The most basic unit of matter.
What is an atom?
Between a metal and nonmetal.
What is an ionic bond?
Conductive to heat and electricity, has shiny luster, can be rolled into shapes and sheets.
What are metals?
The number of electrons in the outermost shell.
What are valence electrons?
Turns Litmus paper blue.
The number of electrons in the 3rd shell.
What is 18?
Between a metal and a nonmetal.
What is a covalent bond?
Can conduct electricity under some instances, brittle, and has luster.
What is a metalloid?
The number of dots you would draw around Iodine.
What is 7?
Is sour in taste and can corrode metal.
What is an acid?
Who is Rutherford?
The chemical formula for Lithium Chloride.
Poor conductors of heat and electricity. Looks dull.
What is a nonmetal?
The number of dots you would draw around Arsenic.
What is five?
Turns Litmus paper red.
What is an acid?
Created the Plum Pudding Model to show a sphere of positive charges with negatively charged particles embedded within.
Who is J.J. Thomson?
The charge of an anion.
What is negative?
The word for being able to be pulled into wires.
What is ductile?
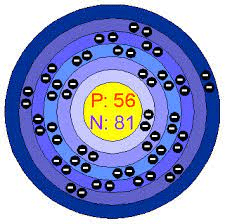 The element shown in this Bohr Model.
The element shown in this Bohr Model.
What is Barium?
Has a pH of 7.
What is neutral?
What is the cloud model?
The name ionic compound name for Ca3P2
The word for being able to be rolled into sheets or shapes.
What is malleable?
The element shown in this Bohr Model.
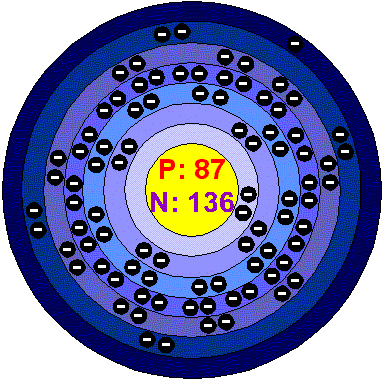
What is Francium?
Feels slippery and tastes bitter.
What is a base?