This is our Sun's classification on the O-M scale indicating that it is relatively cool and yellow.
What is a G2 star?
This is the type of fusion occurring in the core of a main sequence star.
What is HYDROGEN FUSION?
From Unit 4 Lab: Hydrogen fuses into Helium-4 in our sun!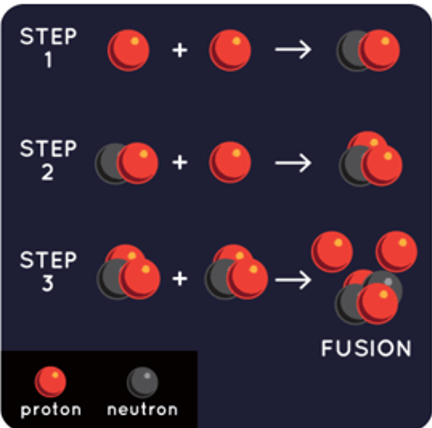
This diagram plots stars by their luminosity and spectral class (temperature).
What is the HERTZSPRUNG-RUSSELL (H-R) DIAGRAM?
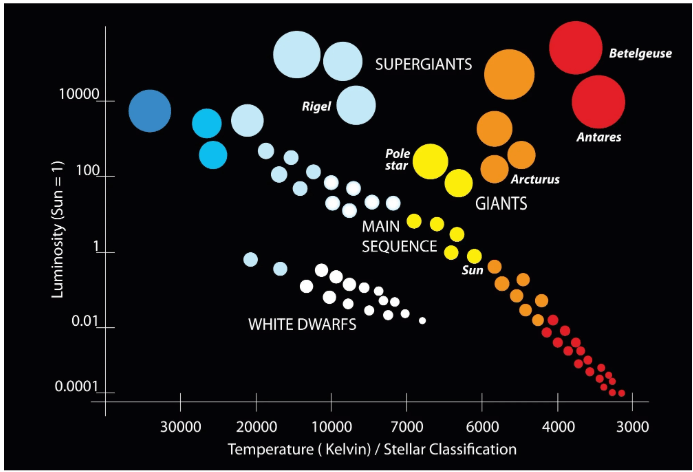
This class contains the hottest and largest stars in the O-M classification categories.
What is Class O?
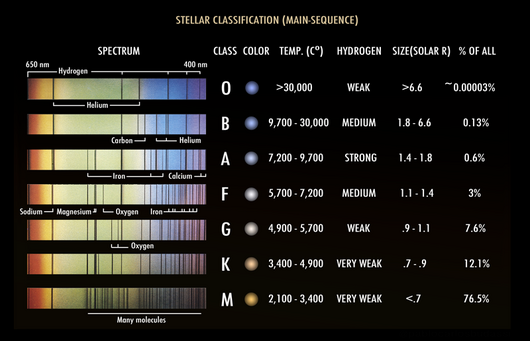
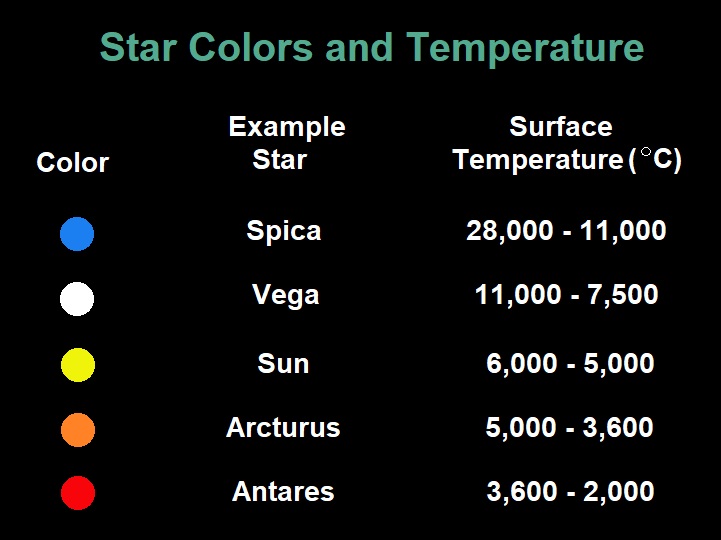
Spectral lines provide this information about stars.
What are their
- SIZE
- DENSITY
- ATMOSPHERIC CONDITIONS
- Also HEAT & ENERGY! (Stars with the narrowest spectral lines are hotter and more energetic.)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nSJqmMN6bC0
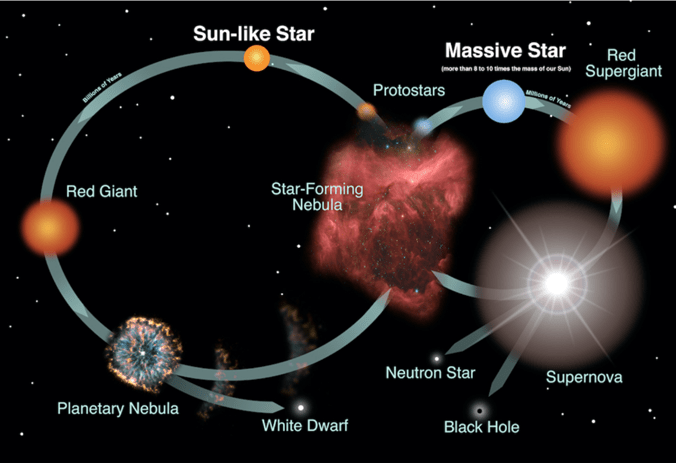
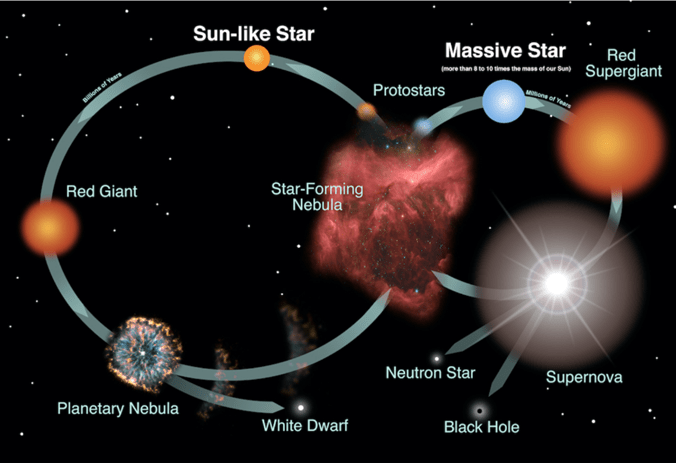
This phase follows the main sequence for a star like the sun.
What is a RED GIANT?
This is the total energy that a star emits per second.
What is LUMINOSITY?

This is how we know the composition of distant stars.
What is EMISSION AND ABSORPTION SPECTROSCOPY?
This is the fate of very massive stars at the end of their life cycle.
What is EXPLODE AS SUPERNOVAE?
Astronomers use these 3 specific characteristics to classify stars.
What are:
MASS
TEMPERATURE
COLOR
This process creates elements heavier than iron in the cores of stars.
What is RAPID NEUTRON CAPTURE (r-process) DURING SUPERNOVA?
This is a hard question! Covered in 4.05 lesson reading:
This is how neutron stars and black holes form.
What is after the death of massive stars?
