a hypothesis that has been supported by a large amount of observations and experiments
theory
a new model that describes observations and is testable
hypothesis
Convert to/from scientific notation:
5.2 × 10-4
0.00052
How many observational or experimental tests does it take to prove a hypothesis false?
One
Is light a particle or a wave?
light can act as a wave AND a particle!
the projection of the Earth’s geographic south pole into space
south celestial pole
a pseudoscience that has roots in astronomical observation (hint: zodiac signs)
astrology
Convert to/from scientific notation
4,410,000
4.41 × 106
Why do stars appear to move across the sky?
because the Earth is rotating on its axis.
Which type of light has the the shortest wavelength?
gamma rays
a simplified scientific model of the sky that assumes all stars, no matter how far they are, are projected onto a sphere around the Earth
celestial sphere
a subset of stars that form a widely recognized shape (hint: not a constellation)
asterism
Order these types of radiation on the EM spectrum from lowest to highest energy:
gamma rays, radio waves, visible light
radio waves < visible light < gamma rays
You see a star rising due East. When this star reaches its highest position above the horizon, where will it be? (direction and height)
high in the Southern sky
Which of the three temperature scales do astronomers use?
Kelvin
unlike chemistry, biology, or physics, astronomy requires _______ more than lab experiments
the projection of the Earth’s equator into space
celestial equator
What is Kepler's 1st law of planetary motion?
each planet moves around the Sun in an orbit that is an ellipse (with the Sun at one focus of the ellipse)
Which of Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion states that “the straight line joining a planet and the Sun sweeps out equal areas in space in equal intervals of time ”?
The second
What does the peak intensity of blackbody radiation depend on?
Temperature
the line where the dome of the sky you can see meets the ground from your point of view
horizon
the line on which the constellations of the zodiac are located, which is tilted at 23.5° with respect to the celestial equator
ecliptic
What is this type of spectrum and how is it formed?
as the light from a blackbody travels through a low density cloud of gas, gas atoms absorb certain colors of light creating black bands in the continuous spectrum
Which law of physics is represented by this equation: F=G(Mm)/r^2 ?
Newton's universal law of gravitation
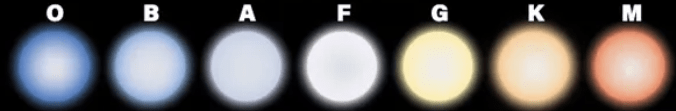
Which star is the hottest?