65 y.o admitted for COPD exacerbation. Pt is c/o of SOB and palpitations. ECG is obtained:

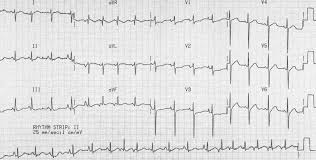
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia
What are the 3 clinical/anatomical criteria for diagnosis of brain death? What are the confirmatory imaging modalities used?
1. widespread cortical destruction (deep coma and unresponsive to all forms of stimuli) 2. global brainstem damage (absent pupillary light reaction, loss of oculovestibular and corneal reflexes) 3. destruction of medulla (complete apnea) Apnea test, Radionuclide brain scan, EEG, Cerebral Angiogram, Transcranial Doppler
Extra Credit: Describe positive Apnea test
Describe Superior vena cava syndrome (SVCS). Clinical manifestations of SVCS? Causes? Treatment?
SVC obstruction-->severe reduction in venous return from head, neck and upper extremities. Symptoms: neck and facial swelling, dyspnea, cough, hoarseness, tongue swelling, headache, nasal congestion, epistaxis/hemoptysis, dysphagia, syncope, lethargy. Leading causes: Lung CA (small cell and squamous), Malignant Lymphomas Tx: Radiation therapy (mainstay), Chemo, steroids (lymphomas), stents, head elevation, diuretics, low salt intake
Extra Credit: List all the paraneoplastic syndromes of Small Cell Lung CA
What is the initial treatment of choice for most patients with Spinal Cord Compression.
Radiation Therapy and glucocorticoids.
Extra Credit: What is Lemierre's Syndrome and common organism that may cause it
What's the CURRENT and most accepted definition of ARDS?
Defined by the ratio of arterial oxygen tension to fraction of inspired oxygen (PaO2/FiO2) -Mild: >200 but <300 -Moderate: >100 but <200 -Severe: <100 Diffuse alveolar infiltrates/pulmonary edema (non-cardiogenic) CVP/PCWP <18

Sarcoid, stage 2
33 y.o pt admitted for status asthmaticus and subsequently had to be intubated and placed on vent. His ventilator settings- 35%/5/PIP 42/Plateu 24. Two hours later, RN calls you for dropping BP and you notice the following changes: 35%/5/PIP 44/Plateu 35. You order a STAT CXR:
What is your next step:

Needle decompression
What are the metabolic causes of ALOC/metabolic encephalopathy in the ICU setting? What's the Pathophy of elevation of pCO2 in causing ALOC/AMS
Hypercarbic Encephalopathy (hypoventilation syndrome), hepatic encephalopathy, Hypo/hyperglycemia, Hyper/hyponatremia.. High pCO2 causes cerebral vasodilation and increased ICP.
DOUBLE JEOPARDY
Malignant pericardial effusion/tamponade is most commonly seen in which types of cancer? Treatment?
Lung CA, Breast CA, leukemias and lymphomas. Tx: Pericardiocenthesis, pericardial window, complete pericardial stripping, cardiac irradiation, chemo
Extra Credit: Tx for below
How is diagnosis of Neoplastic Meningitis made?
Diagnosis is made by demonstrating malignant cells in the CSF. Up to 40% of patients have false negative CSF cytology; Elevated protein in CSF is almost always present.
Lymphocytes in CSF: causes
What are the Pathological stages of ARDS?
1. Exudative or Inflammatory phase (0-7 days) 2. Proliferative phase (7-21 days) 3. Fibrotic phase (>21 days)
Pt with sepsis presents with ALOC, anemia/low platelets and AKI. No active bleed with normal coags. LP is negative and blood smear shows the following:
Tx for this condition?
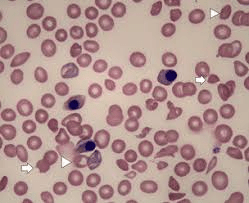
TTP: Tx- plasma exchange
Identify these 3 fungi:
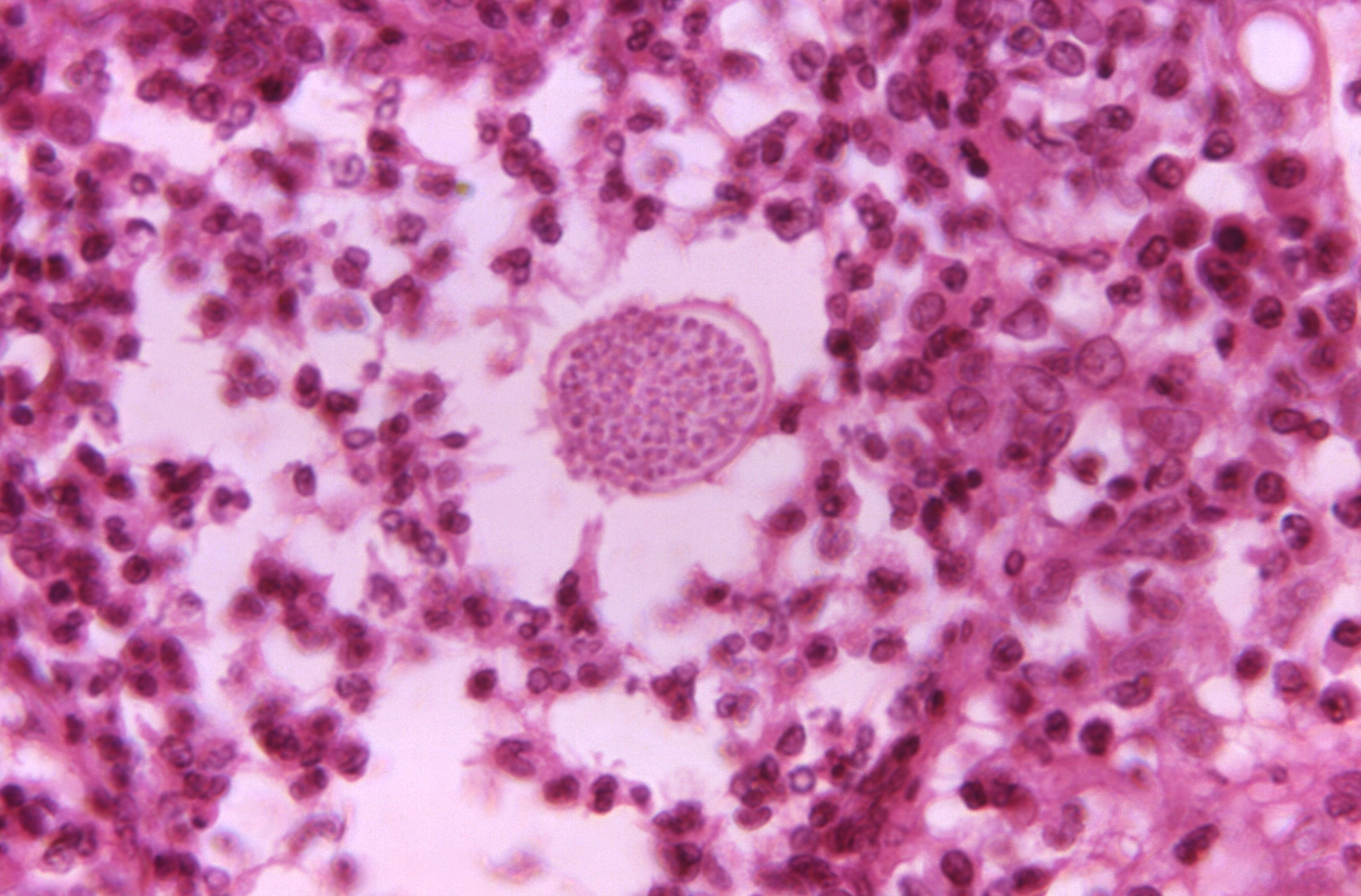
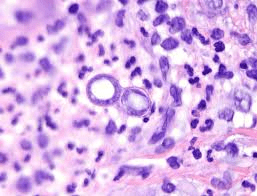
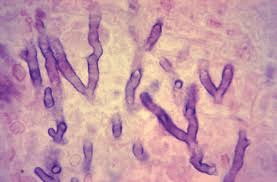
1. Cocci
2. Blastomycosis
3. Aspergillosis
Extra Credit: Tx for DM pt with nasophayngral Mucormycosis
Describe Central Pontine Myelinosis? Presentation, Imaging, prevention?
Presents with quadriplegia and pseudobulbar palsy. Predisposing factors include severe underlying medical illness or nutritional deficiency; rapid correction of HypoNa or with Hyperosmolar states. The pathology consists of demyelination without inflammation in the base of the pons (MRI). Restoration of severe hypoNa should be </= 10mmol/L within 24 hrs and 20mmol/L within 48 hrs.
Describe Hyperleukocytosis/Lekostasis? In which conditions is it most commonly associated with? Clinical manifestations? Treatment?
Associated with acute Leukemia (esp. Myeloid leukemia-AML, ALL). Peripheral blast cell count >100,000/mL. Organs effected mostly are Brain (stupor, HA, dizziness, tinnitus, visual disturbances, ataxia, confusion, coma, death) and Lungs (hypoxemia, ARDS, pulm hemorrhage, resp. failure) Tx: Hydroxyurea, Leukapheresis
Describe the ARDS Clinical Trial of Low Tidal Volume Ventilation (ARDSnet)?
-Lower TV (6mL/Kg) vs. Higher (12mL/Kg) results in improved mortality (31 vs. 40%); Lower TV avoids barotrauma/volutrama of healthy alveoli -Keep Pplat <30, RR <35, PEEP 5-12, Permissive Hypercapnea is OK
Male pt in 40s presents with hemoptysis and AKI with nephritic syndrome..
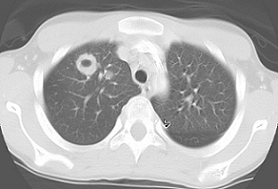
Granulomatosis with Polyangitis (GPA)
55 yo incarcerated smoker present with dyspnea, hemoptysis and weight loss over 6 months. CXR reveals the following. What would you do NEXT:
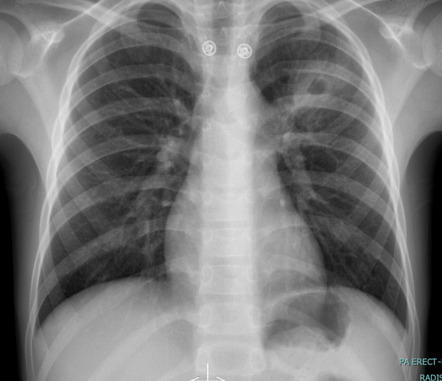
Isolate and collect 3 sputum samples for AFB.
Extra credit: What is the most common type of PNA seen in pts with AIDS.
What are the common causes of Wernicke's Disease? What is the characteristic clinical triad? MRI finding? Treatment?
Causes: ALCOHOLISM, malnutrition from hyperemesis, starvation, renal dialysis, cancer, AIDS, gastric surgery. Triad: Opthalmoplegia (horizontal nystagmus, lateral gaze), ataxia, global confusion MRI: abnormal enhancement of the mammillary bodies Tx: IV Thiamine (100 mg IV daily) before dextrose solutions
Define massive hemoptysis? What urgent interventions need to be done before any imaging/procedure..? Most common fungus associated with hemoptysis Treatment?
1. >200-600mL of blood/24h..Any hemoptysis can be considered massive if it threatens life. 2. Airway, Oxygenation, Hemodynamic stabilization. 3. They should be placed bleeding side down, O2 support 4. Bronchoscopy to localize, YAG-laser therapy, Bronchial Artery Embolization, lobectomy/pneumonectomy. 5. Fungus-Aspergillus sp. cavitate into bronchial Artery and cause bleed.
Extra Credit: If able, how would you intubate these pts/specific modality or technique?
Describe/explain the Fluid liberal vs. Fluid conservative therapy in patients with ARDS?
-Conservative fluid strategy may help patients by reducing edema formation. 2006 ARDSnet -Conservative or liberal fluid management for 7 days--> CVP <4 vs. CVP >10 -Conservative strategy improved oxygenation index, lung injury scores, increased ventilator free days and ICU free days - 60 day mortality unaltered

Stress/depression, fatigue, Parkinson's, HIV.
Describe below:
High AutoPEEP-->increased intrathoracic pressure-->decrease venous return-->Hypotension
Extra credit: dx??
Describe Critical Illness Neuropathy/Myopathy or Neuromyopathy? Aggravating factors? Dx/Tx?
Occurs after a prolonged critical illness/ICU stay (several weeks). It's a diffuse axonal degeneration of the peripheral nervous system or muscular atrophy diagnosed with NCV and EMG. Factors- NMBAs, glucocorticoids, sepsis, poor glycemic control, prolonged mechanical ventilation, Renal Failure, Females, elderly, Certain Abx (aminoglycosides?) Tx: supportive, PT/OT/OOB, majority cases are reversible but takes weeks to months.
1. What are the characteristics of TLS? 2. How would one differentiate acute hyperuricemic nephropathy with renal failure due to other causes? 3. What's pseudohyperkalemia and how can one obtain a true K level in pts with high leukcyte count/TLS?
1. HYPERuricemia, HYPERkalemia, HYPERphosphatemia, HYPOcalcemia. Renal Failure is common. 2. Urinary UA to urinary Cr >1 (acute hyperuricemic nephropathy) vs. ratio is <1 3. PLASMA K level instead of SERUM K should be followed; No electrocardiographic abnormalities are present in PseudohyperK.
Outline (in detail) the Prevention and Treatment of TLS?
1. Hydration w/ 1/2 NS or NS 2. Keep Urine pH at 7 or greater w/NaHCO3 3. Allopurinol 4. Monitor serum Chemistry If after 24 hrs Serum UA>8; start Rasburicase w/ Allopurinol; if UA still >8 then HD (delay Chemo) OR If after 24 hrs Serum UA <8 and Urine pH >7 then continue Chemo, D/C NaHCO3 and monitor serum chemistry very closely.
Outline ALL the therapeutic modalities that have been tried/utilized as part of the management of ARDS.
1. Low TV Ventilation 2. Higher PEEP 3. Permissive Hypercapnea 4. Conservative Fluid Balance 5. Prone Positioning 6. NMBAs 7. Steroids 8. Recruitment Maneuvers 9. NO 10. Rescue Ventilator modes (APRV, Inverse Ratio PC, HFPV, VDR) 11. ECMO
DOUBLE JEOPARDY

Main Tx for this condition
PJP: Tx IV Bactrim