This term describes atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons.
Isotopes
Atoms become ions when they lose or gain these subatomic particles.
electrons
This subatomic particle has a positive charge
proton
The element with this atomic symbol (H)
hydrogen
The atomic number of aluminum
13
Aristotle
The mass number of carbon-14
14
The charge of an ion with 17 protons and 18 electrons.
-1
These particles orbit the nucleus of an atom
electron
The element with this atomic symbol (Na)
Sodium
These elements are located in Group 17 of the periodic table.
halogens
Coined the idea that matter may not be broken down further, "attomos"
Democritus
Isotopes have the same number of these subatomic particles.
protons
This is the term for a positively charged ion.
cation
The subatomic particle with no charge
neutron
The element with this atomic symbol (Ho)
Holmium
A horizontal row on the periodic table is called this
period
Scientist that discovered this model
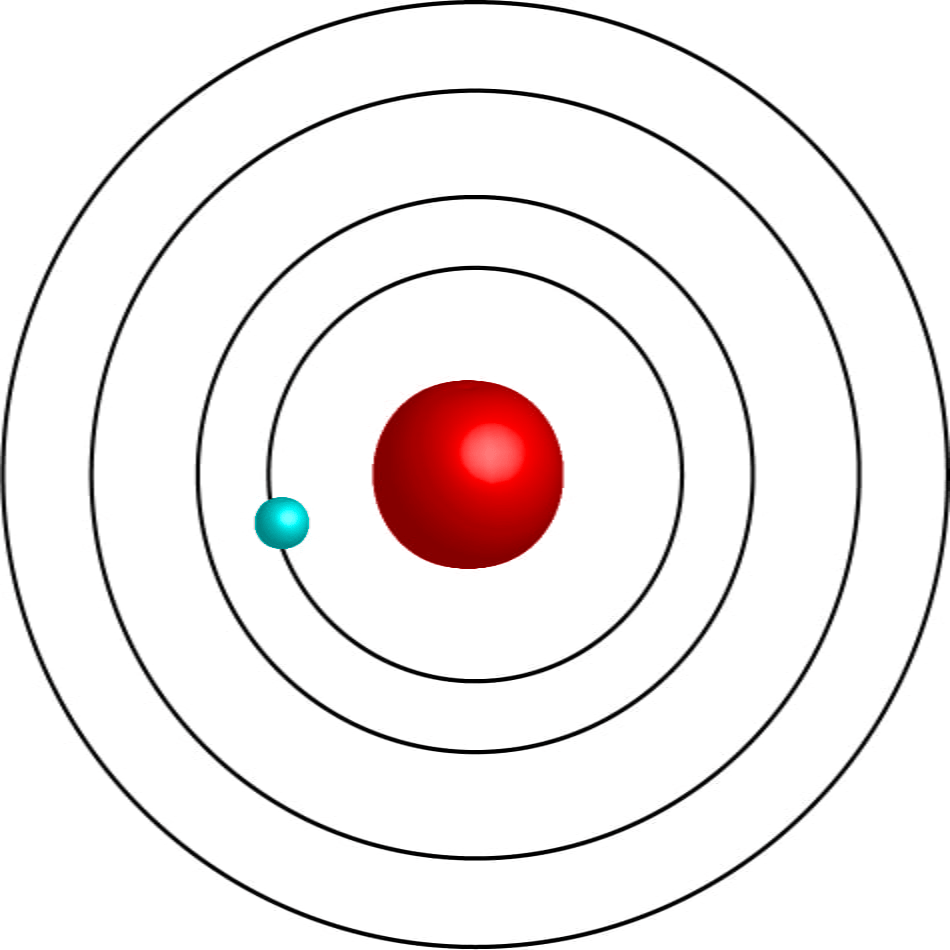
Bohr
The scientist who introduced the concept of the atom as indivisible.
Democritus
The ion formed by oxygen when it gains two electrons.
O2-
The location where protons and neutrons are found
nucleus
Hg
The scientist credited with organizing the periodic table by atomic mass
Dmitri Mendeleev
Discovered there were nuclei using gold foil
Rutherford
The isotope with 11 protons, 12 neutrons, and 11 electrons.
sodium-23
The notation for an ion with 26 protons, 30 neutrons, and a 3+ charge
5626Fe3+
This particle determines the atomic number of an element
proton
The elemental symbol for Antimony
Sb
The element that has 22 neutrons and an atomic number of 18
Argon
The scientist that proposed this model.
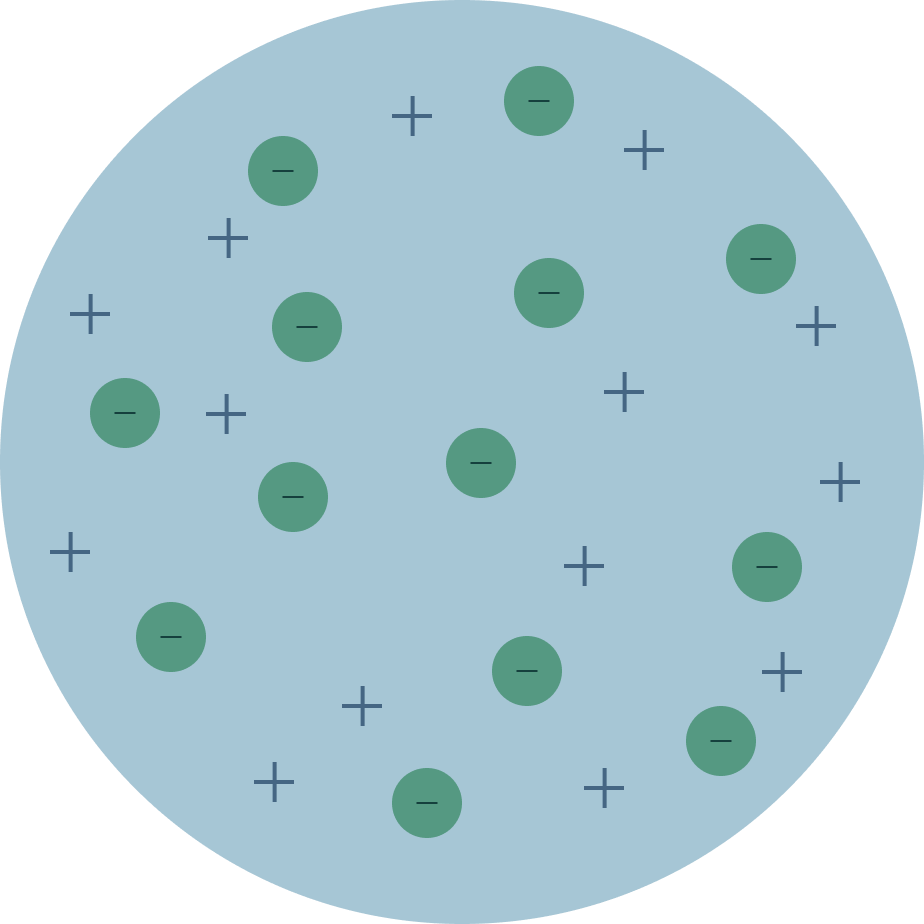
Tompson