Identify this flat, single-layered tissue lining blood vessel?

Simple squamous epithelium.
What type of epithelial tissue allows for rapid diffusion and filtration?
Simple Squamous Epithelium Tissue
Where is the simple squamous epithelium located?
Alveoli of the lungs
Identify this tissue type shown here with multiple layers and protects against abrasion?

Stratified squamous epithelium.
What type of connective tissue stores energy and insulates the body?
Adipose Tissue
Where is the Simple Columnar Epithelium located?
Lining of the small and large intestines.
This tissue has cilia and appears layered, but it is not. What is the name of the cell?
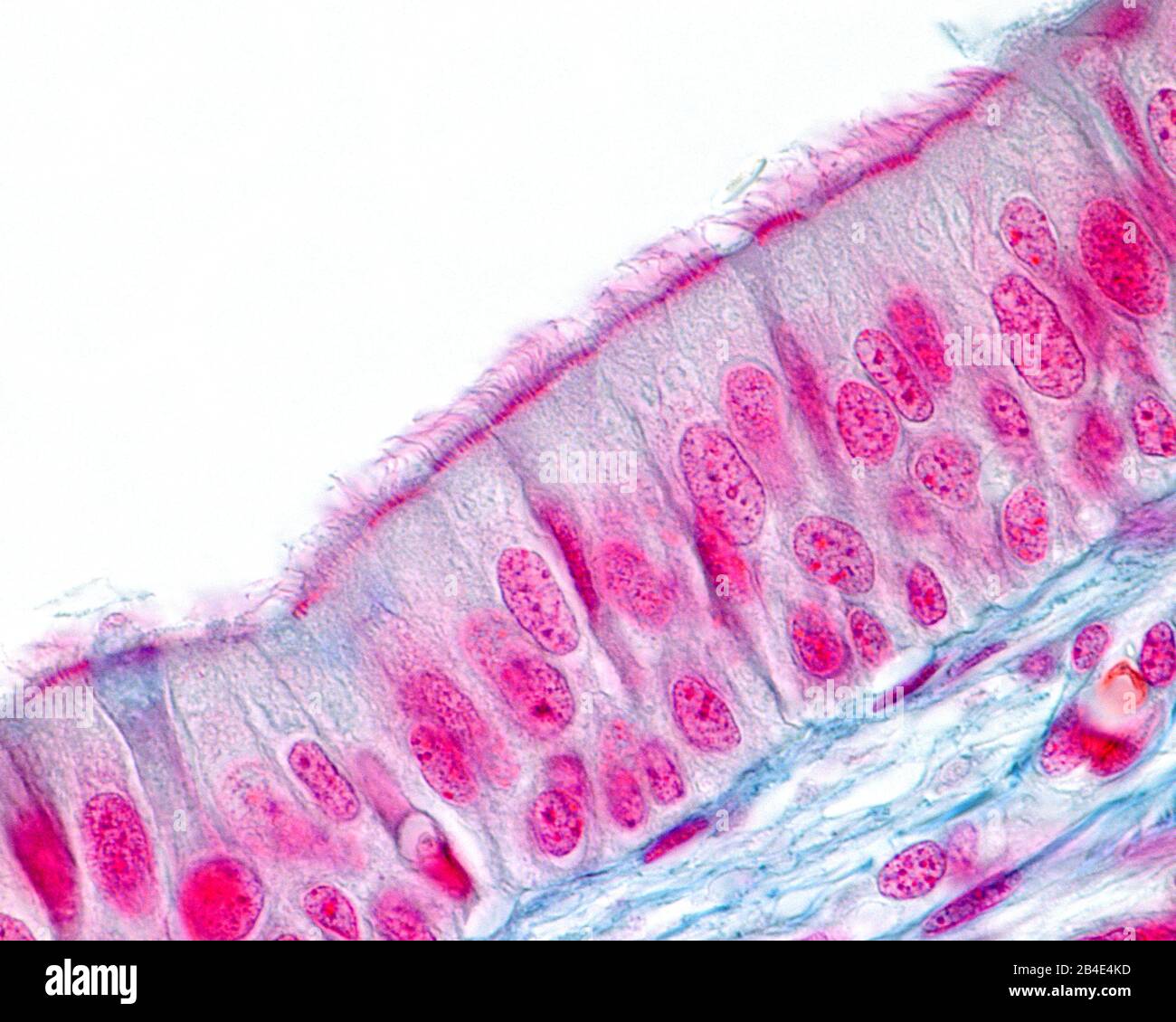
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium.
What type of epithelial tissue helps trap and move particles via cilia?
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium Tissue.
Where is the blood smear connective tissue located?
Heart, arteries &veins and capillaries.
Identify the name for this connective cell?

Dense regular connective tissue.
What type of connective tissue resists tension and connects muscles to bones?
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
Where is the pseudostratified columnar epithelium located?
Lining of the respiratory tract
Identify the name for this image?

Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium Tissue.
Which type of connective tissue plays a role in immune surveillance and signaling through circulating cytokines and chemokines.
Blood Smear Connective Tissue
Where is dense regular connective tissue found?
Tendons and ligaments