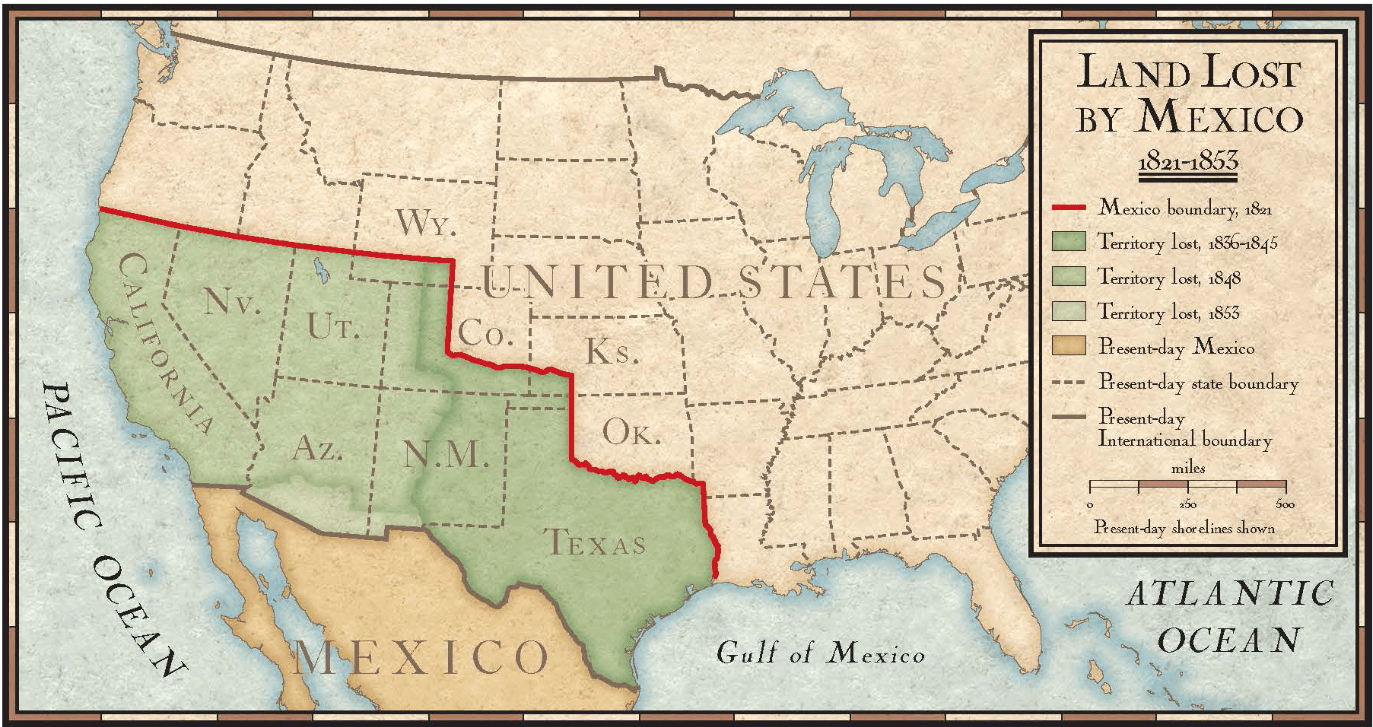
Mexican Cession
A foundational document in the Woman's Suffrage Movement written at the Seneca Falls Convention that proclaimed women's equality and demanded rights like suffrage, education, and legal standing.
Declaration of Sentiments
This 1807 law, signed by President Jefferson, prohibited American ships from engaging in all foreign trade in an attempt to pressure Britain and France into respecting U.S. neutrality, but instead devastated the American economy and led to widespread smuggling.
Embargo Act
A highly contagious viral disease introduced to the Americas by Europeans, which decimated Native American populations due to a lack of immunity.
Small pox
The ________________ were British laws that enforced mercantilism by restricting colonial trade to England, requiring goods to be carried on English ships, and taxing specific colonial exports to benefit the mother country.
Navigation Acts
Victory in this battle was a turning point in the Revolutionary War. Convinced France to provide crucial military and financial support instrumental in winning the war.
Battle of Saratoga
New technology (steamboat, telegraph), improved transportation (canals, railroads), and introduction of factory systems (Lowell, Slater Mills) were effects of this economic transformation in the 1820s.
Market Revolution
Formed in 1848 by antislavery members of existing parties, this group adopted the slogan "free soil, free speech, free labor, and free men" and sought to prohibit the expansion of slavery into new western territories.
Free-Soil Party
1796 document where George Washington warned against political partisanship and foreign entanglements, advocating for national unity and a policy of neutrality in European affairs. He published it when declining a third term, setting a two term precedent.
Washington's Farewell Address
This 1854 legislation, proposed by Stephen Douglas, created two new territories and used the principle of popular sovereignty to decide the issue of slavery, effectively repealing the Missouri Compromise and leading to the violence known as "Bleeding Kansas".
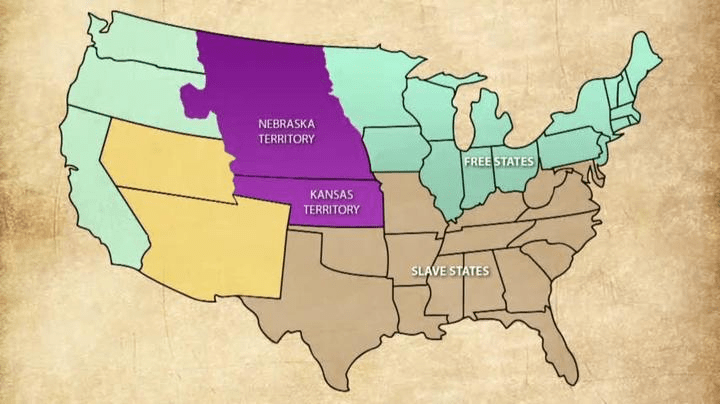
Kansas-Nebraska Act
A 16th-century religious movement in Europe that challenged the authority of the Roman Catholic Church and contributed to exploration and colonization in the Americas.
Protestant Reformation
Unofficial British policy of loosely enforcing parliamentary laws in the American colonies, allowing them a high degree of autonomy. This hands-off approach fostered a sense of independence that led to the Revolutionary War.
Salutary neglect
Post-Revolution ideology that a women's primary role was to raise virtuous, educated citizens for the new American republic.
Republican Motherhood
These women lived in company-owned boarding houses under strict moral codes, curfews, and supervision. The system offered wages and educational opportunities, providing a rare chance for economic independence for women at the time.
Lowell Girls
This all-white, pro-Democratic Party political coalition in the post-Civil War South aimed to "save" Southern society by dismantling Republican-controlled state governments, removing Black Americans from political office, and implementing discriminatory laws like Jim Crow.
Redeemers
A collection of 85 essays, written by James Madison, Alexander Hamilton, and John Jay, that urged ratification of the U.S. Constitution by arguing for a strong federal government. Opposed a Bill of Rights.
Federalist Papers
This package of five bills, passed in 1850, admitted California as a free state, utilized popular sovereignty in the Utah and New Mexico territories, and, most controversially, enacted a strict new Fugitive Slave Act.
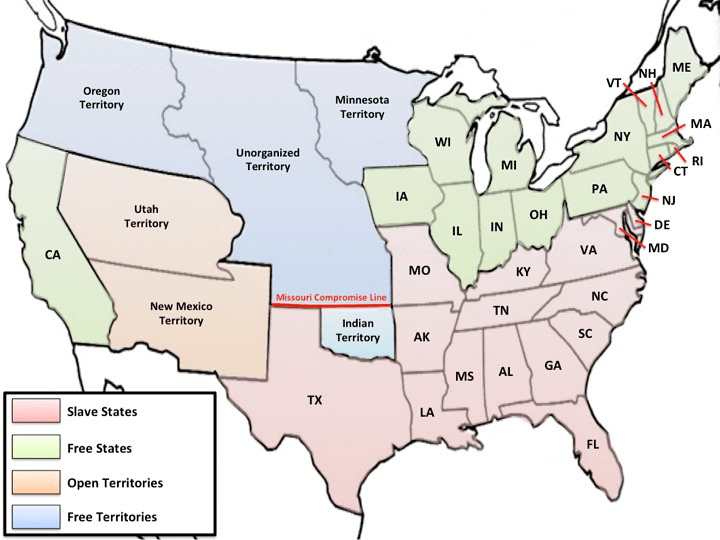
Compromise of 1850
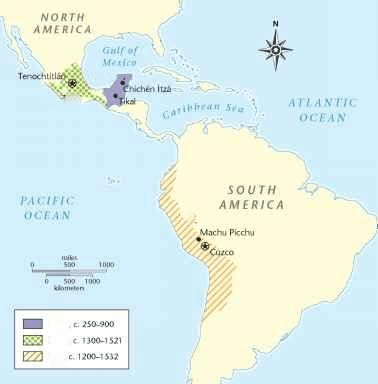
Name the three pre-Columbus Native American societies pictured in the map.
Aztec, Maya, Inca
First elected legislative assembly in American colonies, established in Virginia in 1619. Represented landowners and allowed them to elect representatives to make laws and levy taxes, laying the groundwork for self-governance and representative democracy.
House of Burgesses
Armed uprising in western Massachusetts from 1786-1787 by debt-ridden farmers protesting high taxes. Exposed weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation, which ultimately led to the Constitutional Convention.
Shays Rebellion
A 19th-century middle/upper-class ideology defining the ideal woman as pious, pure, submissive, and domestic, confined to the private sphere of home, family, and moral guidance.
Cult of Domesticity
Created by Congress in 1865, this federal agency provided food, clothing, medical care, and education to newly emancipated slaves and white refugees in the South, achieving its greatest success in establishing black schools.
Freedmen's Bureau
Published in 1854 by George Fitzhugh, this book argued that Northern capitalism was a failure and that slavery was a 'positive good' superior to 'wage slavery' because masters provided lifetime care for their 'happy' and 'content' workers.
Sociology for the South
A Supreme Court decision in 1857 that ruled African Americans, whether enslaved or free, were not citizens and therefore had no right to sue in federal court; it also declared the Missouri Compromise unconstitutional, stating Congress could not prohibit slavery in U.S. territories.
Dred Scott v. Sandford
A Spanish colonial labor system where the Spanish Crown granted colonists the right to extract labor and tribute (gold, agricultural products) from specified indigenous populations in exchange for the promise of protection and Christian instruction.
Encomienda System
Land grant policy primarily in Virginia, that gave 50 acres of land to settlers who paid for their own or another person's passage to the colonies. Encouraged settlement and addressed labor shortages, incentivizing wealthy colonists to import laborers, including indentured servants.
Headright System
Basis of the social contract in the Constitution. It is the division and sharing of power between the national (federal) government and state governments.
Federalism
An alleged political deal where Henry Clay, the Speaker of the House, convinced the House of Representatives to elect John Quincy Adams as president over Andrew Jackson.
Corrupt Bargain of 1824
Favoring native-born Americans over immigrants, this sentiment often led to hostility, discrimination, and the formation of groups like the Know-Nothing Party.
Nativism
Influential anti-slavery newspaper founded by Frederick Douglass in 1847.
The North Star
This informal agreement resolved the disputed 1876 presidential election, leading to Republican candidate Hayes winning the election in exchange for all remaining federal troops removed from the South, ending Reconstruction.
Compromise of 1877
A contract granted by the Spanish crown that gave individuals or companies the exclusive right to supply enslaved Africans to Spain's American colonies, replacing the Native American forced labor system.
Asiento System
An armed uprising in Virginia in 1676 when frontier farmers and indentured servants revolted against Governor Berkeley. Led to a shift in labor from indentured servitude to race-based African slavery.
Bacon's Rebellion
Violent tax protest by western Pennsylvania farmers from 1791-1794 against the federal excise tax on whiskey, proposed by Alexander Hamilton to pay off the Revolutionary War debt. Demonstrated federal government's power to enforce federal law.
Whiskey Rebellion
Uniquely American philosophical and literary movement emphasizing individualism, self-reliance, intuition, and a deep connection to nature.
Transcendentalism
In the 1840s, this aggressive slogan, associated with President James K. Polk's Manifest Destiny platform, referred to the latitude line that some Americans demanded as the entire northern boundary of the Oregon Territory in negotiations with Great Britain.
"54-40 or Fight!"
1649 Maryland law granting religious freedom to all Christians, providing protection against discrimination based on their faith.
Act of Toleration
Passed by Congress in 1872, this act restored the right to vote and hold office to over 150,000 former Confederates.
Amnesty Act
Spanish Dominican friar and missionary who became a fierce advocate for the rights of Native Americans in the early colonial period.
Bartolome de Las Casas
Jonathan Edwards is a key example of a "___________" preacher as his sermons like "Sinners in the Hands of an Angry God" were central to sparking the Great Awakening revival movement and were known for their emotional intensity.
New Light
Laws passed by the Federalist-controlled Congress in 1798 that restricted immigration and suppressed criticism of the government, targeted at the pro-French Democratic-Republican Party.
Alien & Sedition Acts
Evangelist Charles Grandison Finney led many Second Great Awakening revivals in this district, whose name comes from the notion that the spiritual "fuel" in the area was all used up.
"Burned over district"
Which additions to the Constitution attempted to fulfill Lincoln's promise of "a new birth of freedom" after the Civil War?
Reconstruction Amendments (13th, 14th, & 15th)
This controversial 1794 treaty with Great Britain led to strong disagreements over policy that promoted the development of political parties, Federalist (supported) and Democratic-Republicans (opposed).
Jay Treaty
An 1830s protective tariff favoring Northern industry by taxing imported goods, which Southerners vehemently opposed as it harmed cotton exports to Britain and intensified debates over states' rights, leading directly to South Carolina's Nullification Crisis.
Tariff of Abominations
A series of Spanish reforms passed after the Valladolid Debates designed to regulate the treatment of indigenous people in the Americas and end the worst abuses of the encomienda system.
New Laws of 1542
A New York printer was acquitted of seditious libel for printing articles that criticized the colonial governor. Acquittal was a major victory for the freedom of the press setting a precedent for a freer press in the colonies.
John Peter Zenger Trial
Written in protest to the Alien & Sedition Acts by asserting that states had the right to declare unconstitutional federal laws "null and void," introducing the doctrine of nullification.
Kentucky & Virginia Resolutions
An antebellum reform effort to create free, tax-supported public schools for all children, led by figures like Horace Mann.
Common School Movement
After the Civil War, this system allowed freed African Americans and poor whites to work land for a landowner in exchange for a portion of the harvest, but it often resulted in a cycle of debt and poverty.
Sharecropping
1494 agreement between Spain and Portugal that divided newly discovered lands outside Europe between the two nations, giving Spain control over most of the Western Hemisphere.
Treaty of Tordesillas
Landmark Massachusetts Supreme Court case that ruled labor unions were legal and not criminal conspiracies in 1842.
Commonwealth v. Hunt