The hybridization of the central atom in methane.
What is Sp3?
This functional group contains a carbon double-bonded to an oxygen and single-bonded to a hydroxyl group.

What is a carboxylic acid?
This term describes the rearrangement of atoms within a molecule to form a different isomer.
What is a tautomeric shift?
(Tautomer is okay)
This spectroscopic technique uses the absorption of light to measure the concentration of a substance in solution.
What is UV-VIS?
This is the point group for this molecule:
What is C2V?
This thermodynamic function is defined as the internal energy of a system plus the product of its pressure and volume.
What is enthalpy?
This is a diagram of a very important piece of equipment.
What is schlenk line?
This principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers.
What is the Pauli Exclusion Principle?
This term describes the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule that results in two non-superimposable mirror images.
What is Chirality?
In this type of NMR spectroscopy, the chemical shift of a hydrogen atom is measured to provide information about its chemical environment.
What is H-NMR?
This is a diagram of a instrument.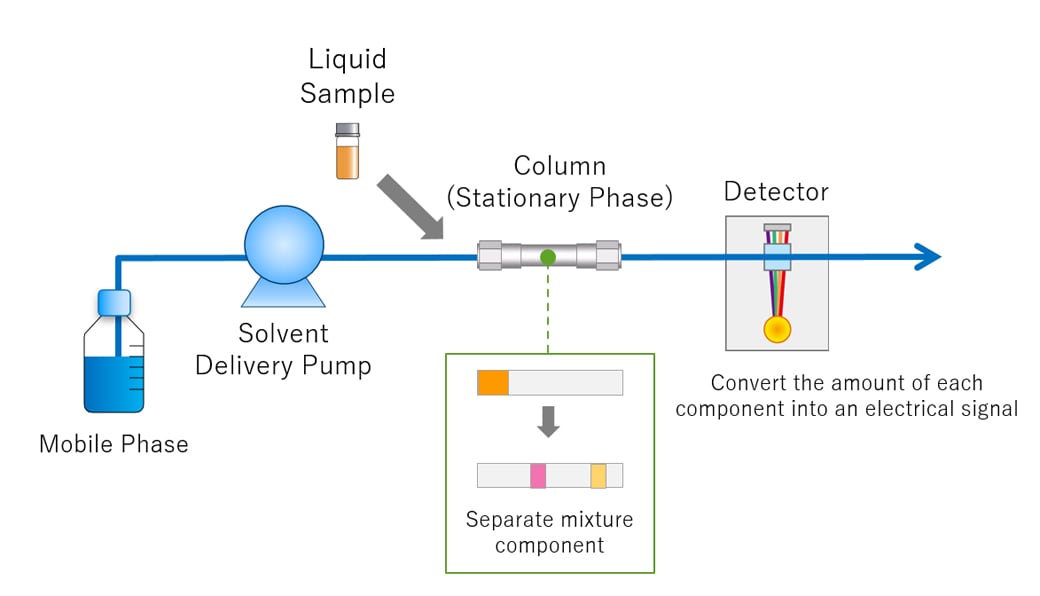
What is HPLC?
This phenomenon occurs when electrons in nonbonding orbitals contribute to the overall magnetic moment of a molecule, as predicted by molecular orbital theory.
What is paramagnetism?
This term describes a process in which the system exchanges heat with its surroundings at a constant temperature
What is an isothermal process?
This method is used to separate the components of a mixture based on their different boiling points
What is fractional distillation?
The maximum number of electrons that can occupy the d subshell.
What is 10 electrons?
This is the special catalyst used to hydrogenate alkynes into alkenes.
What is lindlar's catalyst?
This is called.
What is an Enolate?
This is not a strong acid:
- Hydroiodic acid: HI
- Nitric acid: HNO3
- Perchloric acid: HClO4
- Hydrofluoric acid: HF
- Nitric acid: HNO3
What is 4. Hydrofluoric acid?
This is considered the first molecule ever created in the universe.
What is He-H?
This value for G means that the reaction is spontaneous in terms of Gibbs free energy.
What is -G?
NaH and other reactive metals are commonly submerged in this substance.
What is mineral oil?
This concept defines acids and bases in terms of their ability to accept or donate a pair of electrons.
What is the Lewis theory of acids and bases?
This Molecule is Antiaromatic:
C)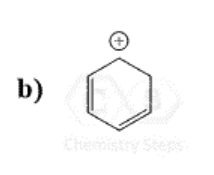
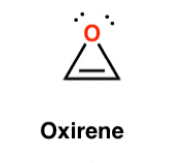
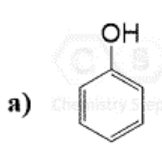
D)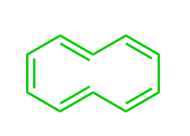
What is Oxirene?
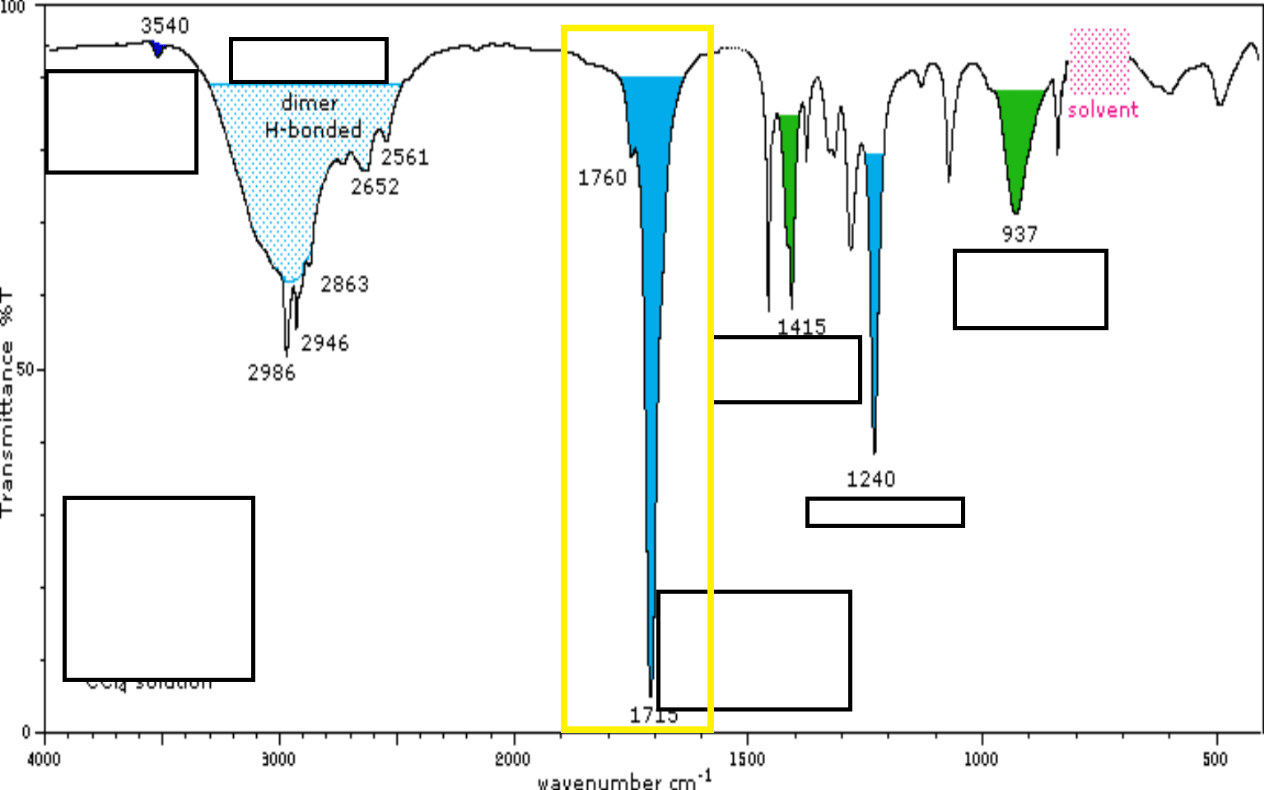
This highlighted in yellow section is known as this stretch.
This invention finally allowed the connection between LC and MS.
What is electrospray?
This is the matrix representation of the 'I' operation.
(-1 0 0
0 -1 0
0 0 -1)
This approximation method is used to calculate the electronic structure of molecules by considering them as a combination of atomic orbitals.
What is the Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals (LCAO) method?
This approach involves adding a known amount of a compound, which is not present in the sample, to both the sample and the standards to correct for variations in the analytical procedure.
What is internal standard?
This term refers to molecular orbitals that are formed from the combination of atomic orbitals with opposite phases, resulting in a node between the nuclei and higher energy than the original atomic orbitals.
What are antibonding molecular orbitals?
This group is both a deactivating group and an ortho-para director in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions.
What are Halogens?
This reaction goes through these steps:
- reaction 1: acid-base reaction.
- reaction 2: nucleophilic substitution.
- reaction 3: ester hydrolysis (using saponification)
- reaction 4: decarboxylation.
What is malonic ester synthesis?
This highlighted section is a component within a mass spectrometer.
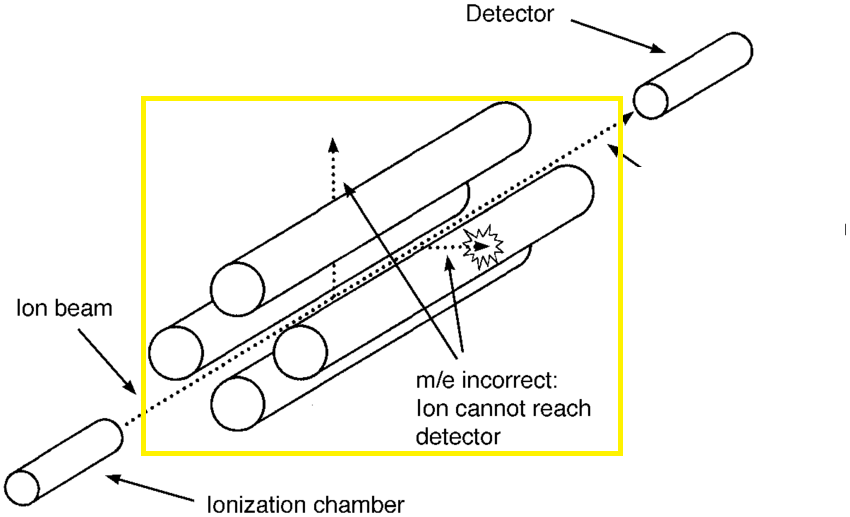
What is quardropole.
This type of semiconductor is doped with a more electronegative element.
What is a n-type semiconductor?
This approximation method in quantum chemistry is used to simplify the calculation of molecular orbitals by assuming that the electron-electron interactions can be averaged out.
What is the Hartree-Fock method?
This atom is required to be part of a molecule for a NMR solvent.
What is Deuterium?
This quantum number describes the shape of an atomic orbital.
What is the azimuthal quantum number (l)?
This is the name for this molecule:

What is 2-Amino- 4 – Hydroxybenzoic acid?
This molecule is considered a nebulous addition to monosaccharides.
What is D-Galactose.
This light source has a wave length of around 190 – 370 nm and contains an isotope of a common element.
What is D2 lamp.
This is the point group for cubane: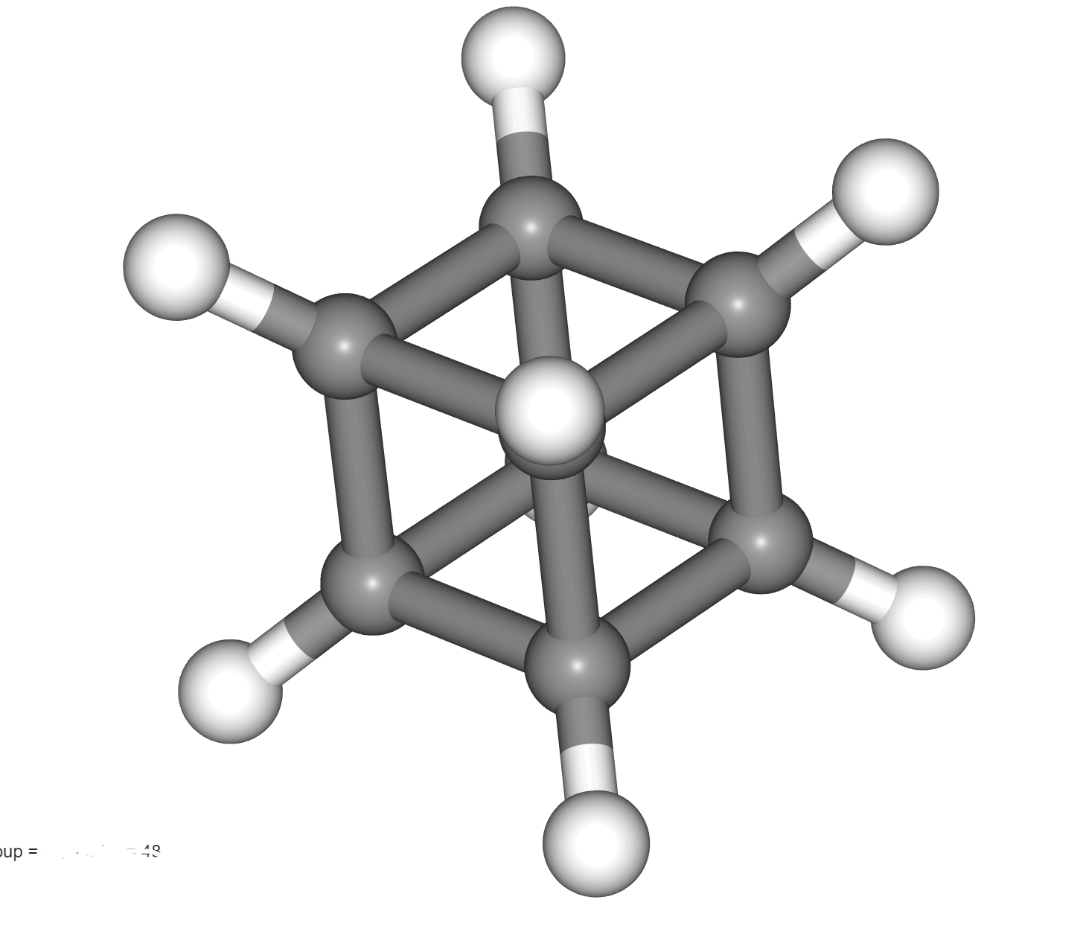
What is Oh (Octahedral)
This is the relationship between Boltzmann's constant and the R constant.
What is R=k*avagadro's number?
This is the most common way to dry solvents.
What is put over molecular sieves?