He combined the idea of elements with the Greek theory of the atom to form a 4 part atomic theory still used today.
John Dalton
This is the center portion of the atom where the protons and neutrons are located.
Nucleus
All matter is made up of these.
Atoms
This is a chart made up of elements.
The periodic table
Non-metals are located on this side of the periodic table.
Right side
He discovered negatively charged particles, electrons, which are part of every atom.
JJ Thomson
These are positively charged particles of an atom.
Protons
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
Atomic number of an element
This is a substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances.
An element
This element is on the "wrong" side of the periodic table, according to its characteristics.
Hydrogen
He discovered the nucleus of an atom.
Ernest Rutherford
These subatomic particles are found OUTSIDE of the nucleus.
Electrons
The number of neutrons PLUS the number of protons.
Mass number/atomic mass/atomic weight of an element
This is a characteristic of metals that allows them to be able to be drawn (pulled/stretched) into wires.
Ductile
This characteristic of metals allows it to be able to be hammered or rolled into sheets.
Malleable
He discovered the electron cloud and energy levels (orbitals) of an atom.
Niels Bohr
These subatomic particles have no charge and are found in the nucleus of an atom.
Neutrons
This is how the periodic table is arranged - or how the periodic table is organized.
By increasing the atomic number
Metalloids are able to conduct electricity, but not as well as metals. This term means to be able to partially conduct electricity.
Semiconductor
What is the lewis dot diagram for bromine

Father of the atomic bomb
J. Robert Oppenheimer
This is another name for the energy levels of an atom, where the electrons are located.
Orbitals
These have the same number of protons but different number of neutrons.
Isotopes of an element
This element is the only metal that is liquid at room temperature, not solid.
Mercury
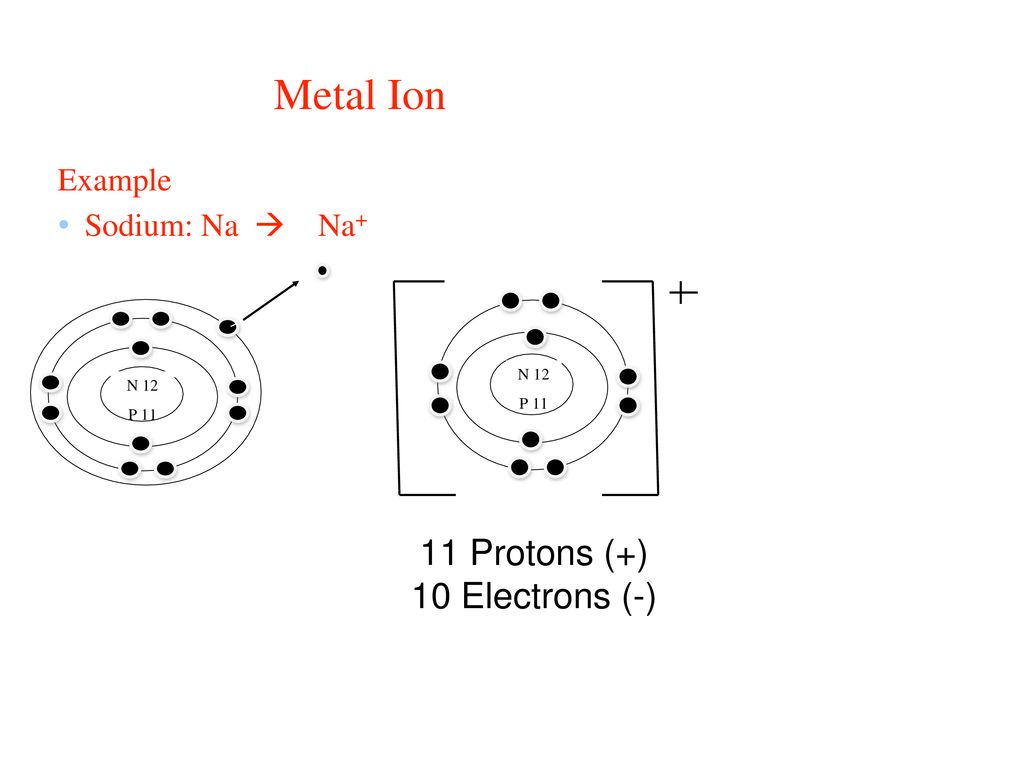
What is the bohr/element model for Na1+?