Name 3 different separation techniques that we learned about in class.
Distillation, Evaporation, Chromatography, Magnetism, Filtration, Density
Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
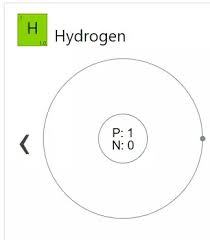
Draw an atomic model for Hydrogen (H).
Valence Electrons
For a covalent bond, what happens to the valence electrons of the bonding atoms?
The valence electrons are shared.
Which separation technique is best used when you are trying to separate a soluble solid from a solution? (Hint: You do not need to keep the solvent.)
Evaporation
For each subatomic particle, name their charge.
Protons = +
Neutrons = 0
Electrons = -
Draw an atomic model for Carbon (C).
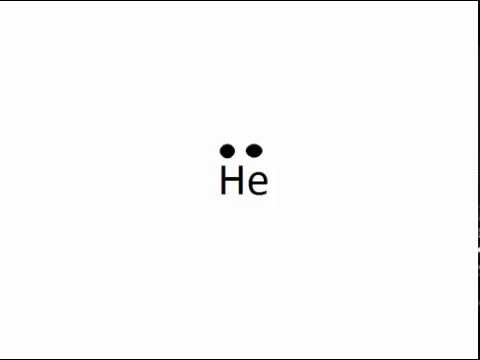
Draw the Lewis Dot Structure for Helium (He).
How many electrons does Bromine (Br) need to add to have a full shell?
1
Which separation technique is best used when you are trying to separate a solvent from a solution? (Hint: You need to keep the solvent.)
Distillation
For each subatomic particle, name their location in the atom.
Protons and Neutrons = Nucleus
Electrons = Electron Cloud
Draw an atomic model for Neon (Ne).
Draw the Lewis Dot Structure for Boron (B).

How many electrons does Sulfur (S) need to add to have a full shell?
2
What does filtration separate?
An insoluble solid from a solution
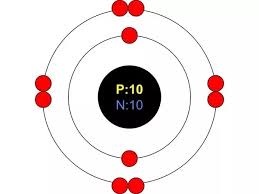
For Rubidium (Rb), list the numbers of protons, neutrons, and electrons that are present in a neutral atom.
Protons = 37
Electrons = 37
Neutrons = 48
Draw an atomic model for Magnesium (Mg).

Draw the Lewis Dot Structure for Phosphorus (P).

Draw the Lewis Dot Structure for a hydrogen molecule (H2).

Describe 1 example of using a separation technique that we learned about in class in your everyday life.
Answers will vary.
For Gold (Au), list the numbers of protons, neutrons, and electrons that are present in a neutral atom.
Protons = 79
Neutrons =118
Electrons = 79
Draw an atomic model for Chlorine (Cl).
Draw the Lewis Dot Structure for Radon (Rn).

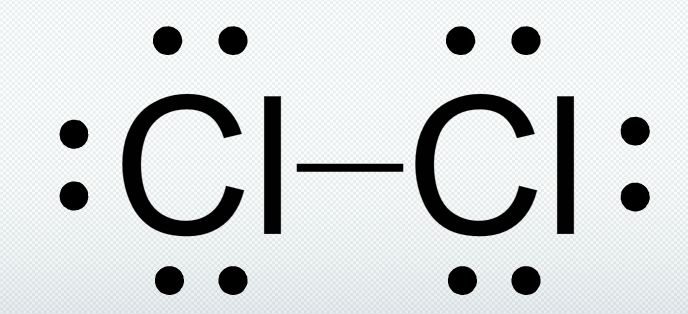
Draw the Lewis Dot Structure for a chlorine molecule (Cl2).