Gravity/Inertia
How old is the Universe?
about 14 billion years old
A nearby star exploded causing a shockwave of force. What happened to the nebula?
It began spinning and heating up.
What degree is Earth tilted on its axis?
23.5 degrees
Planets move in an elliptical orbit where the sun is at 1 foci and the other foci is empty space. This is Kepler's 1st Law. What is his first law called?
Law of Orbits
Periods of rise and fall of the ocean water levels
Tides
Nuclear Fusion is when ________ atoms are squeezed together forming _________ atoms.
Hydrogen, Helium
When scientists look into the universe, some objects appear red as they are moving away. What is this phenomenon?
Redshift
The nebula began to flatten due to the spinning motion. What began to form in the middle as Hydrogen particles clumped together and collided into one another?
Protostar
What does the revolution of earth affect?
**Bonus points if you list all 5**
1. Seasons
2. Light intensity
3. Length of day
4. Weather patterns
5. Climate regions
What is the formula for Eccentricity?
E=d/L
Has the greatest difference between high and low tides
Spring Tide
Wavelength
What piece of evidence supporting the Big Bang Theory describes why our universe expanded and continues to expand?
Dark Energy
As ice particles clumped together and matter began to condense, what formed?
Outer Solar System or Outer Planets
What position is Earth in when it is closer to the sun?
Perihelion
A flat line has an eccentricity of:
1
Has minimal difference between high and low tides
Neap Tides
Where does the energy that is produced in the sun come from?
Left over mass from helium atom
The oldest and most distant light/energy left over from the Big Bang.
Cosmic Background Radiation CMB
What celestial body eventually evolved into our modern solar system?
Nebula

Which season is the Northern Hemisphere experiencing in this diagram?
Summer
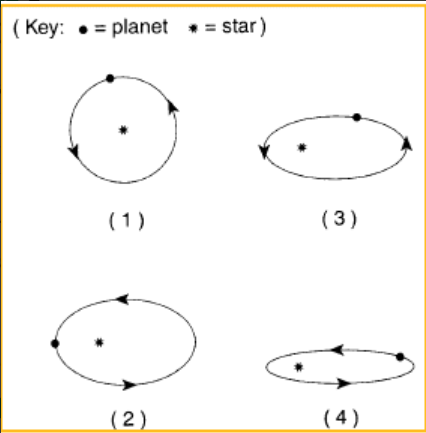
Which diagram shows a planet with the least eccentric orbit?
1
What type of tide does this diagram show?
Neap Tide
Which layer of the sun do our eyes perceive as the visible surface?
Photosphere
Why isn't the Big Bang a good name for the origin of the universe?
It was an expansion, not an explosion
Why is pluto not considered a planet?
It did not clear its own path
There are two times within a year when we experience day and night time periods of 12 hrs each. What is it called when this happens?
Equinox
Which law states that a planets orbit is proportional to the size of its orbit?
Kepler's 3rd Law: Law of Periods
Why does the moon's gravitational pull have more of effect on tides than the sun's gravitational pull?
The moon is closer to the earth than the sun.
A sudden eruption of radiation from the surface of the Sun that produces an enormous amount of energy
Solar Flare
What is the origin of the Big Bang?
A single, very hot, very dense pinpoint of energy.
Accretion
Center or mass between 2 or more objects orbiting each other
Barycenter
A line connecting the planet to the sun sweeps out in equal areas in equal times (faster closer to the sun and lower farther from the sun)
Kepler's 2nd Law: Law of Areas
You are recording tides. Right now, it is 8 am, there is a full moon, and it is high tide.
1. What time will low tide occur?
2. Are you experiencing a spring or a neap tide?
1. 2 pm
2. Spring
Shorter waves like gamma rays have ______ energy.
more