The systematic study of the universe to produce observations, inferences, and models.
What is Science?
Anything that occupies space and has mass.
What is matter?
Scientists had observed that opposite electrical charges attract each other, while same charges repel each other.
What is the law of electrostatic charges?
A law that states the properties of the elements vary in a periodic way with their atomic numbers.
What is the periodic law?
Often the wave changes direction due to the change in medium. Occurs when the wave moves at different speeds in different media.
What is refraction?
Directs us to fill the earth and have dominion over it.
What is the creation mandate?
States that all physical matter exists in the form of particles (atoms or molecules) in constant motion.
What is the particle model of matter?
This model suggested negatively charged electrons embedded in a positive substance.
What is the plum pudding model?
This is a table of the chemical elements arranged in a way that displays their periodic properties in relationship to their atomic numbers.
What is the periodic table?
A mathematical equation that describes how the wave changes direction as itmoves into a new medium.
What is Snell's law?
A system of moral values or a theory of proper conduct.
What are ethics?
The building block of all matter. Consists of protons, electrons, and (usually) neutrons.
What is an atom?
The atom was made up of a dense, positively charged central nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons.
What is the nuclear model?
This is a set of elements in the same column on the periodic table.
What is a family or group?
The bending of waves around an obstacle or through an opening.
What is diffraction?
A workable explanation or description of a phenomenon.
What is a model?
***Daily double***
Brown hypothesized that particles of the fluid were colliding with the parts from the spores, causing their random motion.
What is Brownian motion?
A new branch of physics was born, one that explored the behavior of matter and energy at the atomic subatomic levels.
What is quantum mechanics?
The electrons in the outermost energy level of a neutral atom.
What are valence electrons?
An element, which separates polychromatic light into its constituent wavelengths.
What is diffraction grating?
A model that explains a related set of phenomena.
What is a theory?
A distinct group of two or more atoms covalently bonded together.
What is a molecule?
Spherical regions located at fixed distances from the nucleus.
What are energy levels?
***Daily double***
They are dull and brittle solids.
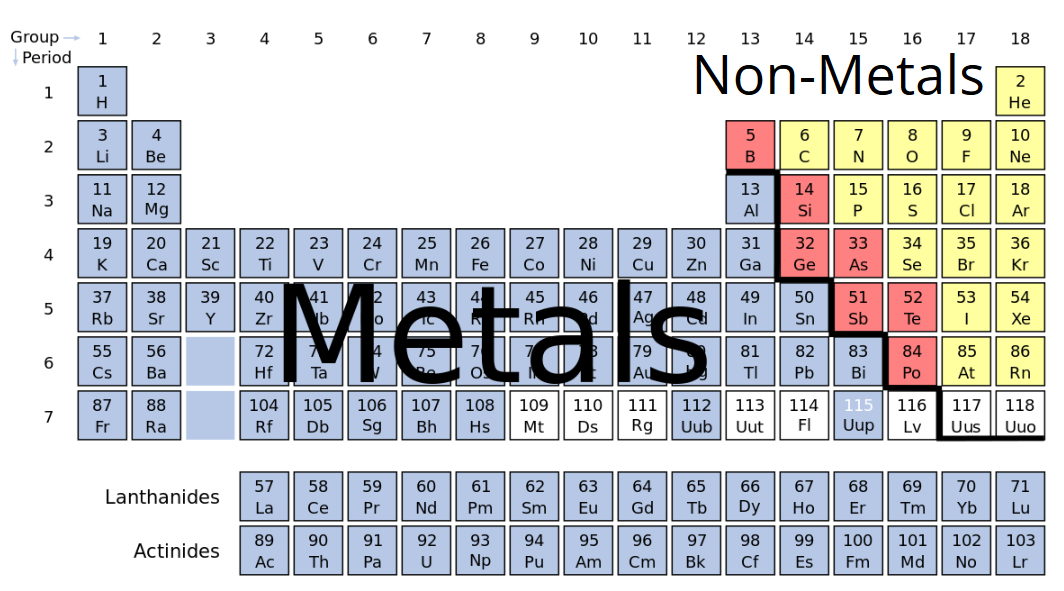
What is not a general property of metals?
Combining of waves where they overlap.
What is interference?